Initial Load
The XAP Data-Grid includes special interceptor that allow users to pre-load the Data-Grid with data before it is available for clients access. This interceptor called Initial Load and has a default implementation that is using the Hibernate Space Persistency implementation to load data from a database directly into the Data-Grid instances.
To enable the initial load activity a SpaceDataSource should be specified. We distinguish between two modes of operation - if SpaceSynchronizationEndpoint is specified the mode is ‘read-write’, otherwise ‘read-only’.
- read-only - Space will be loading data from the persistency layer once started. It will access the persistency layer in case of a cache miss (only when running in LRU cache policy mode).
- read-write - Space will be loading data from the persistency layer once started. It will write changes within the space back into the persistency layer in synchronous manner. For a-synchronous mode, the replication to the Mirror should be enabled and
SpaceSynchronizationEndpointshould not be specified for the space but only for the mirror. The Mirror will be responsible to write the changes into the persistency layer.
Here is an example for a space configuration that performs only initial load from the database without writing back any changes into the database (replication to the Mirror service is not enabled with this example):
<os-core:space id="space" url="/./space" schema="persistent" space-data-source="hibernateSpaceDataSource">
<os-core:properties>
<props>
<!-- Use ALL IN CACHE -->
<prop key="space-config.engine.cache_policy">1</prop>
<prop key="cluster-config.cache-loader.external-data-source">true</prop>
<prop key="cluster-config.cache-loader.central-data-source">true</prop>
</props>
</os-core:properties>
</os-core:space>
<bean id="hibernateSpaceDataSource" class="org.openspaces.persistency.hibernate.DefaultHibernateSpaceDataSourceFactoryBean">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"/>
</bean>
Speeding-up Initial-Load
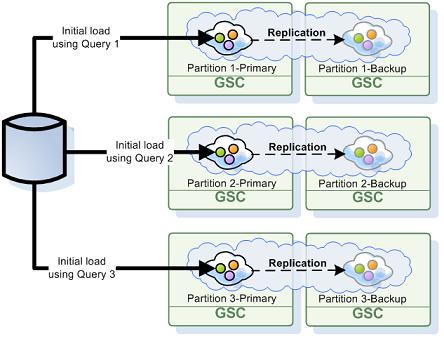
You can load 1TB data into a Data-Grid in less than 30 min by having each partition primary instance query a table column mapped to an object field storing the partition ID. This column should be added to every table. A typical setup to load 1TB in less than 30 min would be a database running on a multi-core machine with 1GB network and few partitions running on multiple multi-core machines. Without such initial-load optimization the more partitions the Data-Grid will have the initial-load time will be increased. Mapping the database files to SSD and using distributed database architecture (Nosql DB) would improve the initial-load time even further.
By default each Data-Grid primary partition loading its relevant data from the database and from there replicated to the backup instances.
All irrelevant objects are filtered out during the data load process. You may optimize this activity by instructing each Data-Grid primary instance to a load-specific data set from the database via a custom query you may construct during the initial load phase.
The Initial Load is supported with the partitioned-sync2backup cluster schema. If you would like to pre-load a clustered space using the Initial-Load without running backups you can use the partitioned-sync2backup and have ZERO as the amount of backups.
Custom Initial Load
To implement your own Initial Load when using the Hibernate SpaceDataSource you should implement the initialDataLoad method to construct one or more DefaultScrollableDataIterator.
See example below:
import org.openspaces.persistency.hibernate.DefaultHibernateSpaceDataSource;
import org.openspaces.persistency.hibernate.iterator.DefaultScrollableDataIterator;
import com.gigaspaces.datasource.DataIterator;
public class SpaceDataSourceInitialLoadExample extends DefaultHibernateSpaceDataSource {
@Override
public DataIterator<Object> initialDataLoad() {
String hquery = "from Employee where age > 30";
DataIterator[] iterators = new DataIterator[1];
int iteratorCounter = 0;
int fetchSize = 100;
int from = -1;
int size = -1;
iterators[iteratorCounter++] = new DefaultScrollableDataIterator(hquery, getSessionFactory(), fetchSize, from, size);
//.. you can have additional DefaultScrollableDataIterator created with multiple queries
return createInitialLoadIterator(iterators);
}
}
Controlling the Initial Load
Additional level of customization can be done by loading only the relevant data into each partition.
In this case you should use the partition ID and total amount of partitions parameters to form the correct database query. The relevant table column mapped to the routing field should have numeric type to allow simple calculation of the matching rows that need to be retrieved from the database and loaded into the partition. This means your database query needs to “slice” the correct data set from the database tables based on the partition ID.
Partition ID retrieval is explained in the Obtaining Cluster Information page. For example:
import org.openspaces.persistency.hibernate.DefaultHibernateSpaceDataSource;
import org.openspaces.persistency.hibernate.iterator.DefaultScrollableDataIterator;
import com.gigaspaces.datasource.DataIterator;
public class SpaceDataSourceInitialLoadExample extends DefaultHibernateSpaceDataSource {
@ClusterInfoContext
private ClusterInfo clusterInfo;
@Override
public DataIterator initialDataLoad() {
String hquery;
if (clusterInfo.getNumberOfInstances() > 1) {
hquery = "FROM com.test.domain.Person WHERE MOD(department,"
+ clusterInfo.getNumberOfInstances() + ") = " + (clusterInfo.getInstanceId() - 1);
} else {
hquery = "from com.test.domain.Person ";
}
DataIterator[] iterators = new DataIterator[1];
int iteratorCounter = 0;
int fetchSize = 100;
int from = -1;
int size = -1;
iterators[iteratorCounter++] = new DefaultScrollableDataIterator(hquery, getSessionFactory() , fetchSize, from, size);
return createInitialLoadIterator(iterators);
}
}
Make sure the routing field (i.e. department) will be an Integer type.
Since each space partition stores a subset of the data , based on the entry routing field hash code value , you need to load the data from the database in the same manner the client load balance the data when interacting with the different partitions.
The database query using the MOD, department, number of partitions and the partition ID to perform identical activity performed by a space client when performing write/read/take operations with partitioned space to rout the operation into the correct partition.
Multi-Parallel Initial Load
The ConcurrentMultiDataIterator can be used for Multi-Parallel load. This will allow multiple threads to load data into each space primary partition. With the example below 4 threads will be used to load data into the space primary partition , each will handle a different MyDataIterator:
public class MySpaceDataSource extends SpaceDataSource{
public DataIterator<Object> initialDataLoad() {
MyDataIterator dataIteratorArry[] = new MyDataIterator [4];
dataIteratorArry[0] = new MyDataIterator(10,20);
dataIteratorArry[1] = new MyDataIterator(30,40);
dataIteratorArry[2] = new MyDataIterator(50,60);
dataIteratorArry[3] = new MyDataIterator(70,80);
int threadPoolSize = dataIteratorArry.length;
ConcurrentMultiDataIterator concurrentIterator =
new ConcurrentMultiDataIterator(dataIteratorArry, threadPoolSize);
return concurrentIterator;
}
}
