Aggregators
With many systems such as pricing systems, risk management, trading and other analytic and business intelligence applications you may need to perform an aggregation activity across data stored within the data grid when generating reports or when running some business process. Such activity can leverage data stored in memory and will be much faster than performing it with a database.
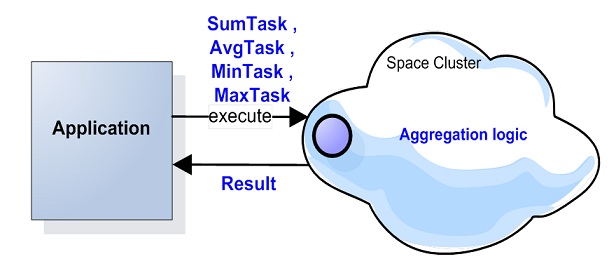
Openspaces comes with built-in aggregators you can use to calculate Min, Max, Avg and Sum for objects stored within the space. There is no need to retrieve the entire data set from the space to the client side , iterate the result set and perform the aggregation. This would be an expensive activity as it might return large amount of data into the client application. The Aggregators allows you to perform the entire aggregation activity at the space side avoiding any data retrieval back to the client side. Only the result of each aggregation activity performed with each partition is returned back to the client side where all the results are reduced and returned to the client application. Such aggregation activity utilize the partitioned nature of the data-grid allowing each partition to execute the aggregation with its local data in parallel, where all the partitions intermediate results are fully aggregated at the client side using the relevant reducer implementation.
Built-in Aggregators
The following built-in Aggregators provided:
| Task | Description |
|---|---|
| AvgTask | An average calculation task accepting a Task to delegate the actual execution to. Implements the reduce(java.util.List) operation to calculate average of all returned values. |
| MaxTask | A minimum calculation task accepting a Task to delegate the actual execution to. Implements the reduce(java.util.List) operation to calculate maximum of all returned values. |
| MinTask | A maximum calculation task accepting a Task to delegate the actual execution to. Implements the reduce(java.util.List) operation to calculate minimum of all returned values. |
| SumTask | A sum calculation task accepting a Task to delegate the actual execution to. Implements the reduce(java.util.List) operation to calculate sum of all returned values. |
The JDBC Driver support aggregate functions. Still , the Built-in Aggregators will perform better, especially when using projections.
Example
Below example using the SumTask to aggregate data using a specific field within the MyData objects. A SQLQuery using a different field to specify the set of objects the aggregation process will be using. To speed up the aggregation process a Projection is used with the SQL Query to read only the specific field required for the aggregation activity (rather the entire space object content).
The example using a SpaceDocument to illustrate a generic data aggregation where the field used to query the space and the field used for the aggregation are parameters for the SumAggregatorTask constructor.
The basic usage of the SumAggregatorTask demonstrated with the following:
GigaSpace space = ...
SumAggregatorTask sumAggregatorTask = new SumAggregatorTask("queryField", min, max, "aggregatedField");
AsyncFuture<Double> future = space.execute(new SumTask<Double, Double>(Double.class, sumAggregatorTask));
Double result = future.get();
public class MyData {
public MyData (){}
Long id;
Integer queryField;
Double aggregatedField;
String str1;
@SpaceId(autoGenerate=false)
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getStr1() {
return str1;
}
public void setStr1(String str1) {
this.str1 = str1;
}
@SpaceIndex(type=SpaceIndexType.EXTENDED)
public Integer getQueryField() {
return queryField;
}
public void setQueryField(Integer queryField) {
this.queryField = queryField;
}
public Double getAggregatedField() {
return aggregatedField;
}
public void setAggregatedField(Double aggregatedField) {
this.aggregatedField = aggregatedField;
}
}
import org.openspaces.core.GigaSpace;
import org.openspaces.core.executor.Task;
import org.openspaces.core.executor.TaskGigaSpace;
import com.gigaspaces.document.SpaceDocument;
import com.gigaspaces.query.QueryResultType;
import com.j_spaces.core.client.SQLQuery;
public class SumAggregatorTask implements Task<Double>{
@TaskGigaSpace
transient GigaSpace space;
String queryField ;
Integer minValue ;
Integer maxValue ;
String aggregatedField;
public SumAggregatorTask(String queryField , Integer minValue ,
Integer maxValue , String aggregatedField)
{
this.queryField = queryField ;
this.minValue = minValue ;
this.maxValue = maxValue ;
this.aggregatedField= aggregatedField;
}
public Double execute() throws Exception {
SQLQuery<SpaceDocument> query = new SQLQuery<SpaceDocument>(MyData.class.getName(),
queryField + " between ? and ?",QueryResultType.DOCUMENT);
query.setProjections(aggregatedField);
query.setParameter(1, minValue);
query.setParameter(2, maxValue);
double sumValue = 0;
SpaceDocument res[] = space.readMultiple(query);
for (int i = 0; i < res.length; i++) {
sumValue += (Double)res[i].getProperty(aggregatedField);
}
return sumValue ;
}
}
