Replication Filters
When constructing a replicated space topology you may need to call some business logic when data is replicated. GigaSpaces provides the IReplicationFilter plug-in interface com.j_spaces.core.cluster.IReplicationFilter, that allows you to build business logic that is called when data is sent through the replication channel.
The IReplicationFilter methods are called before data is sent to the replication channel from the source space (output mode) and after coming out from the replication channel - i.e. before written to the target space (input mode). The replication filter should implement the IReplicationFilter interface methods.
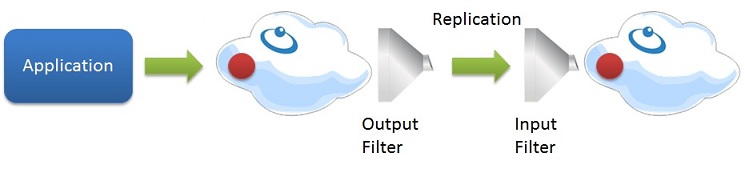
The replication filter can be used to monitor or alter the data passed through the replication channel. The replication channel passes IReplicationFilterEntry objects that store the replicated data. You should DefaultReplicationFilterProviderFactory and set its Replication Filter implementation when constructing the Space. You can use the same replication filter implementation class for both input and output replication modes. Here are the classes you will be using with your Replication Filter implementation:
- IReplicationFilterEntry – stores the space object data that is passed into the
IReplicationFilter. - IReplicationFilter – a replication filter is an interface called when a replication event is triggered. Two types of replication filters can be defined – an input replication and an output replication. If both of the classes specified (for input and output) are the same, only one filter object will be used for both input and output replication.
- ReplicationFilterException – the
ReplicationFilterExceptionis thrown when there are errors that occur in the replication filter. Errors can happen in the source or target space. The error is wrapped as part of theReplicationFilterExceptionand thrown back to the client. TheReplicationFilterExceptionincludes methods that includes information about the origin of the error, replication mode (input/output), the implementation class and the underlying exception. TheReplicationFilterException.getCause()should be used to retrieve the original exception that occurred.
you can control the replication at the operation level, using configuration only. For more details, refer to the Replication Operations section.
Guidelines for Cluster Replication Filters
- In order to block a space object to be replicated, assign a
ReplicationOperationType.DISCARDvalue as the operation type. - Don’t overwrite the
m_Key(serial number) field of the packet. - Object field values (
m_FieldsValuesarray) may be changed, but notice that if the serialization type of the space is not 0 (that is, fields are serialized inside the space) – then each non-native field (i.e. not from the Java.lang package) is stored in the array in a serialized format. - For outgoing replication packets (output replication Filter), if you want to change the values of some fields, deep-cloning of the
m_FieldsValuesarray is needed, since them_FieldsValuesis a reference to the array stored in the space internal data structures. - When using synchronous replication and an error has been occurs at the replication filter implementation,
ReplicationFilterExceptionis thrown back into the relevant thread at the client application. TheReplicationFilterExceptioncan be originated at the source or target space. TheReplicationFilterExceptionwill include the relevant information to identify the origin and the underlying exception that caused the problem. - When using asynchronous replication and an error occurs at the replication filter implementation, the space replication channel will be disabled, and an error will be logged into the space log file and displayed at the space console. The client application continues to function against its source space but there will not be any replication to the target space. In order to enable the replication, you should use the
IRemoteJSpaceAdmin.changeReplicationState(). - All replication packets are sent according to their replication policy. When either the Interval Milliseconds or the Interval Operations times out, a replication event is executed.
ReplicationOperationType.DISCARDpackets are sent when a sequence of operations performed on one space does not need to be performed again on the replicated members. For example, when using asynchronous replication mode, a sequence of write and take on the same object does not need to replicated. Therefore, aReplicationOperationType.DISCARDpacket is sent. In contrast, the take operation is always replicated to ensure data consistency.
Example - Replication Filter
The following example will start two spaces replicating data to each other. The replication filter will display the replicated data that is passed through the replication channel. The example displays all objects sent via the output filter. When an object with the data Block me is passed, it is blocking by setting the replication Operation Type to ReplicationOperationType.DISCARD.
package com.test;
import com.gigaspaces.annotation.pojo.SpaceClass;
import com.gigaspaces.annotation.pojo.SpaceId;
@SpaceClass
public class MyClass {
String id;
String data;
@SpaceId(autoGenerate = false)
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(String data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
package com.test;
import org.openspaces.core.GigaSpace;
import org.openspaces.core.GigaSpaceConfigurer;
import org.openspaces.core.space.UrlSpaceConfigurer;
import org.openspaces.core.space.filter.replication.DefaultReplicationFilterProviderFactory;
public class ReplicationFilterTestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
DefaultReplicationFilterProviderFactory repFactory = new DefaultReplicationFilterProviderFactory ();
repFactory.setOutputFilter(new RepFilter());
repFactory.afterPropertiesSet();
GigaSpace gigaspace1 = new GigaSpaceConfigurer(
new UrlSpaceConfigurer("/./space?cluster_schema=sync_replicated&total_members=2&id=1")
.replicationFilterProvider(repFactory)).
gigaSpace();
GigaSpace gigaspace2 = new GigaSpaceConfigurer(
new UrlSpaceConfigurer("/./space?cluster_schema=sync_replicated&total_members=2&id=2")).
gigaSpace();
MyClass o1 = new MyClass();
o1.setId("1");
o1.setData("AAA");
gigaspace1.write(o1);
MyClass o2 = new MyClass();
o2.setId("2");
o2.setData("Block me");
gigaspace1.write(o2);
MyClass o3 = gigaspace2.readById(MyClass.class,"1");
if (o3 != null)
System.out.println("Replicated Object ID 1 value is:" + o3.getData());
MyClass o4 = gigaspace2.readById(MyClass.class,"2");
if (o4 != null)
System.out.println("Replicated Object ID 2 value is:" + o4.getData());
else
System.out.println("Object ID 2 has not been replicated");
}
}
package com.test;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import org.openspaces.core.GigaSpace;
import org.openspaces.core.GigaSpaceConfigurer;
import com.j_spaces.core.IJSpace;
import com.j_spaces.core.client.ClientUIDHandler;
import com.j_spaces.core.cluster.IReplicationFilter;
import com.j_spaces.core.cluster.IReplicationFilterEntry;
import com.j_spaces.core.cluster.ReplicationOperationType;
import com.j_spaces.core.cluster.ReplicationPolicy;
public class RepFilter implements IReplicationFilter{
@Override
public void close() {
}
GigaSpace gigaspace = null;
@Override
public void init(IJSpace space, String paramUrl,
ReplicationPolicy replicationPolicy) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
gigaspace = new GigaSpaceConfigurer(space).gigaSpace();
System.out.println("Rep Filter - Created "+gigaspace);
}
AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override
public void process(int direction,
IReplicationFilterEntry replicationEntry,
String remoteSpaceMemberName) {
String filterDirectionStr = "";
String operationCodeStr = "";
switch( direction ) {
case IReplicationFilter.FILTER_DIRECTION_INPUT:
filterDirectionStr="INPUT";
break;
case IReplicationFilter.FILTER_DIRECTION_OUTPUT:
filterDirectionStr="OUTPUT";
break;
}
counter.incrementAndGet(); // increment the number of entries processed.
System.out.println(
"\nDefaultReplicationFilter"
+ "\n\t | Space: " + gigaspace
+ "\n\t | Packet No."+ counter
+ "\n\t | Direction: "+ filterDirectionStr
+ "\n\t | Operation code: "+ operationCodeStr
+ "\n\t | Entry packet UID: "
+ "\n\t | 2Str: "+ replicationEntry.toString()
+ replicationEntry.getUID() + "\n");
/*
* Lets Block the "Block me" object on its way out
*/
if (direction == IReplicationFilter.FILTER_DIRECTION_OUTPUT
&& replicationEntry.getOperationType().equals(ReplicationOperationType.WRITE)
&& replicationEntry.getFieldsValues() != null
&& replicationEntry.getFieldValue("data").equals("Block me"))
{
System.out.println("\t | ==> Filter blocked outgoing object\n");
// dismiss replication packet:
replicationEntry.discard();
}
}
}
