XAP Considerations
The Runtime Environment (GSA, LUS, GSM and GSC)
In a dynamic environment where you want to start GSCs and GSMs remotely, manually, or dynamically, the GSA is the only component that should be running on the machine hosting the XAP runtime environment. This lightweight service acts as an agent and starts a GSC/GSM/LUS when needed.
Plan the initial number of GSCs and GSMs based on the application memory footprint, and the amount of processing you might need. The most basic deployment should include 2 GSMs (running on different machines), 2 lookup services (running on different machines), and 2 GSCs (running on each machine). These host your data Grid or any other application components (services, web servers, Mirror) that you deploy.
In general, the total amount of GSCs that should be running across the machines hosting the system depends on:
- The amount of data you want to store in memory.
- The JVM maximum heap size.
- The processing requirements.
- The number of users the system needs to serve.
- The total number of CPU cores the machine is running.
The recommended number of GSCs a machine should host is half of the amount of total CPU cores, each having no more than a 10GB maximum heap size.
Configuring the Runtime Environment
JVM parameters (system properties, heap settings, etc.) that are shared between all components are best set using the EXT_JAVA_OPTIONS environment variable. Specific GSA JVM parameters can be easily passed using XAP_GSA_OPTIONS which will be appended to EXT_JAVA_OPTIONS. As good practice, add all the components’ environment variables ( XAP_GSA_OPTIONS, XAP_GSM_OPTIONS, XAP_GSC_OPTIONS, XAP_LUS_OPTIONS) within the GSA script, or in a wrapper script and the values will be passed to corresponding components.
#Wrapper Script
export XAP_GSA_OPTIONS='-Xmx256m'
export XAP_GSC_OPTIONS='-Xmx2048m'
export XAP_GSM_OPTIONS='-Xmx1024m'
export XAP_LUS_OPTIONS='-Xmx1024m'
#call gs-agent.sh
. ./gs-agent.sh
@rem Wrapper Script
@set XAP_GSA_OPTIONS=-Xmx256m
@set XAP_GSC_OPTIONS=-Xmx2048m
@set XAP_GSM_OPTIONS=-Xmx1024m
@set XAP_LUS_OPTIONS=-Xmx1024m
@rem call gs-agent.bat
call gs-agent.bat
The above LUS configuration will serve up to 50 partitions running on 100 GSCs.With larger environments you must increase the heap size and perform GC tuning.
Running Multiple Groups
You may have a set of LUS/GSM managing GSCs associated to a specific group. To “break” your network into 2 groups, start the GigaSpaces XAP runtime environment as follows:
export XAP_LOOKUP_GROUPS=GroupX
gs-agent.sh gsa.global.lus 0 gsa.lus 1 gsa.global.gsm 0 gsa.gsm 1 gsa.gsc 0
export XAP_LOOKUP_GROUPS=GroupX
gs-agent.sh gsa.global.lus 0 gsa.lus 0 gsa.global.gsm 0 gsa.gsm 0 gsa.gsc 4
export XAP_LOOKUP_GROUPS=GroupX
gs-agent.sh gsa.global.lus 0 gsa.lus 1 gsa.global.gsm 0 gsa.gsm 1 gsa.gsc 0
export XAP_LOOKUP_GROUPS=GroupY
gs-agent.sh gsa.global.lus 0 gsa.lus 0 gsa.global.gsm 0 gsa.gsm 0 gsa.gsc 2
export XAP_LOOKUP_GROUPS=GroupX
gs deploy-space -cluster schema=partitioned total_members=4 spaceX
export XAP_LOOKUP_GROUPS=GroupY
gs deploy-space -cluster schema=partitioned total_members=2 spaceY
Running Multiple Locators
You may have a set of LUS/GSM managing GSCs associated to a specific locator. To “break” your network into 2 groups using different lookup locators, start the GigaSpaces XAP runtime environment as follows:
export XAP_LUS_OPTIONS=-Dcom.sun.jini.reggie.initialUnicastDiscoveryPort=8888
export XAP_LOOKUP_LOCATORS=127.0.0.1:8888
export EXT_JAVA_OPTIONS=-Dcom.gs.multicast.enabled=false
gs-agent.sh gsa.global.lus 0 gsa.lus 1 gsa.global.gsm 0 gsa.gsm 1 gsa.gsc 0
export XAP_LOOKUP_LOCATORS=127.0.0.1:8888
export EXT_JAVA_OPTIONS=-Dcom.gs.multicast.enabled=false
gs-agent.sh gsa.global.lus 0 gsa.lus 0 gsa.global.gsm 0 gsa.gsm 0 gsa.gsc 4
export XAP_LUS_OPTIONS=-Dcom.sun.jini.reggie.initialUnicastDiscoveryPort=9999
export XAP_LOOKUP_LOCATORS=127.0.0.1:8888
export EXT_JAVA_OPTIONS=-Dcom.gs.multicast.enabled=false
gs-agent.sh gsa.global.lus 0 gsa.lus 1 gsa.global.gsm 0 gsa.gsm 1 gsa.gsc 0
export XAP_LOOKUP_LOCATORS=127.0.0.1:9999
export EXT_JAVA_OPTIONS=-Dcom.gs.multicast.enabled=false
gs-agent.sh gsa.global.lus 0 gsa.lus 0 gsa.global.gsm 0 gsa.gsm 0 gsa.gsc 2
export XAP_LOOKUP_LOCATORS=127.0.0.1:8888
gs deploy-space -cluster schema=partitioned total_members=4 spaceX
export XAP_LOOKUP_LOCATORS=127.0.0.1:9999
gs deploy-space -cluster schema=partitioned total_members=2 spaceY
On top of the Lookup Service, there is also an alternative way to export the space proxy, via the RMI registry (JNDI). It is started by default within any JVM running a GSC/GSM. By default, the port used is 10098 and above. This option should be used only in special cases where there is no way to use the default Lookup Service. Since this is the usual RMI registry, it suffers from known problems, such as being non-distributed, non-highly-available, etc.
The Lookup Service runs by default as a standalone JVM process started by the GSA. You can also embed it to run together with the GSM. In general, you should run two Lookup Services per system. Running more than two Lpokup Services may cause increased overhead due to the chatting and heartbeat mechanism performed between the services and the lookup service, to signal the existence of the service.
Zones
The XAP zone allows you to “label” a running GSC(s) before starting it. The XAP zone should be used to isolate applications and a data grid running on the same network. It has been designed to allow users to deploy a processing unit into specific set of GSCs, where they all share the same set of LUSs and GSMs.
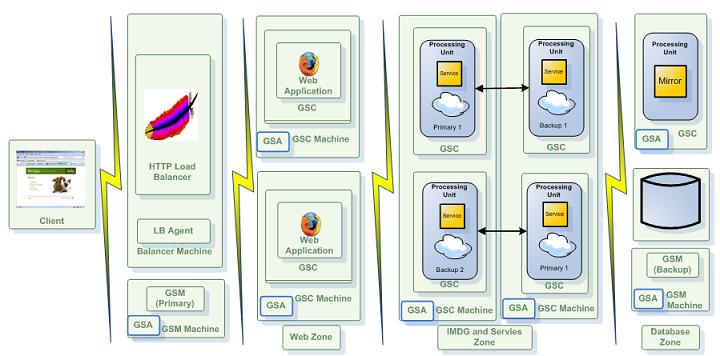
The Zone property can be used for example to deploy your data grid into a specific GSC(s) labeled with specific zone(s). The zone is specified prior to the GSC startup, and cannot be changed after the GSC has been started.
Verify that you have an adequate number of GSCs running, prior to deploying an application whose SLA specifies a specific zone.
To use zones when deploying your PU you should:
export EXT_JAVA_OPTIONS=-Dcom.gs.zones=webZone ${EXT_JAVA_OPTIONS}
gs-agent gsa.gsc 2
gs deploy -zones webZone myWar.war
Running Multiple Zones
You may have a set of LUS/GSM managing multiple zones (recommended) or have a separate LUS/GSM set per zone. If you have a set of LUS/GSM managing multiple zones, you should run them as follows:
gs-agent.sh gsa.global.lus 0 gsa.lus 1 gsa.global.gsm 0 gsa.gsm 1 gsa.gsc 0
export EXT_JAVA_OPTIONS=-Dcom.gs.zones=zoneX ${EXT_JAVA_OPTIONS}
gs-agent.sh gsa.global.lus 0 gsa.lus 0 gsa.global.gsm 0 gsa.gsm 0 gsa.gsc 4
export EXT_JAVA_OPTIONS=-Dcom.gs.zones=zoneY ${EXT_JAVA_OPTIONS}
gs-agent.sh gsa.global.lus 0 gsa.lus 0 gsa.global.gsm 0 gsa.gsm 0 gsa.gsc 2
Runtime File Location
XAP generates some files while the system is running. You can change the location of the generated files using the following system properties:
| System Property | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| com.gigaspaces.logger.RollingFileHandler.filename-pattern | The location of log files and their file pattern. | <gigaspaces-xap root>\logs |
| com.gs.deploy | The location of the deploy directory of the GSM. | <gigaspaces-xap root>\deploy |
| com.gs.work | The location of the work directory of the GSM and GSC. Due to the fact that this directory is critical to the system proper function, it should be set to a local storage in order to avoid failure in case of network failure when a remote storage is used. | <gigaspaces-xap root>\work |
| user.home | The location of system defaults config. Used by the GS-UI, and runtime system components. | |
| com.gigaspaces.lib.platform.ext | PUs shared classloader libraries folder. PU jars located within this folder loaded once into the JVM system classloader and shared between all the PU instances classloaders within the GSC. In most cases this is a better option than the com.gs.pu-common for JDBC drivers and other 3rd party libraries. This is useful option when you want multiple processing units to share the same 3rd party jar files and do not want to repackage the processing unit jar whenever one of these 3rd party jars changes. |
<gigaspaces-xap root>\lib\platform\ext |
| com.gs.pu-common | The location of common classes used across multiple processing units. The libraries located within this folder loaded into each PU instance classloader (and not into the system classloader as with the com.gigaspaces.lib.platform.ext. |
<gigaspaces-xap root>\lib\optional\pu-common |
| com.gigaspaces.grid.gsa.config-directory | The location of the GSA configuration files. The GigaSpaces Agent (GSA) manages different process types. Each process type is defined within this folder in an xml file that identifies the process type by its name. | <gigaspaces-xap root>\config\gsa |
| java.util.logging.config.file | It indicates file path to the Java logging file location. Use it to enable finest logging troubleshooting of various GigaSpaces XAP Services. You may control this setting via the XAP_LOGS_CONFIG_FILE environment variable. |
<gigaspaces-xap root>\config\log\xap_logging.properties |
You can use com.gigaspaces.lib.platform.ext and the com.gs.pu-common to decrease the deployment time if your processing unit contains many third-party JAR files. In this case, each GSC will download the processing unit JAR file (along with all the JARs it depends on) to its local working directory from the GSM. In large deployments spanning tens or hundreds of GSCs, this can be very time consuming. In these cases, consider placing the JARs on which your processing unit depends in a shared location on your network, and then point the com.gs.pu-common or com.gigaspaces.lib.platform.ext directory to this location.
PU Packaging and CLASSPATH
User PU Application Libraries
A Processing Unit JAR file, or a Web Application WAR file should include (within its lib folder) all the necessary JARs required for the application. Resource files should be placed within one of the JAR files within the PU JAR, located under the lib folder. In addition, the PU JAR should include the pu.xml within the META-INF\spring folder.
In order to close LRMI threads when closing application, use:LRMIManager.shutdown().
Data Grid PU Libraries
When deploying a data grid PU, it is recommended to include all space classes and their dependency classes as part a PU JAR file. This PU JAR file should include a pu.xml within the META-INF\spring, to include the space declarations and relevant tuning parameters.
GS-UI Libraries
It is recommended to include all space classes and their dependency classes as part of the GS-UI CLASSAPTH . This ensures that you can query the data via the GS-UI. To set the GS-UI classpath, set the POST_CLASSPATH variable prior to calling the GS-UI script to have the application JARs locations.
To avoid having to load the same library into each PU instance classloader running within the GSC, you should place common libraries (such as JDBC driver, logging libraries, Hibernate libraries and their dependencies) in the <gigaspaces-xap root>\lib\optional\pu-common folder. You can specify the location of this folder using the com.gs.pu-common system property.
Space Memory Management
The Space supports two memory management modes:
ALL_IN_CACHE- this assumes all application data is stored within the space.LRU- this assumes some of the application data is stored within the space, and all the rest is stored in some external data source.
When running with ALL_IN_CACHE, the memory management does the following:
- Stops clients from writing data into the space when the JVM utilized memory crosses the WRITE threshold (percentage of the heap max size).
- Throws a
MemoryShortageExecptionback to the client when the JVM utilized memory crosses thehigh_watermark_percentagethreshold.
When running with ALL_IN_CACHE, ensure that the default memory management parameters are tuned according the JVM heap size. A large heap size (over 2GB RAM) requires special attention. Here is an example of memory manager settings for a 10GB heap size:
<os-core:embedded-space id="space" space-name="mySpace" >
<os-core:properties>
<props>
<prop key="space-config.engine.memory_usage.high_watermark_percentage">95</prop>
<prop key="space-config.engine.memory_usage.write_only_block_percentage">94</prop>
<prop key="space-config.engine.memory_usage.write_only_check_percentage">93</prop>
<prop key="space-config.engine.memory_usage.low_watermark_percentage">92</prop>
</props>
</os-core:properties>
</os-core:embedded-space>
Distributing the Primary Spaces
By default, when running GSCs on multiple machines and deploying a Space with backups, XAP tries to provision primary Dpaces to all available GSCs across all the machines.
The max-instances-per-vm and the max-instances-per-machine deploy parameters should be set when deploying your data grid, to determine how the deployed Processing Unit (e.g. Space) is provisioned into the different running GSCs.
Without setting the max-instances-per-vm and the max-instances-per-machine, XAP might provision a primary and a backup instance of the same partition into GSCs running on the same physical machine. To avoid this behavior, set max-instances-per-vm=1 and max-instances-per-machine=1. This ensures that the primary and backup instances of the same partition are provisioned into different GSCs running on different machines. If there is one machine running GSCs and max-instances-per-machine=1, backup instances are not provisioned.
Here is an example of how to deploy a data grid with 4 partitions, with a backup per partition (total of 8 Spaces), with 2 Spaces per GSC, and the primary and backup running on different machines (even when you have other GSCs running):
gs deploy-space -cluster schema=partitioned-sync2backup total_members=4,1
-max-instances-per-vm 2 -max-instances-per-machine 1 MySpace
After a machine startup (where GSCs are started), when the ESM is not used to deploy the IMDG, spaces do not “re balance” across all the machines to have an even number of primaries per machine. You may have machines running more (or all) primaries, and another machine running only backups.
Total Max Instances per VM
This parameter controls the total amount of PU instances that can be instantiated within a GSC. This is very different than the max-instances-per-vm, which controls how many instances a partition may have within a GSC. To control the Total Max PU Instances hosted by a GSC, use the com.gigaspaces.grid.gsc.serviceLimit system property and set its value before starting the GigaSpaces agent:
set XAP_GSC_OPTIONS=-Dcom.gigaspaces.grid.gsc.serviceLimit=1
The default value of the com.gigaspaces.grid.gsc.serviceLimit is 500. This value may not work well for most production environments. With most production environments that have a static deployment configuration, it is advised to keep the com.gigaspaces.grid.gsc.serviceLimit value to 1. Having multiple space instances within the same GSC makes it hard to handle failures, handle garbage collection and resource configuration such as LRMI thread pool , etc.
By using com.gigaspaces.grid.gsc.serviceLimit=1, you may avoid a scenario where a new Space or failed Space instance is provisioned in a GSC that already hosts a Space instance. This scenario may result in Memory Shortage Exception or Out of Memory Error and may cause a provisioning failure.
Rebalancing - Dynamic Data Redistribution
Automatic Rebalancing
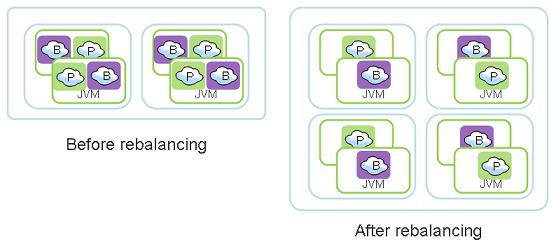
XAP supports automatic discovery, rebalancing (also referred to as Dynamic Redistribution of Data) and expansion/contraction of the IMDG while the application is running. When deploying an IMDG, the system partitions the data (and the co-located business logic) into logical partitions. You can define the number of logical partitions or let XAP calculate this number.
The logical partitions may initially run on certain containers, and later get relocated to other containers (started after the data grid has been deployed) on other machines, allowing the system to expand and increase its memory and CPU capacity while the application is still running. The number of logical partitions and replicas per partition should be determined at deployment time. The number of containers hosting the IMDG instances may be changed during runtime.
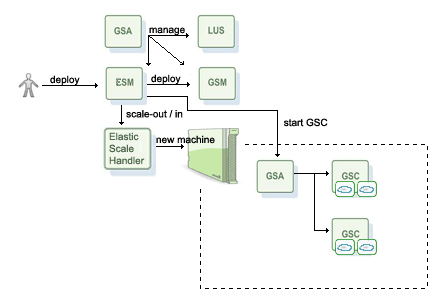
The Elastic Service Manager (ESM) component is responsible for scaling the IMDG during runtime, and is used with the Elastic Processing Unit:
When using the Elastic Processing Unit, instances will be continuously rebalanced across all available machines.
Log Files
XAP generates log files for each running component . This includes the GSA, GSC, GSM, Lookup Service and client-side components. By default, the log files are created within the <gigaspaces-xap-root>\logs folder. After some time, you may end up with a large number of files that are difficult to maintain and search. it is recommended to back up or delete old log files. You can use the logging backup policy to manage your log files.
