Overview
Multiple site replication is the ability to replicate state between different deployed spaces, where each space can be also physically located in a different geographical location (also termed a different deployment site).
Multiple site replication is a very common deployment topology in the following scenarios:
- When planning for disaster recovery - In such cases, each of the deployment sites is located far from the other sites (e.g. a different continent so that if one site is completely destroyed or decommissioned other sites are not affected and can continue to operate normally.)
- For failover purposes - When one site acts as a failover over target for another.
- For maintaining data locality - for each site for performance and latency reasons. For example a global trading application that operates in multiple stock exchanges across the globe need fast access to Global Reference Data, or an application that’s deployed on multiple data centers in the cloud with a need to access the Users Profile Data very quickly.
WAN Gateway Features
The GigaSpaces WAN Gateway features the following:
- Optimized bandwidth and WAN connection usage - With the GigaSpaces WAN Gateway every site using one connection when interacting with remote sites.
- Total Data consistency , ordering with no data lost - Due-to its unique architecture where the WAN Gateway is totally stateless no data lose will ever happen. Transactions at the local site are replicate in atomic manner in the correct order to the remote sites.
- Conflict resolution support - GigaSpaces will identify data conflicts and allow you to decide to override the local copy with the remote replicated copy, reject the remote replicated copy or merge the local and the remote copy.
- Monitoring and Management - The WAN Gateway exposes statistics on every activity going thought the replication to remote sites.
- In-direct replication - The WAN Gateway can replicate a packet from point A to point B via point C to avoid connectivity problems between A and B.
- Multi-Master / Master-Slave support - The WAN Gateway support for all popular replication typologies.
- Site bootstrapping - Once a sites starts it can reload its entire data or specific data from a remote site without introducing data consistency problems.
- Data filtering - The WAN Gateway replication can have custom plug-in that allows users to filter/modify data before it is replicated and after it has been replicated at each source/target node.
- Changing WAN replication topology in runtime - adding or removing remote sites without system shutdown.
This page describe how to establish replication between multiple spaces in a typical WAN environment, where each space is a separate network and there is a need for a designated outbound and inbound gateway machine or machines on each network in order to interact with the other network. If this is not the case, and there is a direct network connection available between all space instances machine like VLAN or VPN please refer to Multi-Space Replication over the LAN or VPN
Supported Toplogies
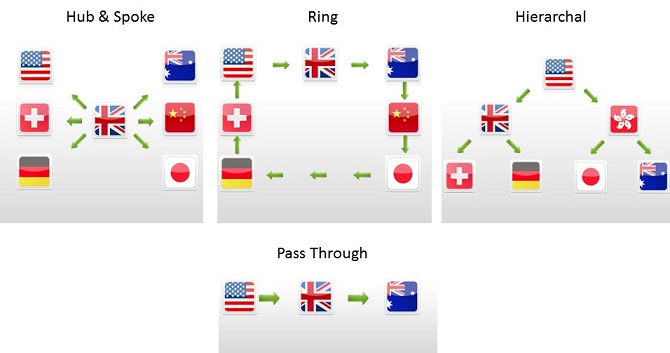
This page will demonstrate two sample multi-site replication topologies. These are not the only supported topologies. In fact, the permutations of topologies are quite extensive, and we’ve chosen to demonstrate two of the more common topologies which can also serve as a basis for other topologies as required by the user:
- Multi-master with two sites, where each site is active and updates its subset of the data.
- Master-slave, where only one site actually updates the data while the rest either serve as a backup or use it in read only mode.
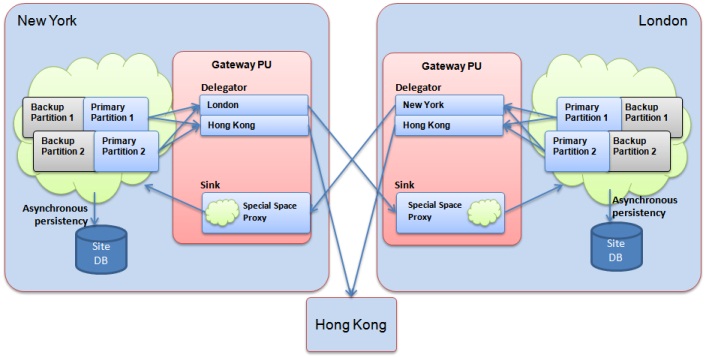
For both of the above topologies, replication is done in in a similar way: Each space is replicating the relevant data to its target space(s) via a local gateway which routes the data to the gateway of the target space(s) and from there to the target space. The data is being replicated asynchronously in a reliable mode, which means that even if a primary space instance fails on the source site, the backup space instance which replaces it will immediately take control and replicate the missing data along with new data that has been generated on the newly elected primary space instance. This is very similar to the Mirror Service replication scheme. The gateway is discussed in full below.
Replication may use Hub & Spoke, Ring, Hierarchical or Pass-Through architecture:
Configuring a Space With Gateway Targets
A replication from one space to the another is basically a replication from a space to a target gateway. The source space is decoupled from the target space. Instead, it is configured to replicate to target space’s local gateway, the local gateway is in charge of dispatching the incoming replication packets to the relevant target space. Each space needs to be made aware of the target gateways to which it replicates the data, by specifying the target gateways in the source space configuration.
From the space’s perspective, a replication from one space to a target gateway is like any other replication channel (e.g mirror, backup…) and the backlog and confirmation state of the replication channel to the target gateway is kept in the source space. As a result, the gateway is stateless as far as holding the replication state is concerned, and only the source space is in charge of the replication progress and state. Each gateway has a unique logical name which usually corresponds to physical site name (e.g. “London” or “New York”). This name is used by remote spaces that are replicating to this space via its local gateway.
The following snippet shows how to configure a space that resides in New York to replicate to two other spaces, one in London and one in Hong Kong:
<os-core:embedded-space id="space" name="myNYSpace" gateway-targets="gatewayTargets"/>
<os-gateway:targets id="gatewayTargets" local-gateway-name="NEWYORK">
<os-gateway:target name="LONDON"/>
<os-gateway:target name="HONGKONG"/>
</os-gateway:targets>
Each of replication channel to the gateways can be configured with more parameters, such parameters can applied to all gateways or specifically per gateway, for example:
<os-core:embedded-space id="space" name="myNYSpace" gateway-targets="gatewayTargets"/>
<os-gateway:targets id="gatewayTargets"
local-gateway-name="NEWYORK" bulk-size="1000"
max-redo-log-capacity="1000000">
<os-gateway:target name="LONDON" />
<os-gateway:target name="HONGKONG" bulk-size="100"/>
</os-gateway:targets>
Here we have specified a global bulk size of 1000 but have specifically overridden it in the replication channel to Hong Kong with 100, and have a global maximum redo log capacity for both targets of 1000000.
For more details about all the available configuration elements of the space gateway targets please refer to the Configuring Space Gateway Targets section.
Use the partitioned-sync2backup cluster schema
You should have the partitioned-sync2backup cluster schema used with the space to enable the replication to the Gateway.
If you are not interested in having backups running but have the replication to the Gateway running, you should have ZERO as the number of backups. See below example of an sla.xml configuration you could use in such a case:
<os-sla:sla cluster-schema="partitioned-sync2backup" number-of-instances="1" number-of-backups="0">
</os-sla:sla>
Note that when there are no backups running any failure of the primary might cause a loss of data.
Configuring and Deploying the Gateway
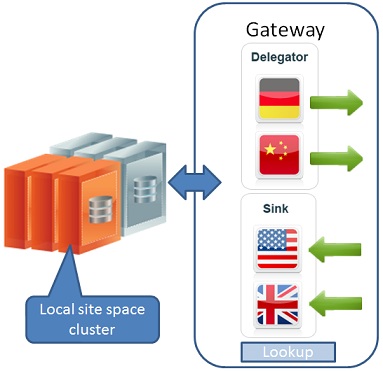
A gateway needs to be deployed locally as a processing unit in each site, and is composed of two different components: The delegator and the sink. The delegator is in charge of delegating outgoing replication from the local site to a remote gateway and the sink is in charge of dispatching incoming replication from remote sites into the local space.
Gateway Lookup
The different gateway components needs to locate each other across the different sites, for example, a delegator needs to locate the sink of the target gateway to which is delegates the replication. This lookup is done by using dedicated lookup services that the gateways are using to register and locate each other. Since this lookup process is usually done across the WAN, the most reasonable way of locating the lookup services is using unicast (multicast is also supported). With the following example we will demonstrate a unicast lookup discovery.
Gateway Basic Configuration
Following the above example, here we demonstrate how to configure the local gateway processing unit in New York, which needs to send replication to London and Hong Kong and also receive replication from these two sites.
<os-gateway:delegator id="delegator"
local-gateway-name="NEWYORK" gateway-lookups="gatewayLookups">
<os-gateway:delegations>
<os-gateway:delegation target="LONDON"/>
<os-gateway:delegation target="HONGKONG"/>
</os-gateway:delegations>
</os-gateway:delegator>
<os-gateway:sink id="sink"
local-gateway-name="NEWYORK"
gateway-lookups="gatewayLookups"
local-space-url="jini://*/*/myNYSpace">
<os-gateway:sources>
<os-gateway:source name="LONDON" />
<os-gateway:source name="HONGKONG" />
</os-gateway:sources>
</os-gateway:sink>
<os-gateway:lookups id="gatewayLookups">
<os-gateway:lookup gateway-name="NEWYORK"
host="ny-gateway-host-machine" discovery-port="10001"
communication-port="7000" />
<os-gateway:lookup gateway-name="LONDON"
host="london-gateway-host-machine" discovery-port="10002"
communication-port="8000" />
<os-gateway:lookup gateway-name="HONGKONG"
host="hk-gateway-host-machine" discovery-port="10003"
communication-port="9000" />
</os-gateway:lookups>
<!--The above ports and host names are randomly selected and
have no meaning, all sites could designate the same ports as well-->
In the above example we see that both the sink and delegator needs a reference to the gateway lookup configuration, and that’s because both components are using this configuration to locate the relevant component or to register themselves. They use their local gateway name to identify themselves to the lookup configuration, where they should be registered and where they should look for their targets.
The delegator and sink components are actually isolated and can even be deployed in separate processing units but the most simple deployment would be to bundle theses two together. However, in some cases you might want to separate this into two or more machines due to system loads or other reasons.
For full details and available configuration please refer to Replication Gateway Components
Gateway and the Mirror Service
A gateway and a Mirror Service are two different components which can co-exist together without any effect on each other. A gateway is just another reliable asynchronous target. Due to this fact, we will not discuss or demonstrate mirror service along side with a gateway because they do not contradict each other or require any special configuration when used in the same space cluster.
Gateway and Distributed Transactions
By default the gateway will preserve distributed transactions atomicity (distributed transactions consolidation), this can be disabled by adding the following property to the space configuration:
<os-core:embedded-space id="space" name="localSpace" gateway-targets="gatewayTargets">
<os-core:properties>
<props>
<prop key="cluster-config.groups.group.repl-policy.processing-type">
global-order
</prop>
</props>
</os-core:properties>
</os-core:embedded-space>
Distributed transaction consolidation is done by waiting for all the transaction participants data before processing is done by the Sink component. In some cases, certain distributed transaction participants’ data might be delayed due to network delay or disconnection and therefore may cause delays in replication. In order to prevent this potential delay, it is possible to set a timeout parameter which indicates how much time to wait for distributed transactions participants data before processing the data individually for each participant.
It is possible to specify the behavior when processing is split to individual participants upon consolidation failure (timeout or other reasons), the unconsolidated transaction can be either aborted or committed.
Please note that while waiting for the pieces of a distributed transaction to arrive at the sink, replication isn’t waiting but keeping the data flow and preventing from conflicts to happen.
The following example demonstrates how to set the timeout for waiting for distributed transaction data to arrive. It is also possible to set the amount of new operations to perform before processing data individually for each participant
<os-gateway:sink id="sink" local-gateway-name="NEWYORK"
gateway-lookups="gatewayLookups"
local-space-url="jini://*/*/myNYSpace">
<os-gateway:sources>
<os-gateway:source name="LONDON" />
<os-gateway:source name="HONGKONG" />
</os-gateway:sources>
<os-gateway:tx-support
dist-tx-wait-timeout-millis="10000"
dist-tx-wait-for-opers="20"
dist-tx-consolidation-failure-action="commit"/> <!--or "abort"-->
</os-gateway:sink>
Distributed transaction participants data will be processed individually if 10 seconds have passed and not all of the participants data has arrived or if 20 new operations were executed after the distributed transaction.
| Attribute | Default Value |
|---|---|
| dist-tx-wait-timeout-millis | 60000 milliseconds |
| dist-tx-wait-for-opers | unlimited (-1 = unlimited) |
| dist-tx-consolidation-failure-action | commit |
Note that by setting the cluster-config.groups.group.repl-policy.processing-type property to global-source all reliable asynchronous replication targets for that space will work in non-distributed transaction consolidation mode (For example, a Mirror would be in non-distributed transaction consolidation mode as well.)
Consolidation failure can occur under normal circumstances, if the target gateway is restarted or crashed during the consolidation process. In a case where the transaction was successfully consolidated and executed on the target cluster but the gateway was stopped while sending confirmation to the transaction participants in the source site and some of them have received the confirmation while others have not. In such case, the transaction is actually successfully executed in the target site and by default when the consolidation failure event will occur the unconfirmed part will reach the conflict resolution handler which by default will abort it and the state will remain consistent.
Due to the above, setting both dist-tx-wait-timeout-millis and dist-tx-wait-for-opers to unlimited (or very high value) is risky and may cause replication backlog accumulation due to a
packet which is unconsolidated and waits for consolidation which may never occur.
Master-Slave Topology
With this architecture, we have a master-slave topology where all data is being manipulated in one site, and two other sites are reading the data but not updating it. In other words, the “other sites” - the slaves - should not replicate data to the other gateways.
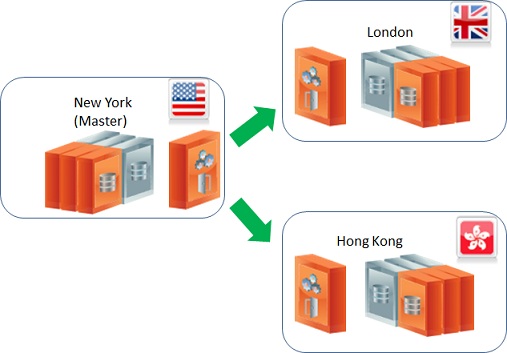
In this case, New York’s site will be the active site while London and Hong Kong will be the passive sites. As explained before, being passive does not necessarily means no work is done in these sites. However, in terms of replication over the WAN, these sites should not replicate to the other sites and usually should not alter data replicated from other sites because it may cause conflicts.
Like all GigaSpaces Processing Units, the configuration details of each of the above components is placed in a pu.xml file. Here are the contents of the files for each of the components:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:os-core="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core"
xmlns:os-events="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events"
xmlns:os-remoting="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting"
xmlns:os-sla="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla"
xmlns:os-gateway="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core/gateway"
spring
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/core/openspaces-core.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/events/openspaces-events.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/remoting/openspaces-remoting.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/sla/openspaces-sla.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core/gateway http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/core/gateway/openspaces-gateway.xsd">
<os-core:embedded-space id="space" name="myNYSpace" gateway-targets="gatewayTargets"/>
<os-gateway:targets id="gatewayTargets" local-gateway-name="NEWYORK">
<os-gateway:target name="LONDON"/>
<os-gateway:target name="HONGKONG"/>
</os-gateway:targets>
</beans>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:os-core="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core"
xmlns:os-events="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events"
xmlns:os-remoting="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting"
xmlns:os-sla="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla"
xmlns:os-gateway="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core/gateway"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
spring
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/core/openspaces-core.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/events/openspaces-events.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/remoting/openspaces-remoting.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/sla/openspaces-sla.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core/gateway http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/core/gateway/openspaces-gateway.xsd">
<os-gateway:delegator id="delegator"
local-gateway-name="NEWYORK" gateway-lookups="gatewayLookups">
<os-gateway:delegations>
<os-gateway:delegation target="LONDON"/>
<os-gateway:delegation target="HONGKONG"/>
</os-gateway:delegations>
</os-gateway:delegator>
<!--No sink needed as this site is not receiving replication from any gateway-->
<os-gateway:lookups id="gatewayLookups">
<os-gateway:lookup gateway-name="NEWYORK" host="ny-gateway-host-machine"
discovery-port="10001" communication-port="7000" />
<os-gateway:lookup gateway-name="LONDON" host="london-gateway-host-machine"
discovery-port="10002" communication-port="8000" />
<os-gateway:lookup gateway-name="HONGKONG" host="hk-gateway-host-machine"
discovery-port="10003" communication-port="9000" />
</os-gateway:lookups>
<!-- The above ports and host names are randomly selected and has no meaning,
all sites could designate the same ports as well-->
</beans>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:os-core="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core"
xmlns:os-events="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events"
xmlns:os-remoting="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting"
xmlns:os-sla="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla"
xmlns:os-gateway="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core/gateway"
spring
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/core/openspaces-core.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/events/openspaces-events.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/remoting/openspaces-remoting.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/sla/openspaces-sla.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core/gateway http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/core/gateway/openspaces-gateway.xsd">
<os-core:embedded-space id="space" name="myLondonSpace/">
<!-- No gateway targets needed as this space
is not replicating to any gateway-->
</beans>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:os-core="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core"
xmlns:os-events="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events"
xmlns:os-remoting="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting"
xmlns:os-sla="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla"
xmlns:os-gateway="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core/gateway"
spring
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
spring
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/core/openspaces-core.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/events/openspaces-events.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/remoting/openspaces-remoting.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/sla/openspaces-sla.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core/gateway http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/core/gateway/openspaces-gateway.xsd">
<!--No delegator needed as this site is not replicating to any gateway-->
<os-gateway:sink id="sink" local-gateway-name="LONDON"
gateway-lookups="gatewayLookups" local-space-url="jini://*/*/myLondonSpace">
<os-gateway:sources>
<os-gateway:source name="NEWYORK" />
</os-gateway:sources>
</os-gateway:sink>
<os-gateway:lookups id="gatewayLookups">
<os-gateway:lookup gateway-name="LONDON"
host="london-gateway-host-machine" discovery-port="10002"
communication-port="8000" />
</os-gateway:lookups>
<!-- Only the lookup parameters of this site is needed since
the sink will only register itself in the lookup service and no delegator
exists so there is no need to find a remote gateway -->
</beans>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:os-core="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core"
xmlns:os-events="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events"
xmlns:os-remoting="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting"
xmlns:os-sla="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla"
xmlns:os-gateway="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core/gateway"
spring
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/core/openspaces-core.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/events/openspaces-events.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/remoting/openspaces-remoting.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/sla/openspaces-sla.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core/gateway http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/core/gateway/openspaces-gateway.xsd">
<os-core:embedded-space id="space" name="myHKSpace"/>
<!-- No gateway targets needed as this space
is not replicating to any gateway-->
</beans>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:os-core="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core"
xmlns:os-events="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events"
xmlns:os-remoting="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting"
xmlns:os-sla="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla"
xmlns:os-gateway="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core/gateway"
spring
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
spring
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/core/openspaces-core.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/events/openspaces-events.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/remoting/openspaces-remoting.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/sla/openspaces-sla.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core/gateway http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/core/gateway/openspaces-gateway.xsd">
<!-- No delegator needed as this site is not
replicating to any gateway-->
<os-gateway:sink id="sink" local-gateway-name="HONGKONG"
gateway-lookups="gatewayLookups"
local-space-url="jini://*/*/myHKSpace">
<os-gateway:sources>
<os-gateway:source name="NEWYORK" />
</os-gateway:sources>
</os-gateway:sink>
<os-gateway:lookups id="gatewayLookups">
<os-gateway:lookup gateway-name="HONGKONG"
host="HK-gateway-host-machine" discovery-port="10003"
communication-port="9000" />
</os-gateway:lookups>
<!-- Only the lookup parameters of this site is
needed since the sink will only register itself in
the lookup service and no delegator
exists so there is no need to find a remote gateway -->
</beans>
Multi-Master Topology
With this architecture, we will have a multi-master topology where data is being generated and manipulated in all sites.
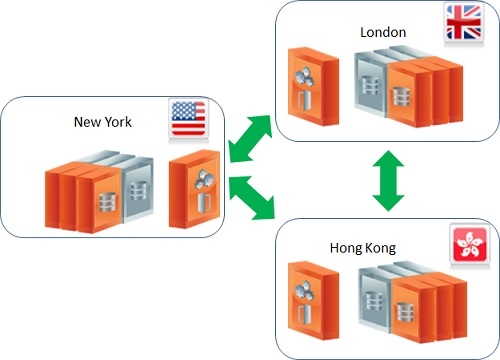
We will demonstrate this using two sites but any number of sites is supported in the same manner. In a master-slave topology, each site should try to modify different subsets of the data as much as possible because many conflicts can occur if multiple sites are changing the same space entries at the same time. Such conflict can be resolved using a conflict resolver which will be discussed fully at Multi-Site Conflict Resolution.
With the example below we will have only New York and London as the two active sites.
Here are the contents of the files for each of the components:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:os-core="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core"
xmlns:os-events="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events"
xmlns:os-remoting="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting"
xmlns:os-sla="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla"
xmlns:os-gateway="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core/gateway"
spring
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/core/openspaces-core.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/events/openspaces-events.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/remoting/openspaces-remoting.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/sla/openspaces-sla.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core/gateway http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/core/gateway/openspaces-gateway.xsd">
<os-core:embedded-space id="space" name="myNYSpace" gateway-targets="gatewayTargets"/>
<os-gateway:targets id="gatewayTargets" local-gateway-name="NEWYORK">
<os-gateway:target name="LONDON"/>
</os-gateway:targets>
</beans>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:os-core="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core"
xmlns:os-events="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events"
xmlns:os-remoting="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting"
xmlns:os-sla="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla"
xmlns:os-gateway="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core/gateway"
spring
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
spring
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/core/openspaces-core.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/events/openspaces-events.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/remoting/openspaces-remoting.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/sla/openspaces-sla.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core/gateway http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/core/gateway/openspaces-gateway.xsd">
<os-gateway:delegator id="delegator"
local-gateway-name="NEWYORK" gateway-lookups="gatewayLookups">
<os-gateway:delegations>
<os-gateway:delegation target="LONDON"/>
</os-gateway:delegations>
</os-gateway:delegator>
<os-gateway:sink id="sink" local-gateway-name="NEWYORK"
gateway-lookups="gatewayLookups" local-space-url="jini://*/*/myNYSpace">
<os-gateway:sources>
<os-gateway:source name="LONDON" />
</os-gateway:sources>
</os-gateway:sink>
<os-gateway:lookups id="gatewayLookups">
<os-gateway:lookup gateway-name="NEWYORK"
host="ny-gateway-host-machine" discovery-port="10001"
communication-port="7000" />
<os-gateway:lookup gateway-name="LONDON"
host="london-gateway-host-machine" discovery-port="10002"
communication-port="8000" />
</os-gateway:lookups>
<!--The above ports and host names are randomly selected
and have no meaning,
all sites could designate the same ports as well-->
</beans>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:os-core="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core"
xmlns:os-events="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events"
xmlns:os-remoting="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting"
xmlns:os-sla="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla"
xmlns:os-gateway="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core/gateway"
spring
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/core/openspaces-core.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/events/openspaces-events.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/remoting/openspaces-remoting.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/sla/openspaces-sla.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core/gateway http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/core/gateway/openspaces-gateway.xsd">
<os-core:embedded-space id="space" name="myLondonSpace"
gateway-targets="gatewayTargets"/>
<os-gateway:targets id="gatewayTargets" local-gateway-name="LONDON">
<os-gateway:target name="NEWYORK"/>
</os-gateway:targets>
</beans>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:os-core="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core"
xmlns:os-events="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events"
xmlns:os-remoting="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting"
xmlns:os-sla="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla"
xmlns:os-gateway="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core/gateway"
spring
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
spring
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/core/openspaces-core.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/events/openspaces-events.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/remoting/openspaces-remoting.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/sla/openspaces-sla.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core/gateway http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/core/gateway/openspaces-gateway.xsd">
<os-gateway:delegator id="delegator" local-gateway-name="LONDON"
gateway-lookups="gatewayLookups">
<os-gateway:delegations>
<os-gateway:delegation target="NEWYORK"/>
</os-gateway:delegations>
</os-gateway:delegator>
<os-gateway:sink id="sink" local-gateway-name="LONDON"
gateway-lookups="gatewayLookups" local-space-url="jini://*/*/myLondonSpace">
<os-gateway:sources>
<os-gateway:source name="NEWYORK" />
</os-gateway:sources>
</os-gateway:sink>
<os-gateway:lookups id="gatewayLookups">
<os-gateway:lookup gateway-name="NEWYORK"
host="ny-gateway-host-machine" discovery-port="10001"
communication-port="7000" />
<os-gateway:lookup gateway-name="LONDON"
host="london-gateway-host-machine" discovery-port="10002"
communication-port="8000" />
</os-gateway:lookups>
<!--The above ports and host names are randomly selected and have no meaning,
all sites could designate the same ports as well-->
</beans>
In this example, the gateway pu.xml is quite symmetric, the only difference is the local gateway name and the target gateway name. In such cases, it may be more convenient to create a single gateway pu.xml and use place holders to override the relevant properties at deploy time by injecting values for these properties:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:os-core="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core"
xmlns:os-events="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events"
xmlns:os-remoting="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting"
xmlns:os-sla="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla"
xmlns:os-gateway="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core/gateway"
spring
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
spring
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/core/openspaces-core.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/events/openspaces-events.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/remoting/openspaces-remoting.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/sla/openspaces-sla.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core/gateway http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/core/gateway/openspaces-gateway.xsd">
<bean id="propertiesConfigurer"
class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"/>
<os-gateway:delegator id="delegator"
local-gateway-name="${localGatewayName}" gateway-lookups="gatewayLookups">
<os-gateway:delegations>
<os-gateway:delegation target="NEWYORK"/>
<os-gateway:delegation target="LONDON"/>
</os-gateway:delegations>
</os-gateway:delegator>
<os-gateway:sink id="sink"
local-gateway-name="${localGatewayName}"
gateway-lookups="gatewayLookups" local-space-url="${localSpaceUrl}">
<os-gateway:sources>
<os-gateway:source name="NEWYORK" />
<os-gateway:source name="LONDON" />
</os-gateway:sources>
</os-gateway:sink>
<os-gateway:lookups id="gatewayLookups">
<os-gateway:lookup gateway-name="NEWYORK"
host="ny-gateway-host-machine" discovery-port="10001"
communication-port="7000" />
<os-gateway:lookup gateway-name="LONDON"
host="london-gateway-host-machine" discovery-port="10002"
communication-port="8000" />
</os-gateway:lookups>
<!--The above ports and host names are randomly selected and have no meaning,
all sites could designate the same ports as well-->
</beans>
In the above we have configured both LONDON and NEWYORK at the sources of the sink and as delegation target, the delegator and the sink will filter a gateway target and source if they match their local name. Using the above technique may simplify scenarios which are symmetric but it is not recommended when the scenarios are not symmetric as it can be unnecessarily confusing.
Multi-Master Running example The Multi-Master running example includes a three-way setup replicating data between three sites.
Filtering Replication Between Gateways
In some cases, there can be data that should not be replicated between the sites but should still be replicated locally to the backup or a mirror service. Hence, specifying the object is not replicated does not fit. Since a replication channel to a gateway is like any other replication channel, a custom Replication Filter at the source space can be used to filter the relevant data from being sent to the target gateway. This filtering should be based on the replication target name in order to identify that the replication filter is called for the correct outgoing replication to the gateway.
For full details and example please refer to Replication Gateway Filtering
Bootstrap One Site From Another Site
Bootstrapping a site from another site is a process in which one site space is starting fresh and it is being populated with the data of another site space. This can be useful after a very long disconnection where the replication redo-log in the source spaces that replicates to this site was dropped due to breaching capacity limitations, and the disconnected site should start fresh. Other reasons may be an explicit planned downtime due-to some maintenance of one site which lead to a complete system bootstrap once restarted.
For full details of how to enable the bootstrap mechanism refer to Replication Gateway Bootstrapping Process
Changing Sites Topology During Runtime
The topology might change during runtime, for instance a new site can be added and the existing sites should be familiar with it and start replicating to it and receive replication from it. On the other hand a site can be removed and the existing should stop holding replication backlog for it and drop it from their list of gateway targets.
For full details of how to add and remove sites during runtime refer to Changing Multi-Site Deployment during Runtime
Read More
The following pages in this section provide more details on the Multi-Site Replication module:
