MemoryXtend Overview
XAP 10 introduces a new storage model called BlobStore Storage Model, which allows an external storage medium (one that does not reside on the JVM heap) to store the IMDG data. This page describes the general architecture and functionality of this storage model, that is leveraging both on-heap, off-heap and SSD implementation, called MemoryXtend.
This storage model leverages on-heap LRU cache (deserialized form) and off-heap LRU cache (serialized form) to store data, on-heap to store indexes and external storage device to store the raw data in a serialized form.
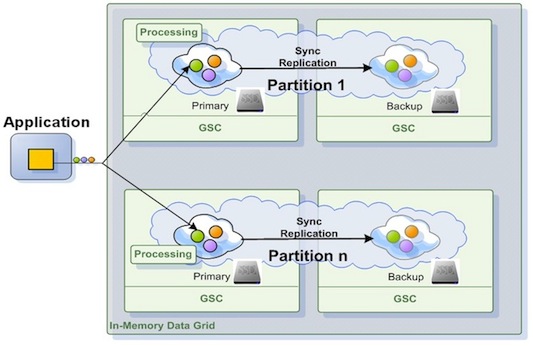
The JVM heap is used as a first level LRU cache for frequently used data. Repetitive read operations (by Id, by template or using a SQL query) for the same data will be loaded from off-heap LRU cache or from an external storage medium (SSD) upon the first request and later be served from the on-heap or off-heap based cache.
How BlobStore Storage Model Different from the Traditional XAP Persistence Model?
Unlike the traditional XAP persistence model, where the IMDG backing store is usually a database with relatively slow response time, located in a central location, the storage interface assumes very fast access for write and read operations, and a local, dedicated data store that supports a key/value interface. Each IMDG primary and backup instance across the grid is interacting with its dedicated storage medium (in our case SSD drive) independently in an atomic manner.
When running a traditional persistence configuration, the IMDG serves as a front-end to the database, and is acting as a transactional cache storing a subset of the data. In this configuration data is loaded in a lazy manner to the IMDG with the assumption that the heap capacity is smaller than the entire data set.
With the external storage medium mode, the entire data set is kept on the external SSD drive. The assumption is the SSD capacity across the grid is large enough to accommodate for the entire data set of the application.
Reduced Garbage Collection Activity
Since the IMDG raw data is stored outside of the JVM heap (the default implementation is using an SSD device) the garbage collector does not need to manage this memory. This reduces the garbage collection pauses. This in turn allows the IMDG to manage significantly larger data sets using the SSD drive’s capacity (typically several TBs of data) and not be constrained by the size of the JVM heap. When using multiple IMSG nodes, a single data grid cluster can easily manage a few tens of TBs.
Supported SSD Devices
All Enterprise flash drives are supported. SanDisk, Fusion-IO, Intel® SSD , etc are supported with the IMDG storage technology. Central SSD (RAID) devices such as Tegile, Cisco Whiptail, DSSD, and Violin Memory are also supported.
Supported XAP APIs
All XAP APIs are supported with the BlobStore configuration. This includes the Space API (POJO and Document), JDBC API, JPA API, JMS API, and Map API.
How It Works?
XAP is using SanDisk ZetaScale library, which uses direct flash access. It circumvents OS level storage interfaces when writing an object to the space, its indexed data maintained on Heap where the Storage interface implementing using the ZetaScale libraries to interact with the underlying flash drive.
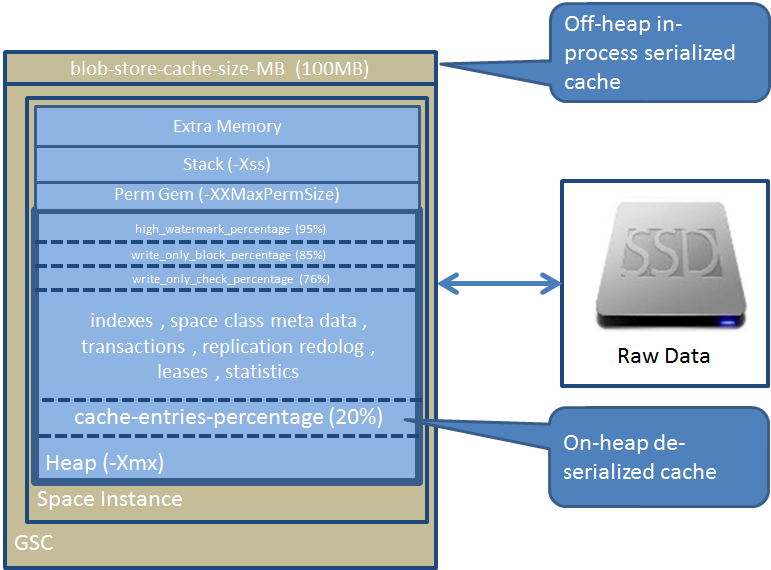
The indexes maintain in RAM (on-heap) allowing the XAP query engine to evaluate the query without accessing the raw data stored on the flash device. This allows XAP to execute SQL based queries extremely efficiently even across large number of nodes. All XAP Data Grid APIs are supported including distributed transactions, leasing (Time To live) , FIFO , batch operations , etc. All clustering topologies supported. All client side cache options are supported.
The BlobStore Configuration
The BlobStore settings includes the following options:
| Property | Description | Default | Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| devices | Flash devices. Comma separated available devices. The list used as a search path from left to right. The first one exists will be used. | required | |
| volume-dir | Directory path contains a symbolic link to the the SSD device. | required | |
| blob-store-capacity-GB | Flash device allocation size in Gigabytes. | 200 | optional |
| ZetaScale internal LRU based off-heap in-process cache size in Megabytes. Keeps data in serialized format. | 100 | optional | |
| write-mode | WRITE_THRU - the data grid writes the data immediately into the blobstore and synchronously acknowledge the write after ZetaScale fully commits the operation. WRITE_BEHIND - the data grid writes the data immediately into the blobstore. ZetaScale asynchronously commits the operation to the SSD. This option improves write performance but may have a consistency issue with a sudden hardware failure. |
WRITE_THRU |
optional |
| enable-admin | ZetaScale admin provides a simple command line interface (CLI) through a TCP port. ZetaScale CLI uses port 51350 by default. This port can be changed through the configuration parameter FDF_ADMIN_PORT. |
false | |
| statistics-interval | Applications can optionally enable periodic dumping of statistics to a specified file (XAP_HOME/logs). This is disabled by default. | optional | |
| durability-level | SW_CRASH_SAFE - Guarantees no data loss in the event of software crashes. But some data might be lost in the event of hardware failure. HW_CRASH_SAFE- Guarantees no data loss if the hardware crashes.Since there are performance implication it is recommended to work with NVRAM device and configure log-flash-dir to a folder on this device. |
SW_CRASH_SAFE | optional |
| log-flush-dir | When HW_CRASH_SAFE used , point to a directory in a file system on top of NVRAM backed disk. This directory must be unique per space, you can add ${clusterInfo.runningNumber} as suffix to generate a unique name |
as volume-dir | optional |
The IMDG BlobStore settings includes the following options:
| Property | Description | Default | Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| blob-store-handler | BlobStore implementation | required | |
On-Heap cache stores objects in their native format. This cache size determined based on the percentage of the GSC JVM max memory(-Xmx). If -Xmx is not specified the cache size default to 10000 objects. This is an LRU based data cache. |
20% | optional | |
| avg-object-size-KB | Average object size. | 5KB | optional |
| recover-from-blob-store | Whether to recover from blob store or not | required |
Prerequisites
MemoryXtend currently supports Linux CentOS 6.x only.
Check that your user is part of disk groups.
$ groups
If your user is not part of disk groups, add it by calling:
$ sudo usermod -G disk <username>
and re-login.
The number of of flash devices/partitions should be aligned with the space instances number that you want to deploy on a machine. For creating partitions you can use fdisk like explained here.
- Make sure your user has read/write permissions to flash devices
- Make sure your user has read/write permissions to /tmp
Installation
Step 1.
Dwonload the XAP 10 distribution and the MemoryXtend RPM with the ZetaScale libraries.
Step 2.
Install XAP as usual. Unzip the gigaspaces-xap-premium-10.0.1-ga-b11800.zip.
Step 3. Install ZetaScale libraries:
$ sudo XAP_HOME=<XAP HOME> sh -c "yum -y install blobstore-10.0.1-11800_RELEASE_1.noarch.rpm"
If the RPM installation fails , please run the following yum install commands using root user:
sudo yum -y install snappy
sudo yum -y install snappy-devel
sudo yum -y install libaio
sudo yum -y install libaio-devel
sudo yum -y install libevent
sudo yum -y install libevent-devel
sudo yum -y install glibc-devel
Step 4.
Use the XAP HOME\bin\gs-agent-blobstore.sh to start GigaSpaces Grid Agent that configured to load the ZetaScale libraries.
Uninstall
To uninstall the blobstore libraries run the following command:
$ sudo XAP_HOME=<XAP HOME> sh -c "yum -y remove blobstore-10.0.1-11800_RELEASE_1.noarch"
Configuration
Configuring an IMDG (Space) with BlobStore should be done via the SanDiskBlobStoreDataPolicyFactoryBean, or the SanDiskBlobStoreConfigurer. For example:
PU XML Configuration
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:os-core="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core"
xmlns:blob-store="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/blob-store"
spring
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/core/openspaces-core.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/blob-store http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/blob-store/openspaces-blobstore.xsd">
<bean id="propertiesConfigurer" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"/>
<blob-store:sandisk-blob-store id="myBlobStore" blob-store-capacity-GB="100" blob-store-cache-size-MB="100"
devices="/dev/sdb1,/dev/sdc1" volume-dir="/tmp/data${clusterInfo.runningNumber}" durability-level="SW_CRASH_SAFE">
</blob-store:sandisk-blob-store>
<os-core:embedded-space id="space" name="mySpace" >
<os-core:blob-store-data-policy blob-store-handler="myBlobStore" cache-entries-percentage="10" avg-object-size-KB="5" recover-from-blob-store="true"/>
</os-core:embedded-space>
<os-core:giga-space id="gigaSpace" space="space"/>
</beans>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:os-core="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core"
spring
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core http://www.openspaces.org/schema/10.0/core/openspaces-core.xsd">
<bean id="propertiesConfigurer" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"/>
<bean id="blobstoreid" class="com.gigaspaces.blobstore.storagehandler.SanDiskBlobStoreHandler">
<property name="blobStoreCapacityGB" value="200"/>
<property name="blobStoreCacheSizeMB" value="50"/>
<property name="blobStoreDevices" value="/dev/xvdb,/dev/xvdc"/>
<property name="blobStoreVolumeDir" value="/tmp/data${clusterInfo.runningNumber}"/>
<property name="blobStoreDurabilityLevel" value="SW_CRASH_SAFE"/>
</bean>
<os-core:embedded-space id="space" name="mySpace">
<os-core:blob-store-data-policy blob-store-handler="blobstoreid" cache-entries-percentage="10"
avg-object-size-KB="5" recover-from-blob-store="true"/>
</s-core:embedded-space>
<os-core:giga-space id="gigaSpace" space="space"/>
</beans>
Programmatic API
Programmatic approach to start a BlobStore space:
SanDiskBlobStoreConfigurer configurer = new SanDiskBlobStoreConfigurer();
configurer.addDevices("/dev/xvdb,/dev/xvdc");
configurer.addVolumeDir("/tmp");
configurer.setBlobStoreCapacityGB(200);
configurer.setBlobStoreCacheSizeMB(50);
configurer.setDurabilityLevel(DurabilityLevel.SW_CRASH_SAFE);
SanDiskBlobStoreHandler blobStoreHandler = configurer.create();
BlobStoreDataCachePolicy cachePolicy = new BlobStoreDataCachePolicy();
cachePolicy.setAvgObjectSizeKB(5l);
cachePolicy.setCacheEntriesPercentage(10);
cachePolicy.setRecoverFromBlobStore(true);
cachePolicy.setBlobStoreHandler(blobStoreHandler);
UrlSpaceConfigurer urlConfig = new UrlSpaceConfigurer("/./mySpace");
urlConfig.cachePolicy(cachePolicy);
gigaSpace = new GigaSpaceConfigurer(urlConfig).gigaSpace();
The above example:
- Configures the SanDisk BlobStore bean.
- Configures the Space bean (Data Grid) to use the blobStore implementation.
Automatic Data Recovery and ReIndexing
Once the Data grid is shutdown and redeployed it may reload its entire data from its flash drive store. Loading data from a local drive may provide fast data recovery - much faster than loading data from a central database. The data reload process iterate the data on the flash drive and generate the indexed data based on the indexed data list per space class. As each data grid partition perform this reload and reindexing process in parallel across multiple servers it may complete this indexing process relatively fast. With a single machine with 8 cores, running 4 partitions data grid with four SSD drives , 100,000 items / second (1K payload) may be scanned and re-indexed. To enable the Data Recovery and ReIndexing activity the recover-from-blob-store should be set to true.
To allow the data grid to perform an automatic data recovery from the right flash device on startup you should use Instance level SLA .
With this SLA you control where a specific space instance will be provisioned. You may find a bloblstore data grid processing unit template at XAP_HOME/deploy/templates/blobstore-datagrid. Within this template there is an sla configuration file blobstore-datagrid/META_INF/spring/sla.xml you may use.
You can copy the XAP_HOME/deploy/templates/blobstore-datagrid into XAP_HOME/deploy with the same folder name or a different name to have a customized blobstore-datagrid PU.
SLA Examples
Partitioned with a backup SLA
With the following sla.xml example we have a single partition with a backup where the first instance is provisioned into HostA , and the second instance for the same partition is provisioned into HostB.
<os-sla:sla>
<os-sla:instance-SLAs>
<os-sla:instance-SLA instance-id="1">
<os-sla:requirements>
<os-sla:host ip="HostA"/>
</os-sla:requirements>
</os-sla:instance-SLA>
<os-sla:instance-SLA instance-id="1" backup-id="1">
<os-sla:requirements>
<os-sla:host ip="HostB"/>
</os-sla:requirements>
</os-sla:instance-SLA>
</os-sla:instance-SLAs>
</os-sla:sla>
Partitioned without a backup SLA
With the following sla.xml we have a partitioned (2 partitions) data grid without backups SLA example where both instances are provisioned into the HostA:
<os-sla:sla>
<os-sla:instance-SLAs>
<os-sla:instance-SLA instance-id="1">
<os-sla:requirements>
<os-sla:host ip="HostA"/>
</os-sla:requirements>
</os-sla:instance-SLA>
<os-sla:instance-SLA instance-id="2">
<os-sla:requirements>
<os-sla:host ip="HostA"/>
</os-sla:requirements>
</os-sla:instance-SLA>
</os-sla:instance-SLAs>
</os-sla:sla>
Make sure you provide the
sla.xml location at the deploy time (-sla deploy command option) or locate it at the root of the processing unit jar or under the META-INF/spring directory, alongside the processing unit’s pu.xml file.Device Allocation
The device allocation per a machine is managed via the /tmp/blobstore/devices/device-per-space.properties file. You can specify this file location using the com.gs.blobstore-devices system property when setting the GSC_JAVA_OPTIONS. Each time a new blobstore space is deployed an Entry is added to this file listing the data grid instances provisioned on the machine.
BlobStore Space re-deploy
When you undeploy a blobstore space use the XAP_HOM/bin/undeploy-grid.groovy that comes with the RPM. It undeploys the blobstore space and restarts all its GSCs.
export PATH:/gigaspaces-xap-premium-10.0.0/bin/tools/groovy/bin/
cd /gigaspaces-xap-premium-%currentversion%}}/bin/tools/groovy/bin
$ groovy undeploy-grid.groovy <LUS HostName> <BlobStore-Space-Name>
Controlling blobStore mode at the Space Class Level
By default any Space Data Type is blobStore enabled. When decorating the space class with its meta data you may turn off the blobStore behavior using the @SpaceClass blobstoreEnabled annotation or gs.xml blobstoreEnabled tag.
Here is a sample annotation disabling blobStore mode:
@SpaceClass(blobstoreEnabled = false)
public class Person {
.......
}
Here is a sample xml decoration for a POJO class disabling blobStore mode:
<gigaspaces-mapping>
<class name="com.test.Person" "blobstoreEnabled"="false" >
.....
</class>
</gigaspaces-mapping>
BlobStore Management
You may use the ZetaScale Management command line to access underlying SSD storage runtime. This allows you to access statistics that can be used to tune performance and analyze performance problems. These statistics counters used to monitor events within the FDF subsystem. Most events are counted on a per FDF container basis as well as for all containers within the FDF instance.
Statistics
- Counts of FDF access types
- Counts of various flash activities
- Histogram of key sizes
- Histogram of data sizes in bytes
- Histogram of access latencies in microseconds
- Number of events , Minimum , Maximum , Average , Geometric mean , Standard deviation
- Overwrite/Write-‐Through Statistics
- Total number of created objects
- Number of get/put/delete operations
- Number of hash/flash/invalid evictions
- Number of objects in flash
- Number of soft/hard overflows in hast table
- Number of pending IO’s
- Flash space allocated/consumed in bytes
- Number of overwrites
- Number of hash collisions for get/set operations
Applications can optionally enable periodic dumping of statistics to a specified file. This is disabled by default. It can be enabled using the configuration parameter FDF_STATS_FILE=<filepath>. The dump interval can be configured using FDF_STATS_DUMP_INTERVAL=<interval in secs>. The dump interval can also be dynamically changed through the CLI.
Per Container Statistics
Container Properties:
name = e12e3940
cguid = 419
Size = 0 kbytes
persistence = enabled
eviction = disabled
writethrough = enabled
fifo = disabled
async_writes = disabled
durability = Periodic sync
num_objs = 7645
used_space = 3914240
Application requests:
num_set_objs_with_expiry = 7645
completed_enumerations = 1
active_enumerations = 1
objects_enumerated = 402
cached_objects_enumerated = 402
Overwrite and write-through statistics:
num_new_entries = 7645
num_writethrus_to_flash = 7645
Cache to Flash Manager requests:
cache_misses = 0
cache_hits = 0
num_set_objs_and_put = 7645
Flash Manager responses to cache:
num_set_objs_completed = 7645
Flash Manager requests/responses:
num_set_objs = 7645
Flash layer return codes:
num_success = 7645
Overall FDF Statistics
Flash statistics:
num_items_flash = 2167157
num_items_created = 2188567
num_overwrites = 21410
num_put_ops = 2188567
flash_space_allocated = 1409286144
flash_space_consumed = 36186112
Flash type:
flash_class_map 27 15 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
flash_slab_map 1705845 461327 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Application requests:
num_put_objs = 1233
num_set_objs_with_expiry = 72018
num_get_objs = 419
num_del_objs = 1221
num_flush_objs = 2479
num_sync_to_flash = 2479
num_flush_container = 408
Overwrite and write-through statistics:
Cache to Flash Manager requests:
cache_misses = 0
cache_hits = 0
num_delete_objs = 1221
num_get_objs_to_read = 419
num_put_objs = 1233
num_set_objs_and_put = 72018
Flash Manager responses to cache:
FDF Programming Guide – 1.2 Sandisk Confidential 35
num_delete_objs_completed = 1221
num_get_objs_to_read_failed = 419
num_put_objs_completed = 1233
num_set_objs_completed = 72018
Flash Manager requests/responses:
num_get_objs = 419
num_get_objs_failed = 419
num_delete_objs = 1221
num_delete_completed = 1221
num_set_objs = 73251
Flash layer return codes:
num_success = 74472
num_errors_objects_not_found = 419
Cache statistics:
num_hash_buckets_in_cache = 100000
num_cache_partitions = 10000
num_objects_in_cache = 66252
max_cache_capacity = 100000000
current_data_size_in_cache = 14434903
current_key_and_data_size_in_cache = 19129759
num_modified_objs_in_cache = 4601
num_bytes_of_modified_objs_in_cache = 889931
num_mod_objs_flushed = 245891
num_mod_objs_flushed_by_bgflush = 838438
background_flush_progress = 93
num_background_flushes = 363
max_parallel_flushes = 8
max_parallel_bg_flushes = 8
time_to_wait_after_bgflush_for_nodirty_data = 1000
max_percent_limit_on_modifiable_cache = 100
num_cache_ops_in_progress = 18
Command Line Interface
ZetaScale provides a simple command line interface (CLI) through a TCP port. The ZetaScale CLI uses port 51350 by default. This port can be changed through the configuration parameter FDF_ADMIN_PORT=<port number>. The CLI functionality can be disabled by setting configuration property FDF_ADMIN_ENABLED=0. The CLI supports the following commands.
| Command | Description |
|:——–|:————|
|container list|Lists all of the container names|
|container stats <container name>[v] | Prints stats of the given container. The option v (verbose) prints extended stats.|
|container stats_dump <container name|all> [v] | Prints stats of a given container or all containers to the stats file configured through FDF_STATS_FILE. The option v(verbose) prints extended stats.
|container autodump <enable/disable/interval/printcfg> [interval in secs] | This command enables or disables periodic stats dump, and configures the dump interval.|
|log_level <set/get> [fatal/error/warning/info/diagnostic/ debug/trace/trace_low/devel]| Sets the log level|
|help | Prints help for all supported commands|
|quit |Quits the telnet session|
[root@xen200v03]~# telnet localhost 51350
Trying 127.0.0.1...
Connected to localhost.localdomain (127.0.0.1).
Escape character is '^]'.
help
Supported commands:
container stats <container name> [v]
container stats_dump <container name|all> [v]
container autodump <br><enable/disable/interval/printcfg> [interval in secs]
container list
log_level <set/get> [fatal/error/warning/info/diagnostic/debug/trace/trace_low/devel]
help
quit
container list
container-4819c940
container stats container-4819c940
Timestamp:Tue May 7 12:06:45 2013
Per Container Statistics
Container Properties:
name = container-4819c940
cguid = 4
Size = 1048576 kbytes
persistence = enabled
eviction = disabled
writethrough = enabled
fifo = disabled
async_writes = disabled
durability = Periodic sync
num_objs = 1
used_space = 512
Application requests:
num_set_objs_with_expiry = 1
num_get_objs_and_check_expiry = 1
completed_enumerations = 1
objects_enumerated = 1
cached_objects_enumerated = 1
Overwrite and write-through statistics:
num_new_entries = 1
num_writethrus_to_flash = 1
Cache to Flash Manager requests:
cache_misses = 0
cache_hits = 1
num_set_objs_and_put = 1
Flash Manager responses to cache:
num_set_objs_completed = 1
Flash Manager requests/responses:
num_set_objs = 1
Flash layer return codes:
num_success = 1
The BlobStoreStorageHandler Interface
The BlobStoreStorageHandler Interface provides the following methods. You may customize it to have your specific functionality:
abstract class BlobStoreStorageHandler
{
public void initialize(String spaceName, Properties properties, boolean warmStart){};
public abstract Object add(java.io.Serializable id,java.io.Serializable data, BlobStoreObjectType objectType);
public abstract java.io.Serializable get(java.io.Serializable id, Object position, BlobStoreObjectType objectType);
public abstract Object replace(java.io.Serializable id,java.io.Serializable data, Object position, BlobStoreObjectType objectType);
public abstract void remove(java.io.Serializable id, Object position, BlobStoreObjectType objectType);
public List<BlobStoreBulkOperationResult> executeBulk(List<BlobStoreBulkOperationRequest> operations, BlobStoreObjectType objectType, boolean transactional)
public DataIterator<BlobStoreGetBulkOperationResult> iterator(BlobStoreObjectType objectType)
public Properties getProperties(){};
public void close(){};
}
Considerations
- All classes that belong to types that are to be introduced to the space during the initial metadata load must exist on the classpath of the JVM the Space is running on.
- The current MemoryXtend release support a single blobstore space instance per GSC.
Answers to frequently asked questions about MemoryXtend for SSD can be found here
