Overview
Replication is the process of duplicating or copying application data and operations, from a source space to a target space, or to multiple target spaces. Replication is used mainly for high-availability, where a replica space is running in backup mode or for sharing local site data with remote sites. The operations that are replicated are the modifying operations, i.e. those that actually affect the data that is stored in the space instance, such as Write/Take/Update and Lease cancel/renewal.
Replication Topologies
The replication topologies are split into three groups:
- Primary backup
- Primary backup with a mirror (reliable asynchronous replication)
- Active-Active (fully replicated)
Primary-Backup
This topology consists of a group of space instances that are part of the same replication group, one of the space instances is elected and serves as the primary space instance of the group. The application interaction is done with the primary instance while the other instances are serving as the backups of the primary. The backup space instances are an exact replica of the primary and if the primary instance fails they are ready to immediately replace it. This happens without any data loss and is transparent to the space proxy connected to the space instances.
Primary-Backup with a Mirror
This topology extends the previous one by having a mirror service that is part of the primary backup replication group. The mirror service receives the replication data from the primary space instance asynchronously. However, the replication data is kept in a backlog both in the primary and the backups space instances until the mirror acknowledge that is received the replication data. This way, in case of a primary failure, the replacing backup space instance will make sure that the mirror does not lose any replication data, hence the terminology - reliable asynchronous replication.
Active active
This topology consists of a group of space instances that are part of the same replication group, unlike primary backup, all of the space instances are active and the application interacts with all of them. The common usage in this case is to have this topology as part of a multi site deployment where each site is interacting with the local space instance while having all the operations replicated and kept in the other sites as well. Each space instance replicates its data to all the other members thus having all the space instances holding the data of each other.
For more info refer to Replication Topologies
Replication Modes
There are two replication modes:
- Synchronous replication - the data is replicated as part of the modifying space operation
- Asynchronous replication - the data is replicated asynchronously to the space operation
The common usage of these modes is synchronous for Primary-Backup topology and asynchronous for Active-Active topologies.
Synchronous Replication
With synchronous replication, the client receives acknowledgement for any replicated operations only after all the space instances in the replication group have performed the operation.
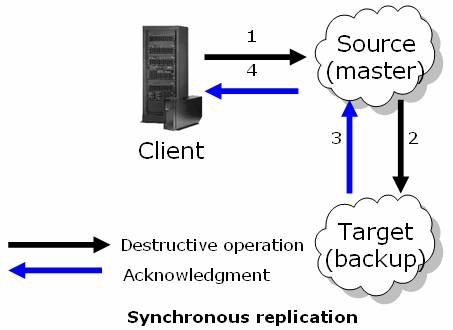
For more info refer to Synchronous Replication
Asynchronous replication
With asynchronous replication, operations are performed in the source space instance, and acknowledgement is immediately returned to the client.
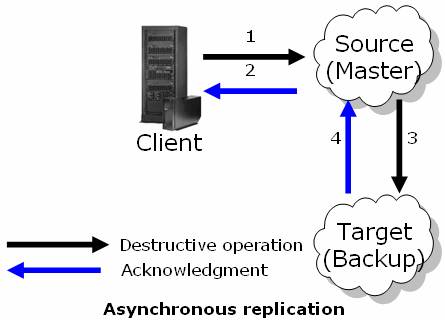
Operations are accumulated in the source space and sent asynchronously to the target space, after a predefined period of time has elapsed, or after a predefined number of operations have been performed (the first of the two to occur). The downside of this replication mode is the possibility of data loss if the source space fails while transferring the accumulated operations to the target space. Another problem is data consistency - the source and the target do not have identical data at all times.
For more info refer to Asynchronous Replication
Replication During Disconnections Between Space Instances
In both replication modes, when a target space instance is not available, the client will receive an acknowledgement from the source space instance. The operation on the target space instance is performed only when the source space instance re-establishes the connection with the target space instance. The source space instance keeps a backlog of all replicated operations until it is able to re-establish a connection with the target space instance.
The table below shows a conceptual comparison between synchronous and asynchronous replication.
| Aspect | Synchronous Replication | Asynchronous Replication |
|---|---|---|
| Data loss | Each space operation waits until completion is confirmed at the source space instance, as well as the target space instances. | May sometimes lose some data (latest operations) if there is a failure at the source space instance. |
| Latency | Less tolerant to high network latency | Highly tolerant of network latency, and can be used when the space instances are located in different geographical sites (different cities). |
| Performance Impact | Cliensx must wait for confirmation of each space operation from the source and target space instances. Performance is mainly dependent on source space instances resources (CPU/memory), target space instance resources (CPU/memory), and the network bandwidth and latency between the source space and the target space instances. |
Client is acknowledged immediately after the source space instances has processed incoming operations. Performance is mainly dependent on source space resources (CPU/memory). |
| Data Integrity | Very accurate | Less accurate |
Configuration
There are many parameters that configure the replication behavior. For a full list of the parameters see Replication Parameters.
Monitoring and Statistics
The replication module can be monitored and exposes various statistics using the Administration and Monitoring API via Replication Statistics
