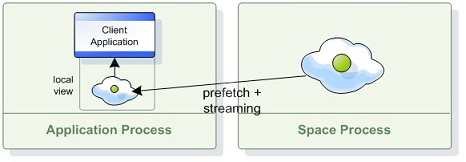
Local View
A Local View is a Client Side Cache that maintains a subset of the master space’s data, allowing the client to read distributed data without performing any remote calls or data serialization.
Data is streamed into the client local view based on predefined criteria (a collection of SQLQuery objects) specified by the client when the local view is created.
During the local view initialization, data is loaded into the client’s memory based on the view criteria. Afterwards, the local view is continuously updated by the master space asynchronously - any operation executed on the master space that affects an entry which matches the view criteria is automatically propagated to the client.
Where the Local View Can be Used?
The Local view can be used with financial applications (e.g. trading , market data , portfolio management) where each client (e.g. trader , broker) might need to access specific products / securities / equities data in real time. In this case, the application instance can generate a client side cache customized for the user needs.
Usage
Creating a local view is similar to creating a GigaSpace instance, except the space should be wrapped with a local view before exposing it as a GigaSpace. The local view can be configured via Spring using LocalViewSpaceFactoryBean or the <os-core:local-view> Spring tag, or in code using LocalViewSpaceConfigurer. For example:
<os-core:space-proxy id="space" name="mySpace"/>
<os-core:local-view id="localViewSpace" space="space">
<os-core:properties>
<props>
<prop key="space-config.engine.memory_usage.write_only_block_percentage">88</prop>
<prop key="space-config.engine.memory_usage.write_only_check_percentage">86</prop>
</props>
</os-core:properties>
<os-core:view-query class="com.example.Message1" where="processed = true"/>
<os-core:view-query class="com.example.Message2" where="priority > 3"/>
</os-core:local-view>
<os-core:giga-space id="localView" space="localViewSpace"/>
<bean id="space" class="org.openspaces.core.space.SpaceProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="name" value="space" />
</bean>
<bean id="viewSpace" class="org.openspaces.core.space.cache.LocalViewSpaceFactoryBean">
<property name="space" ref="space" />
<property name="localViews">
<list>
<bean class="com.j_spaces.core.client.view.View">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="com.example.Message1" />
<constructor-arg index="1" value="processed = true" />
</bean>
<bean class="com.j_spaces.core.client.view.View">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="com.example.Message2" />
<constructor-arg index="1" value="priority > 3" />
</bean>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
// Initialize remote space configurer:
SpaceProxyConfigurer urlConfigurer = new SpaceProxyConfigurer("mySpace");
// Initialize local view configurer
LocalViewSpaceConfigurer localViewConfigurer = new LocalViewSpaceConfigurer(urlConfigurer)
.batchSize(1000)
.batchTimeout(100)
.maxDisconnectionDuration(1000*60*60)
.addProperty("space-config.engine.memory_usage.high_watermark_percentage", "90")
.addProperty("space-config.engine.memory_usage.write_only_block_percentage", "88")
.addProperty("space-config.engine.memory_usage.write_only_check_percentage", "86")
.addProperty("space-config.engine.memory_usage.retry_count", "5")
.addProperty("space-config.engine.memory_usage.explicit", "false")
.addProperty("space-config.engine.memory_usage.retry_yield_time", "50")
.addViewQuery(new SQLQuery(com.example.Message1.class, "processed = true"))
.addViewQuery(new SQLQuery(com.example.Message2.class, "priority > 3"));
// Create local view:
GigaSpace localView = new GigaSpaceConfigurer(localViewConfigurer).gigaSpace();
Read Only Cache
The Local View is a Read-Only client side cache. The following operations are supported - these are served by the local view. The master space is not accessed when calling these:
- read , readMultiple , asyncRead , count , using Template Matching, Id Queries or SQLQuery.
- Notify Container , Session Based Messaging API.
- IteratorBuilder.
The following operations are not supported when using local view, and should be performed using a regular space proxy:
- Any operation that creates or changes data (write, writeMultiple, update, updateMultiple, execute).
- Any operation that removes data: (clean, clear, take, takeById, takeMultiple, asyncTake, etc.).
- Any operation under a transaction.
Memory Management
Data is never evicted from the local view (the cache policy is hardwired to ALL_IN_CACHE). Therefore, specifying a criteria that retrieves large amounts of data from the master space can cause the client to run out of memory.
Multiple Cache Instances within the Same Client
Running multiple local view instances (for different master spaces) within the same client without allocating reasonable headroom for the local view to operate, may cause problems. This will be manifested in MemoryShortageException being thrown sporadically.
The main reason for such issues is the interdependency each cache has on the other caches’ utilized memory. Since the MemoryShortageException is thrown when the JVM’s total utilized memory is above some threshold (and not when a specific cache’s utilized memory is above a certain threshold), an “over-utilized” cache may impact other caches running within the same client. The recommended approach to ensure a deterministic behavior is provide some extra headroom for the client JVM heap size to accommodate the potential total amount of objects stored by all the local views.
For example: Client X runs two local view instances, LV1 for master space A, matching 100,000 objects, and LV2 for master space B, matching 100 objects. Some other clients write data to space A. Since LV1 matches these written/updated objects, LV1 gets these objects automatically (via notifications) and updates its view. At some point, other clients write data into space B. Since LV2 matches these objects, it will have these objects automatically propagated locally.
If the JVM running client X’s available memory breaches the write_only_block_percentage threshold, a MemoryShortageException is thrown once the listener on the client side (for LV1 or LV2) that receives the notifications with the new/updated objects tries to write these into the relevant local view. In this case, the client might not even perform an explicit read. It will have a “phantom” MemoryShortageException thrown that is a result of new/updated objects written into the space by other clients (or by itself). Even if LV2 were to be cleared somehow (as a result of objects taken from space B), a MemoryShortageException will be thrown at the client side once new objects are written into space A.
Synchronization
Starting with XAP 8.0.6, the local view uses replication instead of notifications to synchronize with the master space. The reason for that change is that replication provides higher reliability than notification. In general this is an implementation detail that should not concern the user, except for the following cases:
- Using a view query on a type/class configured to be non-replicable.
- Using a cluster with an Active-Active topology, or a non-clustered space.
In those cases, the local view will automatically revert to notification-based synchronization.
Synchronization Batch
Changes in the server are grouped and sent to the client in batches. The following configuration settings controls synchronization batching:
- Batch Size - When the batch size reaches the configured value, the batch is sent to the client. Default is 1000 packets.
- Batch timeout - When the oldest event in the batch reaches the configured value, the batch is sent to the client. The default is 100 milliseconds.
Setting lower values for batch size and timeout will reduce data staleness but increase network load, and vice versa.
Batch settings can be configured using LocalViewSpaceFactoryBean for Spring, or using LocalViewSpaceConfigurer at runtime. For example:
<os-core:local-view id="localViewSpace" space="space" batch-size="1000" batch-timeout="100">
<os-core:view-query class="com.example.Message1" where="processed = true"/>
</os-core:local-view>
Recovering From Disconnection
When the connection between a local view and remote master space is disrupted, the local view starts trying to reconnect with the remote space.
If the disconnection duration exceeds the maximum disconnection duration, the local view enters a disconnected state, wherein each operation throws an exception stating the view is disconnected.
When the connection to the remote master space is restored, the local view reloads all its data from the master space (same as in the initialization process) before restoring the state to connected, ensuring the local view is consistent when it is accessed.
The maximum disconnection duration can be configured using LocalViewSpaceFactoryBean for Spring, or using LocalViewSpaceConfigurer at runtime (default is 1 minute). For example:
<os-core:local-view id="localViewSpace" space="space" max-disconnection-duration="60000">
<os-core:view-query class="com.example.Message1" where="processed = true"/>
</os-core:local-view>
When the synchronization is replication-based (default), the local view is resilient to failover, which means that if a primary space fails and a backup space replaces it within the maximum disconnection duration, the local view will remain intact during the failover process. When the synchronization is notification-based this is not guaranteed since notifications might be lost during the failover process.
Upgrading From Previous Versions
This section is intended to summarize the changes in 8.0.5 for users upgrading from previous versions.
Maximum Disconnection Duration
In previous versions the max disconnection duration was configured by setting the space-config.dist-cache.events.lease and/or space-config.dist-cache.events.lease-renew.duration custom properties. Configuring the max disconnection duration using these custom properties is still supported, but starting 8.0.5 it is deprecated.
In addition, since the reconnect mechanism has been improved in 8.0.5, the custom properties space-config.dist-cache.retry-connections and space-config.dist-cache.delay-between-retries are no longer required and will be ignored.
Batch Size & Timeout
In previous versions the batch size and timeout were configured by setting the space-config.dist-cache.events.batch.size and space-config.dist-cache.events.batch.timeout custom properties, respectively. Configuring the batch size and timeout using these custom properties is still supported, but starting with 8.0.5 it is deprecated.
Notification
If local view synchronization is done using notifications, the round-trip-time can be configured using the space-config.dist-cache.events.lease-renew.round-trip-time custom property. For more information about this setting refer to Session Based Messaging API.
Configuring from Space URL
Creating a Local View directly from the space url is deprecated - use LocalViewSpaceFactoryBean or LocalViewSpaceConfigurer instead.
Server side local view properties
This properties can be configured on the space side and they will affect all the local views which are created on top of that space.
| Property | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| cluster-config.groups.group.repl-policy.redo-log-local-view-capacity | Specifies the total capacity of replication packets the redo log can hold for a local view replication target | 150000 |
| cluster-config.groups.group.repl-policy.redo-log-local-view-recovery-capacity | Specifies the total capacity of replication packets the redo log can hold for a local view replication target while the local view is in recovery state (initial load process) | 1000000 |
| cluster-config.groups.group.repl-policy.local-view-max-disconnection-time | Specifies the maximum amount of time (in milliseconds) the space will wait for the local view replication target before it is considered disconnected, after which the target will be dropped. | 300000 |
Considerations
When a Local View contains complex objects (nested structure), it is recommended to perform a deep clone once these have been read to allow incoming updates to refresh the state of the cached objects (copy on read). The client application should use the cloned object as the original object returned back from the read operation holds a reference used by the local view.
