MemoryXtend for Flash/SSD
Introduction
XAP MemoryXtend for Flash/SSD delivers built-in high speed persistence leveraging local or attached SSD devices and all-flash-arrays (AFA). It delivers low latency write and read performance, as well as fast data recovery. XAP MemoryXtend for Flash/SSD is based on RocksDB which is a persistent key/value store optimized for fast storage environments.
Architecture and Components
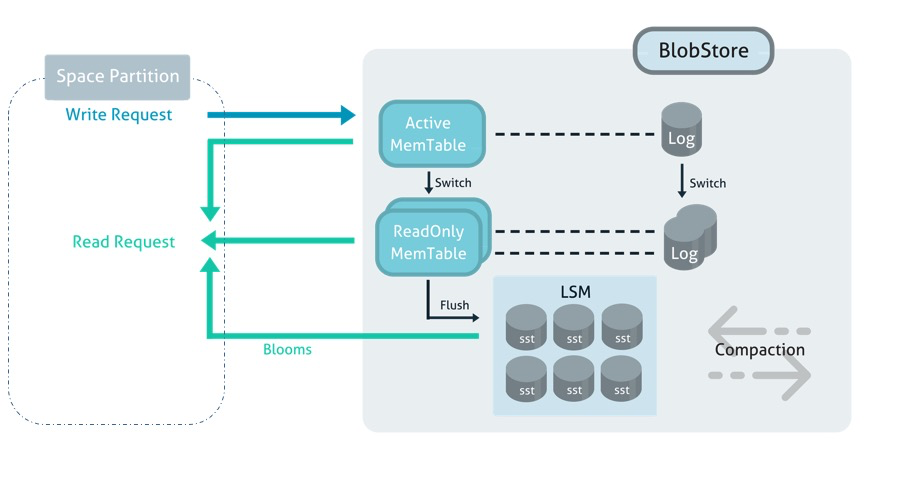
When configured for Flash/SSD, the MemoryXtend architecture tiers the storage of each space partition instance across two components: a space partition instance (managed JVM heap) and an embedded key/value store (the blob store) as shown in the diagram down below.
Space Partition Instance
The space partition instance is a JVM heap which acts as a LRU cache against the underlying blob store. This tier in the architecture stores indexes, space class metadata, transactions, replciation redo log, leases and statistics. Upon a space read operation, if the object exists in the JVM heap (i.e. a cache hit) it will be immediately returned to the space proxy client. Otherwise, the space will load it from the underlying blob store and place it on the JVM heap (known as a cache miss).
Blob Store
The blob store is based on a log-structured merge tree architecture (similar to popular NoSQL databases such as: HBase , BigTable , or Cassandra ). There are three main components in the blob store:
- MemTable: An in-memory data structure (residing on off-heap RAM) where all incoming writes are stored. When a MemTable fills up, itis flushed to a SST file on storage.
- Log: A write ahead log (WAL) which serializes MemTable operations to persistent medium as log files. In the event of failure, WAL files can be used to recover the key/value store to its consistent state, by reconstructing the MemTable from teh logs.
- Sorted String Table (SST) files: SSTable is a data structure (residing on disk) to efficiently store a large data footprint while optimizing for high throughput, sequential read/write workloads. When a MemTable fills up, it is flushed to a SST file on storage and the corresponding write ahead log file can be deleted.
Configuration and Deployment
Any existing XAP space can be configured to integrate a blob store with it. As with a typical processing unit, configuration is done through pu.xml or code. For example:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:os-core="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core"
xmlns:blob-store="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/rocksdb-blob-store"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.1.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core http://www.openspaces.org/schema/12.1/core/openspaces-core.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/rocksdb-blob-store http://www.openspaces.org/schema/12.1/rocksdb-blob-store/openspaces-rocksdb-blobstore.xsd">
<blob-store:rocksdb-blob-store id="myBlobStore" paths="[/mnt/db1,/mnt/db2]" mapping-dir="/tmp/mapping"/>
<os-core:embedded-space id="space" space-name="mySpace" >
<os-core:blob-store-data-policy blob-store-handler="myBlobStore" persistent="true"/>
</os-core:embedded-space>
<os-core:giga-space id="gigaSpace" space="space"/>
</beans>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:os-core="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.1.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core http://www.openspaces.org/schema/12.1/core/openspaces-core.xsd">
<bean id="blobstoreid" class="com.gigaspaces.blobstore.rocksdb.config.RocksDBBlobStoreDataPolicyFactoryBean">
<property name="paths" value="[/mnt/db1,/mnt/db2]"/>
<property name="mappingDir" value="/tmp/mapping"/>
</bean>
<os-core:embedded-space id="space" space-name="mySpace">
<os-core:blob-store-data-policy blob-store-handler="blobstoreid" persistent="true"/>
</os-core:embedded-space>
<os-core:giga-space id="gigaSpace" space="space"/>
</beans>
RocksDBBlobStoreConfigurer rocksDbConfigurer = new RocksDBBlobStoreConfigurer();
rocksDbConfigurer.setPaths("[/mnt/db1,/mnt/db2]");
rocksDbConfigurer.setMappingDir("/tmp/mapping");
BlobStoreDataCachePolicy blobStorePolicy = new BlobStoreDataCachePolicy();
blobStorePolicy.setBlobStoreHandler(rocksDbConfigurer.create());
blobStorePolicy.setPersistent(true);
EmbeddedSpaceConfigurer spaceConfigurer = new EmbeddedSpaceConfigurer("mySpace");
spaceConfigurer.cachePolicy(blobStorePolicy);
GigaSpace gigaSpace = new GigaSpaceConfigurer(spaceConfigurer).gigaSpace();
The following tables describes the configuration options used in rocksdb-blob-store above, along with other parameters that may be specified:
| Property | Description | Default | Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| paths | A comma-separated array of mount paths used for each space partition’s blob store. Th number of paths in the array shall correspond to the number of partition instances in the space (primaries and backups). For instance, for a two-partition space with no backups, /mnt/db1 corresponds to the first partition, while /mnt/db2 to the second one. |
required | |
| mapping-dir | A directory on the filesystem which contains the “partition to blob store” mapping file. This file is automatically generated by MemoryXtend. In the event of a parition re-location, the mapping file will be updated. | required | |
| central-storage | Specifies whether the deployment strategy is for central storage (i.e. SAN configuration) or local storage on each grid machine (default) | false | optional |
| db-options | Specifies the tuning parameters for the persistent data store in the underlying blob store. This includes SST formats, compaction settings and flushes. See Performance Tuning section for details. | optional | |
| Specifies the tuning parameters for the LSM logic and memory tables. See Performance Tuning section for details. | optional | ||
| blob-store-handler | BlobStore implementation | required | |
On-Heap cache stores objects in their native format.This cache size determined based on the percentage of the GSC JVM max memory(-Xmx). If -Xmx is not specified the cache size default to 10000 objects. This is an LRU based data cache.(*) |
20% | optional | |
| avg-object-size-KB | Average object size in KB. avg-object-size-bytes and avg-object-size-KB cannot be used together. | 5 | optional |
| avg-object-size-bytes | Average object size in bytes. avg-object-size-bytes and avg-object-size-KB cannot be used together. | 5000 | optional |
| persistent | data is written to flash, space will perform recovery from flash if needed. | required |
Calculating cache-entries-percentage
The purpose of this settings is to set the maximum number of objects that a GSC heap can hold before it starts evicting. Here is the formula for calculating it:
Number of objects = ((GSC Xmx) * (cache-entries-percentage/100))/average-object-size-KB
Lets say we set a cache entries percentage of 20, and an average object size of 2KB (the default). On a 10GB GSC:
N = {10GB * 1024 * 1024) * (20⁄100) } / 2 = {(10,485,760) * (0.2)} / 2 = {2,097,152} / 2 = 1,048,576 objects can fit in a single GSC before LRU starts evicting.
Deployment Strategies
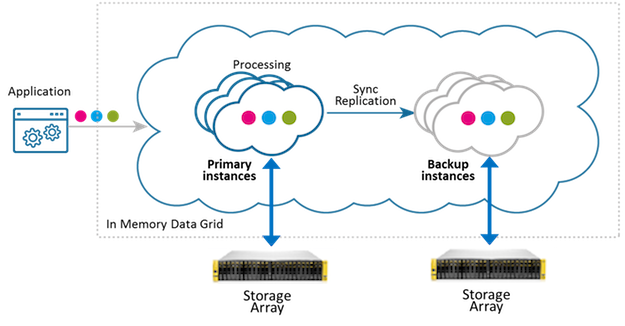
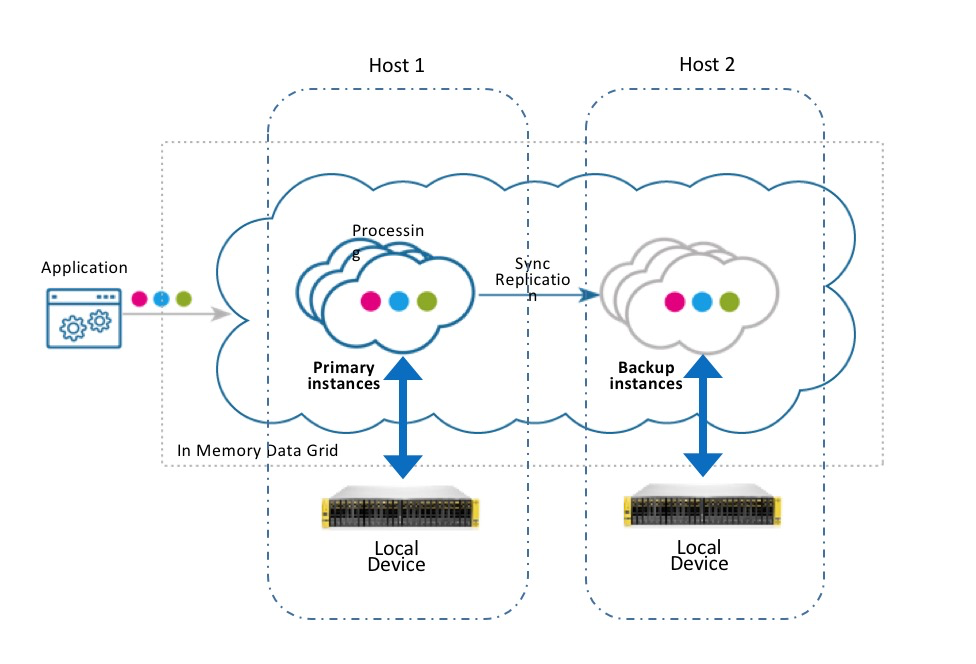
Local Storage
This configuration allows each space partition instance (primary or backup) to use a machine-local storage device (SSD/HDD). With this approach, data locality is leveraged so that the devices local to the machine are used for reads/writes. The local storage deployment strategy provides an easy way to implement a “local persistent store” (also known as native persistence) pattern.
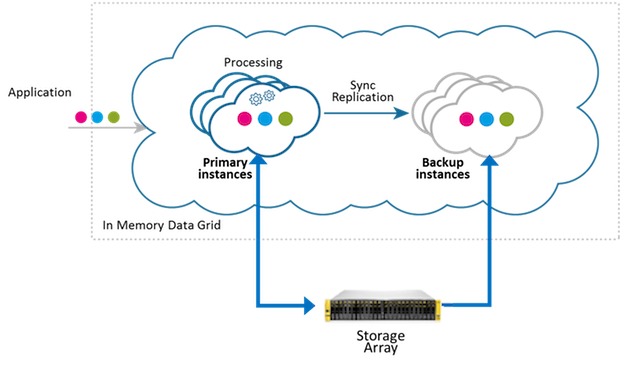
Central Storage
This deployment strategy works well with storage area networks (SAN) , which means that the disk drive devices are installed in a remote storage array but behave as if they’re attached the the local machine. Most storage networks use the iSCSI or Fibre Channel protocol for communication between servers and disk drive devices. This configuration breaks the coupling between a partition instance and a local machin device, thereby allowing seamless relocation of paritions across data grid machines.
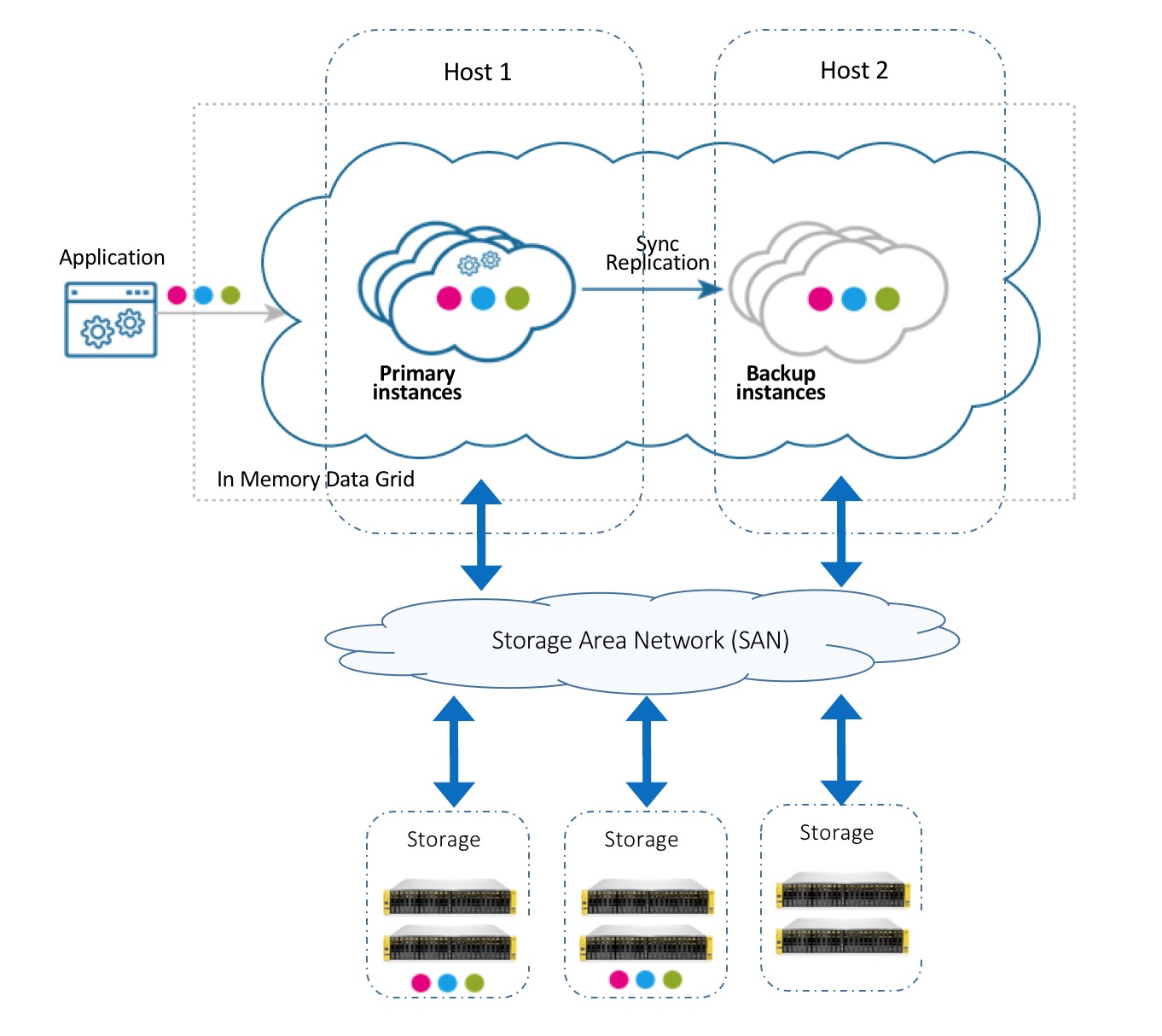
Tiering storage between space partition instances and attached storage can be applied across one or more storage arrays, as shown in the configurations below:
Single storage array
<blob-store:rocksdb-blob-store id="myBlobStore" paths="[/mnt/db1,/mnt/db2,/mnt/db3,/mnt/db4]"/>
Two storage arrays
<blob-store:rocksdb-blob-store id="myBlobStore" paths="[/mnt1/db1,/mnt1/db2],[/mnt2/db1,/mnt2/db2]"/>
Data Recovery on Restart
The MemoryXtend architecture allows for data persisted on the blob store to be available for the data grid upon restart. There are two approaches for pre-loading data into the space: lazy and custom initial load.
Lazy Load
In this approach, MemoryXtend saves only indexes in RAM and the rest of the objects on disk. Meaning, no data is loaded into the JVM heap upon a restart. As read throughput increases from clients, most of the data will eventually load into the data grid RAM tier. This is a preferred approach when the volume of data persisted on flash far exceeds what can fit into memory. To enable lazy load, all what’s needed is to enable the persistent option on the blobstore policy.
<os-core:blob-store-data-policy persistent="true" blob-store-handler="myBlobStore">
Custom Initial Load
The blob-store-cache-query option provides a SQL criteria to pre-load all or specific space objects into the JVM heap upon data grid initialization. This guarantees any subsequent read request will hit RAM, thereby providing predictable latency (avoiding cache misses). This preload pattern is useful in two scenarios:
- The persisted data capacity equals what can fit into RAM (eager pre-load).
- When read latencies for specific class type (e.g. hot data, current day stocks) need to be predictable upfront.
In the example below we are loading Stock instances where the name=a1000 and Trade instances with id > 10000.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:os-core="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core"
xmlns:os-events="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events"
xmlns:os-remoting="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting"
xmlns:blob-store="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/rocksdb-blob-store"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.1.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core http://www.openspaces.org/schema/12.1/core/openspaces-core.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events http://www.openspaces.org/schema/12.1/events/openspaces-events.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting http://www.openspaces.org/schema/12.1/remoting/openspaces-remoting.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/rocksdb-blob-store http://www.openspaces.org/schema/12.1/rocksdb-blob-store/openspaces-rocksdb-blobstore.xsd">
<blob-store:rocksdb-blob-store id="myBlobStore" paths="[/tmp/rocksdb]" mapping-dir="/tmp/mapping"/>
<os-core:embedded-space id="space" name="mySpace">
<os-core:blob-store-data-policy persistent="true" blob-store-handler="myBlobStore">
<os-core:blob-store-cache-query class="com.gigaspaces.blobstore.rocksdb.Stock" where="name = a1000"/>
<os-core:blob-store-cache-query class="com.gigaspaces.blobstore.rocksdb.Trade" where="id > 10000"/>
</os-core:blob-store-data-policy>
</os-core:embedded-space>
<os-core:giga-space id="gigaSpace" space="space"/>
BlobStoreDataCachePolicy blobStorePolicy = new BlobStoreDataCachePolicy();
blobStorePolicy.setBlobStoreHandler(rocksDbConfigurer.create());
blobStorePolicy.setPersistent(true);
blobStorePolicy.addCacheQuery(new SQLQuery(Stock.class, "name = a1000"));
blobStorePolicy.addCacheQuery(new SQLQuery(Trade.class, "id > 10000"));
EmbeddedSpaceConfigurer spaceConfigurer = new EmbeddedSpaceConfigurer("mySpace");
spaceConfigurer.cachePolicy(blobStorePolicy);
GigaSpace gigaSpace = new GigaSpaceConfigurer(spaceConfigurer.space()).gigaSpace();
When the logging com.gigaspaces.cache is turned on the following output is generated:
2016-12-26 07:57:56,378 INFO [com.gigaspaces.cache] - BlobStore internal cache recovery:
blob-store-queries: [SELECT * FROM com.gigaspaces.blobstore.rocksdb.Stock WHERE name = 'a1000', SELECT * FROM com.gigaspaces.blobstore.rocksdb.Stock.Trade WHERE id > 10000].
Entries inserted to blobstore cache: 80.
Performance Tuning
Persistent Data Store Tuning Parameters
XAP uses the default DBOptions class com.com.gigaspaces.blobstore.rocksdb.config.XAPDBOptions.
A list of configuration properties can be found in the org.rocksdb.DBOptionsInterface Java docs.
| Property | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| createIfMissing | Configure whether to create the database if it is missing. Note that this value is always overriden with true. |
true |
| maxBackgroundCompactions | Specifies the maximum number of concurrent background compaction jobs, submitted to the default LOW priority thread pool. If you’re increasing this, also consider increasing number of threads in LOW priority thread pool |
8 |
| maxBackgroundFlushes | Specifies the maximum number of concurrent background flush jobs. If you’re increasing this, also consider increasing number of threads in HIGH priority thread pool. |
8 |
| maxOpenFiles | Number of open files that can be used by the DB. You may need to increase this if your database has a large working set. Value -1 means files opened are always kept open. | -1 |
| tableFormatConfig | Set the config for table format. Default is BlockBasedTableConfig with
rocksdb-blob-store namespace / RocksDBBlobStoreConfigurer if provided, otherwise the following defaults will be used:
|
LSM Logic and MemTables Tuning Parameters
Below are the values for the default class com.com.gigaspaces.blobstore.rocksdb.config.XAPColumnFamilyOptions.
A list of configuration properties can be found in the org.rocksdb.ColumnFamilyOptionsInterface Java docs.
| Property | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| writeBufferSize | Amount of data to build up in memory (backed by an unsorted log on disk) before converting to a sorted on-disk file. Should be in bytes. |
64 MB |
| levelZeroSlowdownWritesTrigger | Soft limit on number of level-0 files. We start slowing down writes at this point. A value < 0 means that no writing slow down will be triggered by number of files in level-0. |
8 |
| maxWriteBufferNumber | The maximum number of write buffers that are built up in memory. | 4 |
| targetFileSizeBase | The target file size for compaction, should be in bytes. | 64 MB |
| softRateLimit | The soft-rate-limit of a compaction score for put delay. | 0 |
| hardRateLimit | The hard-rate-limit of a compaction score for put delay. | 0 |
| levelCompactionDynamicLevelBytes | If true, RocksDB will pick target size of each level dynamically. | false |
| maxBytesForLevelBase | The upper-bound of the total size of level-1 files in bytes. | 512 MB |
| compressionPerLevel | Sets the compression policy for each level | [NO_COMPRESSION, NO_COMPRESSION, SNAPPY_COMPRESSION] |
| mergeOperatorName | Set the merge operator to be used for merging two merge operands of the same key. | put |
| fsync | By default, each write returns after the data is pushed into the operating system. The transfer from operating system memory to the underlying persistent storage happens asynchronously. When configuring sync to true each write operation not return until the data being written has been pushed all the way to persistent storage. This parameter should be set to true while storing data to filesystem like ext3 that can lose files after a reboot. Default is false. If this property is set, the fsync that is passed to the rocksdb-blob-store namespace/RocksDBBlobStoreConfigurer (if any) will be ignored. |
false |
Examples
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:os-core="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core"
xmlns:blob-store="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/rocksdb-blob-store"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.1.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core http://www.openspaces.org/schema/12.1/core/openspaces-core.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/rocksdb-blob-store http://www.openspaces.org/schema/12.1/rocksdb-blob-store/openspaces-rocksdb-blobstore.xsd">
<bean id="dbOptions" class="com.gigaspaces.blobstore.rocksdb.config.XAPDBOptions">
<!-- This will override the default of 8 -->
<property name="maxBackgroundCompactions" value="4" />
<property name="maxBackgroundFlushes" value="4" />
</bean>
<bean id="dataColumnFamilyOptions" class="com.gigaspaces.blobstore.rocksdb.config.XAPColumnFamilyOptions">
<property name="maxBytesForLevelMultiplier" value="20"/>
</bean>
<blob-store:rocksdb-blob-store id="myBlobStore" fsync="false"
cache-size-mb="100" block-size-kb="16"
db-options="dbOptions" data-column-family-options="dataColumnFamilyOptions"
paths="[/tmp/rocksdb,/tmp/rocksdb2]" mapping-dir="/tmp/mapping"/>
<os-core:embedded-space id="space" space-name="mySpace" >
<os-core:blob-store-data-policy blob-store-handler="myBlobStore"/>
</os-core:embedded-space>
<os-core:giga-space id="gigaSpace" space="space"/>
</beans>
RocksDBBlobStoreConfigurer configurer = new RocksDBBlobStoreConfigurer()
.setPaths("[/tmp/rocksdb,/tmp/rocksdb2]")
.setMappingDir("/tmp/mapping")
.setCacheSizeMB(100)
.setBlockSizeKB(16)
.setFsync(false);
XAPDBOptions dbOptions = new XAPDBOptions();
configurer.setDBOptions(dbOptions); // optional
XAPColumnFamilyOptions dataColumnFamilyOptions = new XAPColumnFamilyOptions();
configurer.setDataColumnFamilyOptions(dataColumnFamilyOptions); // optional
RocksDBBlobStoreHandler rocksDBBlobStoreHandler = configurer.create();
BlobStoreDataCachePolicy cachePolicy = new BlobStoreDataCachePolicy();
cachePolicy.setBlobStoreHandler(rocksDBBlobStoreHandler);
EmbeddedSpaceConfigurer embeddedSpaceConfigurer = new EmbeddedSpaceConfigurer("mySpace");
embeddedSpaceConfigurer.cachePolicy(cachePolicy);
gigaSpace = new GigaSpaceConfigurer(embeddedSpaceConfigurer.space()).gigaSpace();