Overview
XAP 10 introduces a new storage model called BlobStore Storage Model, which allows an external storage medium (one that does not reside on the JVM heap) to store the IMDG data. This page describes the general architecture and functionality of this storage model, that is leveraging both on-heap, off-heap and SSD implementation, called MemoryXtend.
This storage model leverages on-heap LRU cache (deserialized form) and off-heap LRU cache (serialized form) to store data, on-heap to store indexes and external storage device to store the raw data in a serialized form.
The JVM heap is used as a first level LRU cache for frequently used data. Repetitive read operations (by Id, by template or using a SQL query) for the same data will be loaded from off-heap LRU cache or from an external storage medium (SSD) upon the first request and later be served from the on-heap or off-heap based cache.
How BlobStore Storage Model Different from the Traditional XAP Persistence Model?
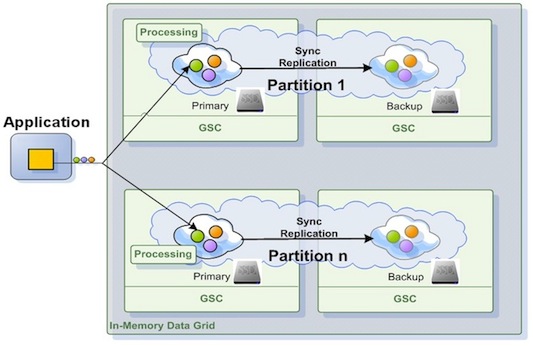
Unlike the traditional XAP persistence model, where the IMDG backing store is usually a database with relatively slow response time, located in a central location, the storage interface assumes very fast access for write and read operations, and a local, dedicated data store that supports a key/value interface. Each IMDG primary and backup instance across the grid is interacting with its dedicated storage medium (in our case SSD drive) independently in an atomic manner.
When running a traditional persistence configuration, the IMDG serves as a front-end to the database, and is acting as a transactional cache storing a subset of the data. In this configuration data is loaded in a lazy manner to the IMDG with the assumption that the heap capacity is smaller than the entire data set.
With the external storage medium mode, the entire data set is kept on the external SSD drive. The assumption is the SSD capacity across the grid is large enough to accommodate for the entire data set of the application.
