Creating a Processing Unit
The PU![]() This is the unit of packaging and deployment in the GigaSpaces Data Grid, and is essentially the main GigaSpaces service. The Processing Unit (PU) itself is typically deployed onto the Service Grid. When a Processing Unit is deployed, a Processing Unit instance is the actual runtime entity. is the fundamental unit of deployment in GigaSpaces. The PU itself runs within a Processing Unit
This is the unit of packaging and deployment in the GigaSpaces Data Grid, and is essentially the main GigaSpaces service. The Processing Unit (PU) itself is typically deployed onto the Service Grid. When a Processing Unit is deployed, a Processing Unit instance is the actual runtime entity. is the fundamental unit of deployment in GigaSpaces. The PU itself runs within a Processing Unit![]() This is the unit of packaging and deployment in the GigaSpaces Data Grid, and is essentially the main GigaSpaces service. The Processing Unit (PU) itself is typically deployed onto the Service Grid. When a Processing Unit is deployed, a Processing Unit instance is the actual runtime entity. Container and is deployed onto the Service Grid
This is the unit of packaging and deployment in the GigaSpaces Data Grid, and is essentially the main GigaSpaces service. The Processing Unit (PU) itself is typically deployed onto the Service Grid. When a Processing Unit is deployed, a Processing Unit instance is the actual runtime entity. Container and is deployed onto the Service Grid![]() A built-in orchestration tool which contains a set of Grid Service Containers (GSCs) managed by a Grid Service Manager. The containers host various deployments of Processing Units and data grids. Each container can be run on a separate physical machine. This orchestration is available for XAP only.. Once a PU is deployed, a PU instance is the actual runtime entity.
A built-in orchestration tool which contains a set of Grid Service Containers (GSCs) managed by a Grid Service Manager. The containers host various deployments of Processing Units and data grids. Each container can be run on a separate physical machine. This orchestration is available for XAP only.. Once a PU is deployed, a PU instance is the actual runtime entity.
There are two types of Processing Unit Containers:
-
Integrated Processing Unit Container A container that runs the PU inside VisualStudio. The integrated processing unit container enables to run the PU inside VisualStudio for testing and debugging purposes.
-
Service Grid Processing Unit Container A Processing Unit Container which runs within a Grid Service Container. It enables running the PU within a service grid, which provides self-healing and SLA capabilities to components deployed on it.
Processing Unit (PU)
The PU is a deployable, independent, scalable unit, which is the building block for the Space![]() Where GigaSpaces data is stored. It is the logical cache that holds data objects in memory and might also hold them in layered in tiering. Data is hosted from multiple SoRs, consolidated as a unified data model. Based Architecture (SBA
Where GigaSpaces data is stored. It is the logical cache that holds data objects in memory and might also hold them in layered in tiering. Data is hosted from multiple SoRs, consolidated as a unified data model. Based Architecture (SBA![]() Space-Based Architecture.
This architecture implementation is a set of Processing Units, with the following properties: Each processing unit instances holds a partitioned space instance and one or more services that are registered on events on that specific partition. Together they form an application cluster. Utlized by Utilized GigaSpaces cloud-native IMDG.). The PU is a combination of service beans and/or an embedded space instance.
Space-Based Architecture.
This architecture implementation is a set of Processing Units, with the following properties: Each processing unit instances holds a partitioned space instance and one or more services that are registered on events on that specific partition. Together they form an application cluster. Utlized by Utilized GigaSpaces cloud-native IMDG.). The PU is a combination of service beans and/or an embedded space instance.
There are several types of PU's; data only, business-logic only, mixed PU's (which contain both data and business logic) and special purpose PU's.
Data Only PU
This type of PU does not include any business logic, only a Space. The PU simply defines the runtime characteristics of the space, i.e. its runtime topology, the number of space replicas/partitions, etc.
Business Logic Only PU
The Business-logic Only PU implements your application code, and does not include any data. Typically, your code interacts with a remote Space which is defined by another PU. By defining the PU as business logic only, you create an application server which is hosted and monitored by the GigaSpaces Service Grid.
Mixed PU
This type of PU's includes both business logic and a space. Typically, the business logic interacts with a local space instance (i.e. a data grid instance running within the same PU instance) to achieve lowest possible latency and best performance.
Creating a Processing Unit
A processing unit is essentially a .NET class library with a deployment descriptor called pu.config. Creating a processing unit is simple:
- In Visual Studio, Create a new
Class Libraryproject. - Add a reference to
GigaSpaces.Core.dllfrom the product'sbinfolder. - Add an xml file called
pu.configto the project. - Right-click
pu.config, select Properties, and modify the Copy to Output Directory to Copy Always (or Copy If Newer). - Copy the following configuration into
pu.config:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<configuration>
<configSections>
<section name="ProcessingUnit" type="GigaSpaces.XAP GigaSpaces eXtreme Application Platform.
Provides a powerful solution for data processing, launching, and running digital services.Configuration.ProcessingUnitConfigurationSection, GigaSpaces.Core"/>
</configSections>
<ProcessingUnit>
<!-- Processing unit configuration goes here -->
</ProcessingUnit>
</configuration>
GigaSpaces eXtreme Application Platform.
Provides a powerful solution for data processing, launching, and running digital services.Configuration.ProcessingUnitConfigurationSection, GigaSpaces.Core"/>
</configSections>
<ProcessingUnit>
<!-- Processing unit configuration goes here -->
</ProcessingUnit>
</configuration>
From here on, processing unit configuration snippets will usually be shortened to focus on the <ProcessingUnit> tag.
Service Level Agreement (SLA)
The SLA definitions can be provided as part of the PU package or during the PU's deployment process. They define the number of PU instances that should be running and deploy-time requirements such as clustering topology for PU's which contain a space. The GSM![]() Grid Service Manager.
This is is a service grid component that manages a set of Grid Service Containers (GSCs). A GSM has an API for deploying/undeploying Processing Units. When a GSM is instructed to deploy a Processing Unit, it finds an appropriate, available GSC and tells that GSC to run an instance of that Processing Unit. It then continuously monitors that Processing Unit instance to verify that it is alive, and that the SLA is not breached. reads the SLA definition, and deploys the PU onto the available GSCs according to it.
Grid Service Manager.
This is is a service grid component that manages a set of Grid Service Containers (GSCs). A GSM has an API for deploying/undeploying Processing Units. When a GSM is instructed to deploy a Processing Unit, it finds an appropriate, available GSC and tells that GSC to run an instance of that Processing Unit. It then continuously monitors that Processing Unit instance to verify that it is alive, and that the SLA is not breached. reads the SLA definition, and deploys the PU onto the available GSCs according to it.
To include the SLA in the processing unit, add an xml file called sla.xml and modify its Copy To Output Directory setting (same as pu.config).
A sample SLA definition is shown below:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:os-sla="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla http://www.openspaces.org/schema/17.1.0/sla/openspaces-sla.xsd">
<os-sla:sla cluster-schema="partitioned"
number-of-instances="2" number-of-backups="1"
max-instances-per-vm="1">
</os-sla:sla>
</beans>
The number of backups per partition is zero or one.
For more information, see the SLA Overview page.
Deployment
When deploying the PU to the Service Grid, the PU is uploaded to the Manager (GSM) and extracted to the deploy directory of the local GigaSpaces installation (located by default under $GS_HOME\deploy). Once extracted, the GSM processes the deployment descriptor and based on that provisions PU instances to the running GigaSpaces containers.
Each GSC![]() Grid Service Container.
This provides an isolated runtime for one (or more) processing unit (PU) instance and exposes its state to the GSM. to which a certain instance was provisioned, downloads the PU from the GSM, extracts it to its local working directory (located by default under $GS_HOME\work\deployed-processing-units) and starts the PU instance.
Grid Service Container.
This provides an isolated runtime for one (or more) processing unit (PU) instance and exposes its state to the GSM. to which a certain instance was provisioned, downloads the PU from the GSM, extracts it to its local working directory (located by default under $GS_HOME\work\deployed-processing-units) and starts the PU instance.
To build directly to the deploy folder, change the PU project output directory to GS_HOME\deploy\[pu-name\], since this is the default path used by the GUI and the command line interface will find the PU's to deploy under this file structure.
Example
Our Online Payment system is expected to handle a large amount of concurrent users performing transactions. The system also needs to be highly available. This is where the PU comes into play. We will create a polling container that takes a payment event as input and processes it. Then, we will deploy this code as a PU onto the data grid. Payment events are being written into a space and the polling container will pick up the events and process them. We will use the pu.config file to define the deployment and add an SLA configuration to it to provide failover and scalability.
Polling Container
First we define a polling container that will handle the business logic upon receiving a payment event. In our example we define a polling container that will receive events when a new payment is created:
using System;
using GigaSpaces.Core.Events;
using GigaSpaces.XAP.Events.Polling;
using GigaSpaces.XAP.Events;
using xaptutorial.model;
[PollingEventDriven]
public class PaymentEventProcessor
{
// Define the event we are interested in
[EventTemplate]
Payment unprocessedData()
{
return new Payment { Status=ETransactionStatus.NEW };
}
[DataEventHandler]
public Payment eventListener(Payment ev)
{
Console.WriteLine("Payment received; processing .....");
// set the status on the event and write it back into the space
ev.Status=ETransactionStatus.PROCESSED;
return ev;
}
}
Processing Unit
Next, we'll configure pu.config to create an embedded space for the polling container:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<configuration>
<configSections>
<section name="ProcessingUnit" type="GigaSpaces.XAP.Configuration.ProcessingUnitConfigurationSection, GigaSpaces.Core"/>
</configSections>
<ProcessingUnit>
<EmbeddedSpaces>
<add Name="eventSpace"/>
</EmbeddedSpaces>
</ProcessingUnit>
</configuration>
Deployment
Now we have all the pieces that are necessary to create the deployment. After we built the project its time to deploy the PU onto the data grid. Again, you can do this in three ways; by script, c# code or via the admin UI. In our example will use the scripts to deploy the PU.
First let's launch gs-agent.exe from the product's bin folder - this is the Grid Service Agent (GSA![]() Grid Service Agent.
This is a process manager that can spawn and manage Service Grid processes (Operating System level processes) such as The Grid Service Manager, The Grid Service Container, and The Lookup Service. Typically, the GSA is started with the hosting machine's startup. Using the agent, you can bootstrap the entire cluster very easily, and start and stop additional GSCs, GSMs and lookup services at will.) that will host our data grid on this machine.
Grid Service Agent.
This is a process manager that can spawn and manage Service Grid processes (Operating System level processes) such as The Grid Service Manager, The Grid Service Container, and The Lookup Service. Typically, the GSA is started with the hosting machine's startup. Using the agent, you can bootstrap the entire cluster very easily, and start and stop additional GSCs, GSMs and lookup services at will.) that will host our data grid on this machine.
Next we deploy the PU onto the data grid:
GS_HOME\bin\gs-cli deploy PaymentProcessor
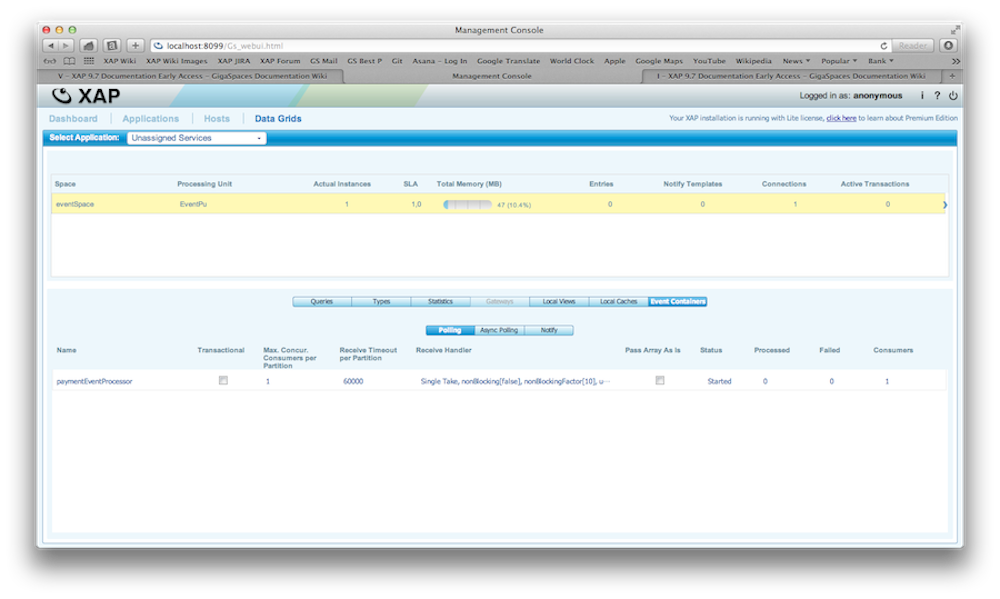
If you start up the Admin UI you will be able to see that through the deployment a space called eventSpace was created and a PU named with the name processing.
Client Interface
Now its time to create a client that creates events and writes them into the space.
using System;
using System.Threading;
using Microsoft.VisualStudio.TestTools.UnitTesting;
using GigaSpaces.Core;
using common;
namespace UnitTest
{
[TestClass]
public class UnitTest
{
private ISpaceProxy proxy;
[TestInitialize]
public void Initialize()
{
proxy = new SpaceProxyFactory("eventSpace").Create();
}
[TestMethod]
public void PostPayment()
{
// Create a payment and write it to the space:
proxy.Write(new Payment { CreatedDate=new DateTime(), MerchantId=1L, PaymentAmount=120.70, Status=ETransactionStatus.NEW });
// Wait for the payment to be processed by the event container
Thread.Sleep(10000);
// Read the payment from the space
payment = proxy.Read<Payment>(new SqlQuery<Payment>("MerchantId=1"));
// Test the payment
Assert.AreEqual(payment.Status, ETransactionStatus.PROCESSED);
}
}
}
When you run this code you should see that the PU deployed onto the IMDG![]() In-Memory Data Grid.
A simple to deploy, highly distributed, and cost-effective solution for accelerating and scaling services and applications. It is a high throughput and low latency data fabric that minimizes access to high-latency, hard-disk-drive-based or solid-state-drive-based data storage. The application and the data co-locate in the same memory space, reducing data movement over the network and providing both data and application scalability. is processing the event, changes the status of the payment to PROCESSED and writes the event back into the space. The client then will receive an event because it has registered a listener that listens for processed payment events.
In-Memory Data Grid.
A simple to deploy, highly distributed, and cost-effective solution for accelerating and scaling services and applications. It is a high throughput and low latency data fabric that minimizes access to high-latency, hard-disk-drive-based or solid-state-drive-based data storage. The application and the data co-locate in the same memory space, reducing data movement over the network and providing both data and application scalability. is processing the event, changes the status of the payment to PROCESSED and writes the event back into the space. The client then will receive an event because it has registered a listener that listens for processed payment events.
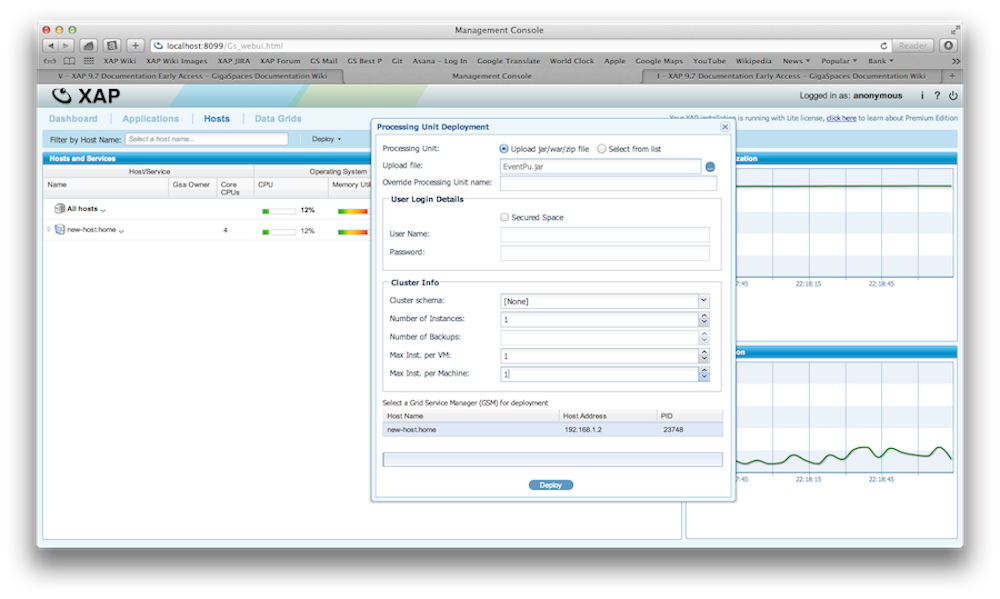
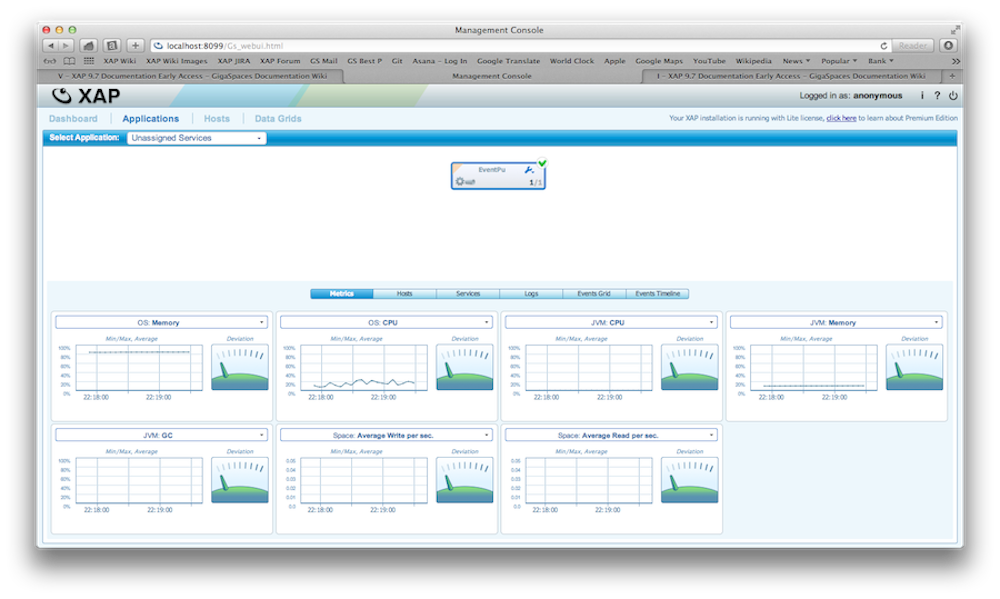
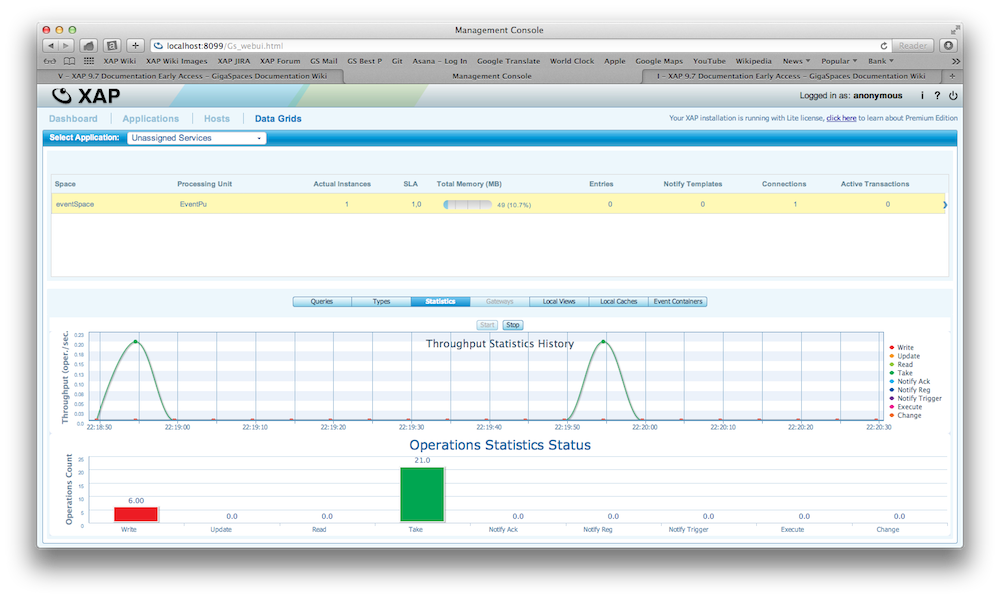
Deploying a PU Using the Web Management Console
There is complete example available of a PU on GitHub. You can download, build and deploy this example. Here is an example how you deploy a PU with the Web Management Console:
|
Deploy PU |
Applications deployed |
Data Grid |
Statistics |
Failover and Scalability
One of our non-functional requirements for our online payment system is that it is highly available and it can handle a large amount of concurrent transactions. This can be accomplish in a couple of ways. We can deploy the PU with multiple concurrent threads and or multiple PU instances on top of the grid.
Multi-Threaded Event Container
By default the event container is single threaded. With a simple annotation you can tell GigaSpaces how many threads the event container should run with.
[PollingEventDriven(Name = "DataProcessor", MinConcurrentConsumers = 1, MaxConcurrentConsumers = 4)]
public class PaymentProcessor
{
//......
}
Multiple PUs
Lets assume that we have two machines available for our deployment. We want to deploy 4 instances of our PU, two on each machine.
The deployment script for this scenario looks like this:
With a stateful PU, embedded space
gs-cli deploy -cluster schema=partitioned total_members=4,0 -max-instances-per-machine 2 eventProcessor
With a stateless PU
gs-cli deploy -cluster total_members=4 -max-instances-per-machine 2 eventProcessor
Deploying with the command line options will override the SLA definitions. For more information, see the Deploy Command Line Interface page.
 In-Memory Data Grid - achieve unparalleled speed, persistence, and accuracy.
In-Memory Data Grid - achieve unparalleled speed, persistence, and accuracy.