Task Execution
GigaSpaces support executing tasks in a collocated Space![]() Where GigaSpaces data is stored. It is the logical cache that holds data objects in memory and might also hold them in layered in tiering. Data is hosted from multiple SoRs, consolidated as a unified data model. (processing unit
Where GigaSpaces data is stored. It is the logical cache that holds data objects in memory and might also hold them in layered in tiering. Data is hosted from multiple SoRs, consolidated as a unified data model. (processing unit![]() This is the unit of packaging and deployment in the GigaSpaces Data Grid, and is essentially the main GigaSpaces service. The Processing Unit (PU) itself is typically deployed onto the Service Grid. When a Processing Unit is deployed, a Processing Unit instance is the actual runtime entity. that started an embedded Space). Space tasks can be executed either directly on a specific cluster member using typical routing
This is the unit of packaging and deployment in the GigaSpaces Data Grid, and is essentially the main GigaSpaces service. The Processing Unit (PU) itself is typically deployed onto the Service Grid. When a Processing Unit is deployed, a Processing Unit instance is the actual runtime entity. that started an embedded Space). Space tasks can be executed either directly on a specific cluster member using typical routing![]() The mechanism that is in charge of routing the objects into and out of the corresponding partitions. The routing is based on a designated attribute inside the objects that are written to the Space, called the Routing Index. value. Space tasks can also be distributed, which means it is executed in a "broadcast" mode on all the primary cluster members concurrently and reduced to a single result on the client side, which is also known as the map reduce pattern which is used in many applications that does parallel processing. Space tasks are dynamic in terms of content, it contains user code that will be executed at the Space as is.
The mechanism that is in charge of routing the objects into and out of the corresponding partitions. The routing is based on a designated attribute inside the objects that are written to the Space, called the Routing Index. value. Space tasks can also be distributed, which means it is executed in a "broadcast" mode on all the primary cluster members concurrently and reduced to a single result on the client side, which is also known as the map reduce pattern which is used in many applications that does parallel processing. Space tasks are dynamic in terms of content, it contains user code that will be executed at the Space as is.
Space Task API
The ISpaceTask interface is defined as follows:
public interface ISpaceTask<T>
{
T Execute(ISpaceProxy spaceProxy, ITransaction tx);
}
Here is a simple implementation of a space task that calculates the number of objects on a single node and prints a message at the single node output.
[Serializable]
public class CountTask : ISpaceTask<int>
{
private String _message;
public CountTask(String message)
{
_message = message;
}
public int Execute(ISpaceProxy spaceProxy, ITransaction tx)
{
System.Console.WriteLine(_message);
return spaceProxy.Count();
}
}
A space task needs to be serializable because it is being serialized and reconstructed at the node. The assembly that contains the task needs to be in the domain of the processing unit that contains the embedded space (present at its deployment directory).
Executing the space task
ISpaceProxy spaceProxy = // obtain a proxy to a space
//Execute the task on a specific node using a specified routing value (2)
//And inserting the calculation result to count variable
int count = spaceProxy.Execute(new CountTask("hello world"), 2);
Distributed Task
A IDistributedSpaceTask is a space task that ends up executing more than once (concurrently) and returns a result that is a reduced operation of all the different execution.
-
Phase 1 - Sending the Space tasks to be executed:
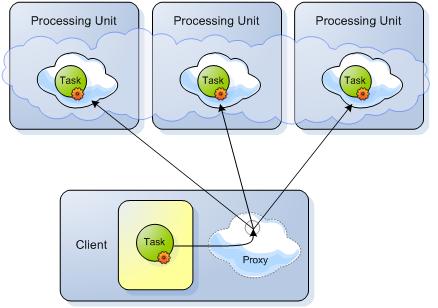
-
Phase 2 - Getting the results back to be reduced:
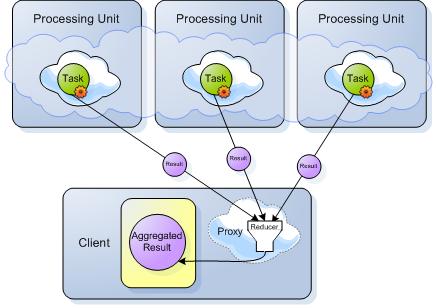
The IDistributedSpaceTask interface is a composition both ISpaceTask and ISpaceTaskResultsReducer interfaces.
The ISpaceTaskResultsReducer is defined as follows:
public interface ISpaceTaskResultsReducer<R, T>
{
R Reduce(SpaceTaskResultsCollection<T> results);
}
Here is a simple example of a distributed space task that extends our previous example:
[Serializable]
public class DistributedCountTask : IDistributedSpaceTask<long, int>
{
private String _message;
public CountTask(String message)
{
_message = message;
}
public int Execute(ISpaceProxy spaceProxy, ITransaction tx)
{
System.Console.WriteLine(message);
return spaceProxy.Count(new Object());
}
public long Reduce(SpaceTaskResultsCollection<int> results)
{
int sum = 0;
foreach(SpaceTaskResult<int> result in results)
{
if (result.Exception != null)
throw result.Exception;
sum += result.Result;
}
return sum;
}
}
This task will execute on each one of the primary nodes in the cluster, it will print the message in each node and it will return the summary of the count result on each node (Equivalent to ISpaceProxy.Count(new Object()) method).
Executing the distributed task
ISpaceProxy spaceProxy = // obtain a proxy to a space
//Execute the task on all the primary nodes with in the cluster
//and inserting the calculation result to count variable
long count = spaceProxy.Execute(new DistributedCountTask("hello world"));
Results Filter
When executing a distributed space task, results arrive in an asynchronous manner and once all the results have arrived, the ISpaceTaskResultsReducer is used to reduce them. The ISpaceTasukResultsFilter can be used as a callback and filter mechanism to be invoked for each result that arrives.
public interface ISpaceTaskResultsFilter<T>
{
SpaceTaskFilterDecision GetFilterDecision(SpaceTaskFilterInfo<T> info);
}
// Controls what should be done with the results of an execution.
public enum SpaceTaskFilterDecision
{
// Continue processing the distributed task.
Continue = 0,
// Break out of the processing of the distributed task and move
// to the reduce phase including the current result.
Break = 1,
// Skip this result and continue processing the rest REpresentational State Transfer. Application Programming Interface
An API, or application programming interface, is a set of rules that define how applications or devices can connect to and communicate with each other. A REST API is an API that conforms to the design principles of the REST, or representational state transfer architectural style. of the results.
Skip = 2,
// Skip this result and breaks out of the processing of the distributed task
// and move to the reduce phase.
SkipAndBreak = 3,
}
REpresentational State Transfer. Application Programming Interface
An API, or application programming interface, is a set of rules that define how applications or devices can connect to and communicate with each other. A REST API is an API that conforms to the design principles of the REST, or representational state transfer architectural style. of the results.
Skip = 2,
// Skip this result and breaks out of the processing of the distributed task
// and move to the reduce phase.
SkipAndBreak = 3,
}
The filter can be used to control if a result should be used or not (the Skip decision). If we have enough results and we can move to the reduce phase (the Break decision). If we should continue accumulating results (the Continue decision). Or if we don't want to use the current result and move to the reduce phase (the SkipAndBreak decision).
The filter can also be used as a way to be identify that results have arrived and we can do something within our application as a result of that. Note, in this case, make sure that heavy processing should be performed on a separate (probably pooled) thread.
Transactions
Space tasks fully support transactions, an execute request can receive a transaction from the client and it will be delegated into the task execution it self once it is being executed at the space node.
When executing a single space task, usually a local transaction will suffice, while when executing a distributed space task, a distributed transaction will be required.
The transaction creation, commit and abort normally should be done at the client according to the result.
Here's a simple example
ISpaceProxy spaceProxy = // obtain a proxy to a space
ITransaction tx = spaceProxy.LocalTransactionManager.Create();
try
{
//Execute the task on a specific node using a specified routing value (2)
//And inserting the calculation result to count variable
int count = spaceProxy.Execute(new ClearMyObjectTask(), 2, tx);
tx.Commit();
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
tx.Abort();
}
[Serializable]
public class ClearMyObjectTask : ISpaceTask<int>
{
public int Execute(ISpaceProxy spaceProxy, ITransaction tx)
{
MyObject template = new MyObject();
int result spaceProxy.Count(template, tx);
spaceProxy.Clear(template, tx);
return result;
}
}
Asynchronous Execution
A space task can also be executed asynchronously with the corresponding BeginExecute EndExecute method. This follows the standard .NET asynchronous API, once the execution is complete the execute invoker is notified by the async result which is received from the BeginExecute method or to a supplied callback. This will be similar to executing a task in a separate thread, allowing to continue local process while waiting for the result to be calculated at the space nodes.
Executing asynchronous space using async result
ISpaceProxy spaceProxy = // obtain a proxy to a space
//Execute the task on all the primary nodes with in the cluster
IAsyncResult<long> asyncResult = spaceProxy.BeginExecute(new DistributedCountTask("hello world"), null /*callback*/, null /*state object*/);
...
//This will block until the result execution has arrived
long count = spaceProxy.EndExecute(asyncResult);
Executing asynchronous space using async result wait handle
ISpaceProxy spaceProxy = // obtain a proxy to a space
//Execute the task on all the primary nodes with in the cluster
IAsyncResult<long> asyncResult = spaceProxy.BeginExecute(new DistributedCountTask("hello world"), null /*callback*/, null /*state object*/);
...
//This will block until the result execution has arrived
asyncResult.AsyncWaitHandle.WaitOne();
//Gets the actual result of the async execution
long count = spaceProxy.EndExecute(asyncResult);
Executing asynchronous space using async call back and a state object
ISpaceProxy spaceProxy = // obtain a proxy to a space
//Execute the task on all the primary nodes with in the cluster
spaceProxy.BeginExecute(new DistributedCountTask("hello world"),ResultCallBack, new MyStateObject());
...
public void ResultCallBack<long>(IAsyncResult<long> asyncResult)
{
//Gets the state object attached to this execution
MyStateObject stateObject = (MyStateObject)asyncResult.AsyncState;
...
//Gets the actual result of the async execution
long count = spaceProxy.EndExecute(asyncResult);
...
}
 In-Memory Data Grid - achieve unparalleled speed, persistence, and accuracy.
In-Memory Data Grid - achieve unparalleled speed, persistence, and accuracy.