Initial Load
The Data Grid includes special interceptor that allow users to pre-load the Data Grid with data before it is available for clients access. This interceptor called Initial Load and has a default implementation that is using the NHibernate Space Persistency implementation to load data from a database directly into the Data-Grid instances.
To enable the initial load activity an ExternalDataSource should be specified. Here is an example for a space configuration that performs only initial load from the database without writing back any changes into the database (replication to the Mirror![]() Performs the replication of changes to the target table or accumulation of source table changes used to replicate changes to the target table at a later time. If you have implemented bidirectional replication in your environment, mirroring can occur to and from both the source and target tables. service is not enabled with this example):
Performs the replication of changes to the target table or accumulation of source table changes used to replicate changes to the target table at a later time. If you have implemented bidirectional replication in your environment, mirroring can occur to and from both the source and target tables. service is not enabled with this example):
<ProcessingUnit>
<EmbeddedSpaces>
<add Name="space">
<Properties>
<!-- Use ALL IN CACHE - No Read Performed from the database in lazy manner -->
<add Name="space-config.engine.cache_policy" Value="1"/>
<!-- Space Where GigaSpaces data is stored. It is the logical cache that holds data objects in memory and might also hold them in layered in tiering. Data is hosted from multiple SoRs, consolidated as a unified data model. properties to enable External Data Source -->
<add Name="cluster-config.cache-loader.external-data-source" Value="true"/>
<add Name="cluster-config.cache-loader.central-data-source" Value="true"/>
</Properties>
<ExternalDataSource Type="GigaSpaces.Practices.ExternalDataSource.NHibernate.NHibernateExternalDataSource" Usage="ReadOnly">
<!-- NHibernate-specific config goes here -->
</ExternalDataSource>
</add>
</EmbeddedSpaces>
</ProcessingUnit>
Where GigaSpaces data is stored. It is the logical cache that holds data objects in memory and might also hold them in layered in tiering. Data is hosted from multiple SoRs, consolidated as a unified data model. properties to enable External Data Source -->
<add Name="cluster-config.cache-loader.external-data-source" Value="true"/>
<add Name="cluster-config.cache-loader.central-data-source" Value="true"/>
</Properties>
<ExternalDataSource Type="GigaSpaces.Practices.ExternalDataSource.NHibernate.NHibernateExternalDataSource" Usage="ReadOnly">
<!-- NHibernate-specific config goes here -->
</ExternalDataSource>
</add>
</EmbeddedSpaces>
</ProcessingUnit>
The Initial Load is supported with the partitioned cluster schema. If you would like to pre-load a clustered space using the Initial-Load without running backups you can use the partitioned and have ZERO as the amount of backups.
Controlling the Initial Load
By default all the entries are loaded from the database into the space, but sometimes only a subset of the data is relevant for the space. This section explains how to control which data is loaded.
Initial Load Entries
The NHibernateExternalDataSource can be configured to load only specific types by configuring the property InitialLoadEntries with a list of fully-qualified type names. For example, to load only entries of type MyEntry:
public class MyExternalDataSource : NHibernateExternalDataSource
{
public MyExternalDataSource()
{
base.InitialLoadEntries = new string[] {"MyCompany.MyProject.MyEntry"};
}
}
Of course we'll need to configure the space to use our custom extension instead of the standard NHibernate implementation:
<ProcessingUnit>
<EmbeddedSpaces>
<add Name="space">
<Properties>
<add Name="space-config.engine.cache_policy" Value="1"/>
<add Name="cluster-config.cache-loader.external-data-source" Value="true"/>
<add Name="cluster-config.cache-loader.central-data-source" Value="true"/>
</Properties>
<ExternalDataSource Type="MyCompany.MyProject.MyExternalDataSource" Usage="ReadOnly">
<!-- NHibernate-specific config goes here -->
</ExternalDataSource>
</add>
</EmbeddedSpaces>
</ProcessingUnit>
Overriding the InitialLoad Method
To implement your own Initial Load when using the NHibernate ExternalDataSource you can override the InitialLoad method to construct one or more IDataEnumerator. For example:
public class MyExternalDataSource : NHibernateExternalDataSource
{
public override IDataEnumerator InitialLoad()
{
var queries = new string[] {"from MyEntry where Foo > 50"};
var enumerators = new List<IDataEnumerator>();
foreach (var query in queries)
enumerators.Add(new NHibernateDataEnumerator(new Query(null, query),
SessionFactory, EnumeratorLoadFetchSize, PerformOrderById));
return new ConcurrentMultiDataEnumerator(enumerators, EnumeratorLoadFetchSize, InitialLoadThreadPoolSize);
}
}
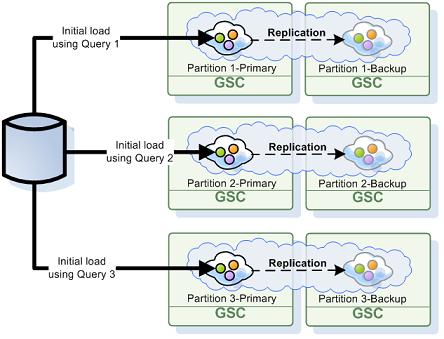
Partitioned Cluster
When using a partitioned cluster, each space partition stores a subset of the data, based on the entry routing![]() The mechanism that is in charge of routing the objects into and out of the corresponding partitions. The routing is based on a designated attribute inside the objects that are written to the Space, called the Routing Index. property hash code value. Each partition performs its own initial load process and checks each loaded entry to verify it belongs to that partition - entries which do not belong are discarded.
The mechanism that is in charge of routing the objects into and out of the corresponding partitions. The routing is based on a designated attribute inside the objects that are written to the Space, called the Routing Index. property hash code value. Each partition performs its own initial load process and checks each loaded entry to verify it belongs to that partition - entries which do not belong are discarded.
While this process protects the partition from storing irrelevant data, its performance is naive - imagine a cluster with 10 partitions which are evenly distributed: each partition will load the entire database and discard 90% of it, i.e. take roughly x10 times longer to load than actually needed.
Fortunately, there's a simple pattern which can be used to load only entries relevant to the partition in most cases. When a space entry has a routing property with a numeric type mapped to a column in the database, we can generate a custom initial load query to load only entries relevant for the partition based on the routing property.
For example, suppose class MyEntry has a routing property called RoutingProperty:
public class MyEntry
{
public int? Foo { get; set; }
[SpaceRouting]
public int? RoutingProperty { get; set; }
}
A customized initial load query would be:
public override IDataEnumerator InitialLoad()
{
var clusterInfo = ProcessingUnitContainer.Current.ClusterInfo;
var queries = new string[]
{
"from MyEntry where Foo > 50 AND RoutingProperty % " + clusterInfo.NumberOfInstances + " = " + (clusterInfo.InstanceId -1)
};
var enumerators = new List<IDataEnumerator>();
foreach (var query in queries)
enumerators.Add(new NHibernateDataEnumerator(new Query(null, query),
SessionFactory, EnumeratorLoadFetchSize, PerformOrderById));
return new ConcurrentMultiDataEnumerator(enumerators, EnumeratorLoadFetchSize, InitialLoadThreadPoolSize);
}
Note that the partition ID and number of partitions are taken from the context of the currently running processing unit![]() This is the unit of packaging and deployment in the GigaSpaces Data Grid, and is essentially the main GigaSpaces service. The Processing Unit (PU) itself is typically deployed onto the Service Grid. When a Processing Unit is deployed, a Processing Unit instance is the actual runtime entity..
This is the unit of packaging and deployment in the GigaSpaces Data Grid, and is essentially the main GigaSpaces service. The Processing Unit (PU) itself is typically deployed onto the Service Grid. When a Processing Unit is deployed, a Processing Unit instance is the actual runtime entity..
This mechanism only works for entries whose routing property type is numeric.
 In-Memory Data Grid - achieve unparalleled speed, persistence, and accuracy.
In-Memory Data Grid - achieve unparalleled speed, persistence, and accuracy.