GigaSpaces Management Center (GS-UI)
version its a sepaerte package that can be downloaded from the supoort oortal
Starting from Version 17, the GS-UI is not part of the installation zip, but is a separate package that can be downloaded from the support portal.
The GigaSpaces Management Center has been deprecated and will be removed in a future release.
For more information see the GS-UI section in our User Guide.
Overview
The GigaSpaces Management Center is a user interface that allows you to do the following:
- View, configure, and maintain Spaces, containers, and clusters in the Space
 Where GigaSpaces data is stored. It is the logical cache that holds data objects in memory and might also hold them in layered in tiering. Data is hosted from multiple SoRs, consolidated as a unified data model. Browser tab.
Where GigaSpaces data is stored. It is the logical cache that holds data objects in memory and might also hold them in layered in tiering. Data is hosted from multiple SoRs, consolidated as a unified data model. Browser tab. - Deploy and manage services in the Deployments tab.
- Manage users and roles, and perform security administration
- Generate a dump file that holds information about the GigaSpaces runtime environment, for a specific container or across the full environment.
Using the GigaSpaces Management Center in Production and Large-Scale Environments
Follow these network guidelines:
- We recommend running the GigaSpaces Management Center on the same network subnet where the data grid and other GigaSpaces runtime components are running.
- The GigaSpaces Management Center communicates with the data grid, GSCs, GSM
 Grid Service Manager.
This is is a service grid component that manages a set of Grid Service Containers (GSCs). A GSM has an API for deploying/undeploying Processing Units. When a GSM is instructed to deploy a Processing Unit, it finds an appropriate, available GSC and tells that GSC to run an instance of that Processing Unit. It then continuously monitors that Processing Unit instance to verify that it is alive, and that the SLA is not breached., GSA
Grid Service Manager.
This is is a service grid component that manages a set of Grid Service Containers (GSCs). A GSM has an API for deploying/undeploying Processing Units. When a GSM is instructed to deploy a Processing Unit, it finds an appropriate, available GSC and tells that GSC to run an instance of that Processing Unit. It then continuously monitors that Processing Unit instance to verify that it is alive, and that the SLA is not breached., GSA Grid Service Agent.
This is a process manager that can spawn and manage Service Grid processes (Operating System level processes) such as The Grid Service Manager, The Grid Service Container, and The Lookup Service. Typically, the GSA is started with the hosting machine's startup. Using the agent, you can bootstrap the entire cluster very easily, and start and stop additional GSCs, GSMs and lookup services at will., and LUS
Grid Service Agent.
This is a process manager that can spawn and manage Service Grid processes (Operating System level processes) such as The Grid Service Manager, The Grid Service Container, and The Lookup Service. Typically, the GSA is started with the hosting machine's startup. Using the agent, you can bootstrap the entire cluster very easily, and start and stop additional GSCs, GSMs and lookup services at will., and LUS Lookup Service.
This service provides a mechanism for services to discover each other. Each service can query the lookup service for other services, and register itself in the lookup service so other services may find it. continuously, so it should have fast connectivity with these components. High-latency connectivity will affect the responsiveness of the interface and its initial bootstrap time.
Lookup Service.
This service provides a mechanism for services to discover each other. Each service can query the lookup service for other services, and register itself in the lookup service so other services may find it. continuously, so it should have fast connectivity with these components. High-latency connectivity will affect the responsiveness of the interface and its initial bootstrap time. - In production environments, use a remote desktop product such as VNC or No Machine.
- Run the GigaSpaces Management Center on the same network subnet as the data grid and the other GigaSpaces runtime components, and run the remote access application on the client side to access the remote machines desktop from the administrator machine desktop.
With relatively large amount of GSCs, Services or data grid partitions (over 20 units), we also recommend increasing the heap size of the GigaSpaces Management Center to 1G (-Xmx1g).
Starting The GigaSpaces Management Center
To start the GigaSpaces Management Center, run the following:
$GS_HOME\bin\gs-ui.bat
$GS_HOME/bin/gs-ui.sh
Main View
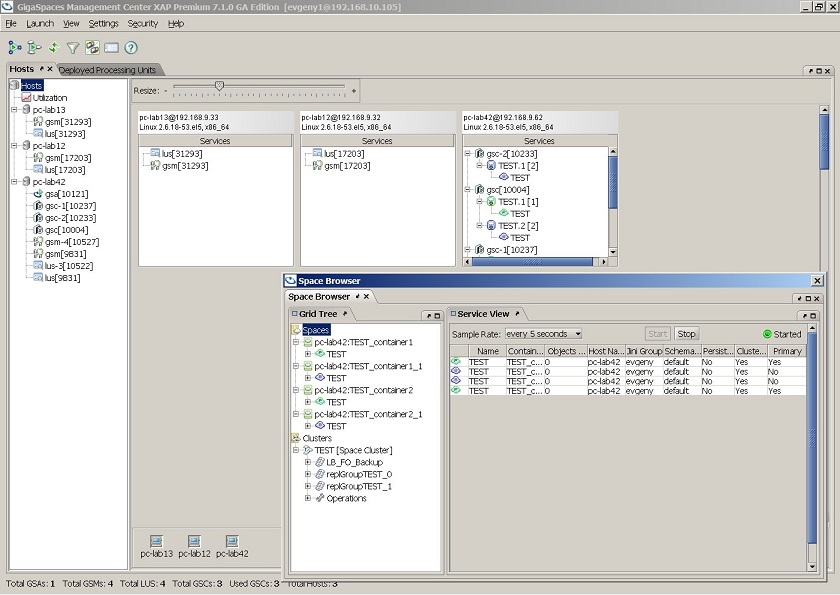
The GigaSpaces Management Center contains 3 tabs:
- Hosts tab - view information about the host machines.
- Deployed Processing Units
 This is the unit of packaging and deployment in the GigaSpaces Data Grid, and is essentially the main GigaSpaces service. The Processing Unit (PU) itself is typically deployed onto the Service Grid. When a Processing Unit is deployed, a Processing Unit instance is the actual runtime entity. - view information about the Processing Units that have been deployed (including events and exceptions) and perform deployment-related tasks.
This is the unit of packaging and deployment in the GigaSpaces Data Grid, and is essentially the main GigaSpaces service. The Processing Unit (PU) itself is typically deployed onto the Service Grid. When a Processing Unit is deployed, a Processing Unit instance is the actual runtime entity. - view information about the Processing Units that have been deployed (including events and exceptions) and perform deployment-related tasks. - Space Browser - view information about the Spaces and clusters in the data grid and perform configuration and maintenance tasks.
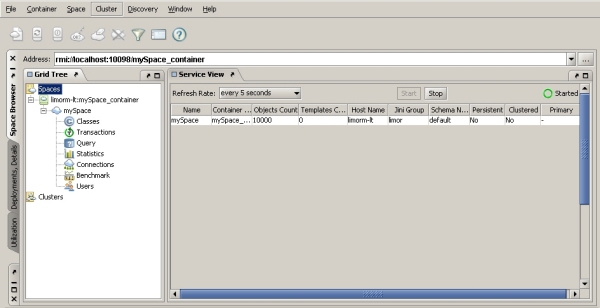
The Space Browser tab has the following components.
Spaces Node
| Icon | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The main Spaces node displays the Space Network view – a table listing all spaces in the network, and different details regarding those spaces. |

|
Container nodes allow you to manage space containers – shutting down the container, creating a space under it, and more. |
|
|
Container nodes allow you to manage space containers – shutting down the container, creating a space under it, and more. |
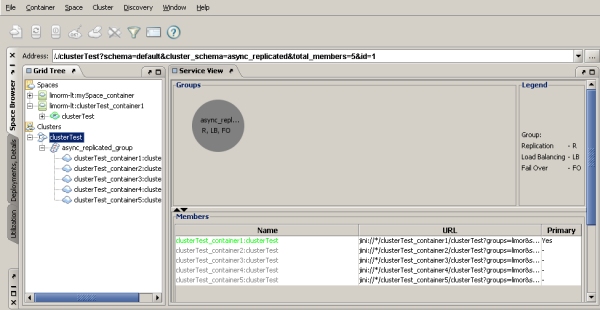
Clusters Node
| Icon | Description |
|---|---|

|
The main Clusters. |
|
|
The main Clusters node that allow you to manage the cluster – stop, start, restart, clean the cluster, and more. |
|
|
Cluster group nodes. |
|
|
cluster members Clicking a cluster member displays a graphic representation of the cluster, and tables showing details regarding replication, failover, load-balancing, and classes. |
For a model that includes nested types, the model jars should be accessible to the gs-ui tool (they can be placed under gs-home/lib/pu-common).
 In-Memory Data Grid - achieve unparalleled speed, persistence, and accuracy.
In-Memory Data Grid - achieve unparalleled speed, persistence, and accuracy.