Space Instance Recovery
Recovery is a process that happens on space instance startup or relocation and used to synchronize the space instance data with another space instance in its replication group.
When space instance is the first to start and doesn't have another space instance to recover from - it's data is loaded from the External Data Source if such was defined, otherwise the space will start empty.
Terminology
- Target space instance - the space instance that recovers the data from another space instance.
- Source space instance - the space instance that the data is recovered from.
- Recovery data - Recovery involves two types of data to recover:
Recovery process
Recovery process has two phases: a snapshot phase and a completion phase.
Snapshot Phase
All space objects are copied from to the target to the source in batches. This is done concurrently by multiple threads. In case the recovery process takes a lot of time, the following configuration can be tuned to decrease the recovery time.
| Property | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| cluster-config.groups.group.repl-policy.recovery-chunk-size | Integer value. Defines how many operations are recovered is a single batch | 200 |
| cluster-config.groups.group.repl-policy.recovery-thread-pool-size | Integer value. Defines how many threads are recovering the data during the snapshot process . | 4 |
Completion Phase
Operations that were performed on the source space during the snapshot phase are not a part of the recovered snapshot, so they are accumulated in the source space instance redo-log and are sent to the target space once the snapshot phase is finished via replication. In case a limited redo log is used the following property defines the maximum size of the redo log during recovery:
| Property | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| cluster-config.groups.group.repl-policy.redo-log-recovery-capacity | Integer value. Defines the maximum size of the redo log kept on the source space during recovery. | 5000000 |
For more info refer to Controlling the Replication Redo Log.
Completion phase is finished according to the consistency requirements of the replication type.
For more info refer to Synchronous Replication Behavior During Recovery and Asynchronous Replication Behavior During Recovery.
Once the recovery process is complete, a full report including the total amount of recovered space objects and notify registrations, and their class types, is logged. During the recovery process, the source space is available, and the target space is unavailable to clients.
- Replication input filter events are called during recovery (on the target).
- Space filter events are not called during recovery.
- The space instance locates a space to recover from using the Jini Lookup Service - each replication group has a unique name. The source space looks for a matching space with the same replication group to recover from.
- Partial recovery - the restarted space recovers only classes with the
@SpaceClass (replicate=true)decoration (turned on only when partial replication is enabled).
Primary-Backup Topology
In primary-backup topologies the recovering space instance is always a backup, primary space instances don't recover their data from other spaces. The recovering backup space instance connects to its primary space instance and recovers its data only from it. If there are other space instances in the same replication group, they don't replicate their data to the recovered space instance.
Primary-Backup Persistent Topology
Primary and Backup space instances use the same database to stored their data. The space is the system of record. The data is usually persisted through the Mirror![]() Performs the replication of changes to the target table or accumulation of source table changes used to replicate changes to the target table at a later time. If you have implemented bidirectional replication in your environment, mirroring can occur to and from both the source and target tables. service.
Which data is recovered depends on the space caching policy.
There is special handling for Transient Entries (
Performs the replication of changes to the target table or accumulation of source table changes used to replicate changes to the target table at a later time. If you have implemented bidirectional replication in your environment, mirroring can occur to and from both the source and target tables. service.
Which data is recovered depends on the space caching policy.
There is special handling for Transient Entries (persist=false), since they can't be persisted - they are always recovered from the primary.
All In Cache Policy
A backup instance recovers all its data from the primary instance - data is not loaded from the database. This is done so that any data changes on the primary during the recovery process are consistent on the backup once recovery finishes.
LRU Cache Policy
A backup instance recovers only transient entries from the primary instance. Data is not loaded from the database.
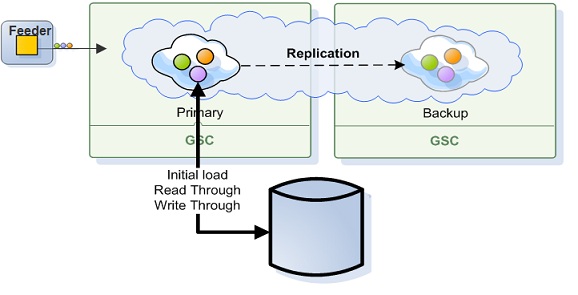
Since primary and backup use the same database instance, the data will be loaded to the backup on demand.
Backup Instance Recovery Failure Handling
If a backup space instance recovery process fails, it is handled in the following way: If the primary space is unavailable for some reason - recovery will be retried until one of the following happens:
- the primary gets reconnected and then the recovery continues normally.
- the space itself becomes primary and then no recovery is necessary.
Any other failure - SpaceMemoryShortageException, Database not available etc. is retried 3 times before failing.
Active-Active Topology
In active-active topologies the recovering space instance connects to one of the space instances in its replication group and recovers all the data from it. If there are other space instances in the same replication group, after recovery other they connect the recovered space instance and replicate their data as well.
Active-Active Persistent Topology
Replicated space instances keep and manage their data in a separate databases.
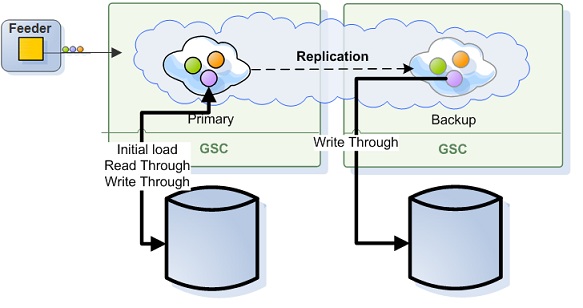
With this scenario:
- If the database is empty –> target space instance recovers everything from the source.
- If database has data –> recover persistent objects from the database + recover transient objects from the source.
For further info and configuration options see Distributed Databases
Space Instance Recovery Failure Handling
If the recovery process fails, it is retried 3 times, by default, before failing.
The number of retries can be configured by setting system property com.gs.recovery-retries.
 In-Memory Data Grid - achieve unparalleled speed, persistence, and accuracy.
In-Memory Data Grid - achieve unparalleled speed, persistence, and accuracy.