Viewing the Deployed Services (Processing Units)
To view information about the deployed GigaSpaces services:
You can see the following information in the Service overview:
- Cluster performance:
- General status of all deployed services (healthy, degraded, unhealthy)
- CPU performance (with average CPU usage, in percent)
- RAM utilization (with current utilization, in percent)
IOPS by operation (reads, writes, takes, and executes)
You can show and hide which operations are shown in the graph.
- Service information (per individual service):
- Service name
- Service type indicated by an icon (stateful, stateless, mirror, web, gateway)
- Actual vs. planned instances
- Number of availability or resource alerts
You can filter the view by service label, type, and RAM utilization. You can sort the view by either alert severity or RAM utilization. You can also do a text search by service name.
To generate and download a service dump, click the icon in the top right corner of the page.
Command
Description
This command lists all the Processing Units in a table with the Processing Unit name, type, Space![]() Where GigaSpaces data is stored. It is the logical cache that holds data objects in memory and might also hold them in layered in tiering. Data is hosted from multiple SoRs, consolidated as a unified data model., topology, status, file name, state, and number of instances.
Where GigaSpaces data is stored. It is the logical cache that holds data objects in memory and might also hold them in layered in tiering. Data is hosted from multiple SoRs, consolidated as a unified data model., topology, status, file name, state, and number of instances.
Input Example
<GS_HOME>/bin/gs pu list
<GS_HOME>/bin/gs.sh pu list
Output Example
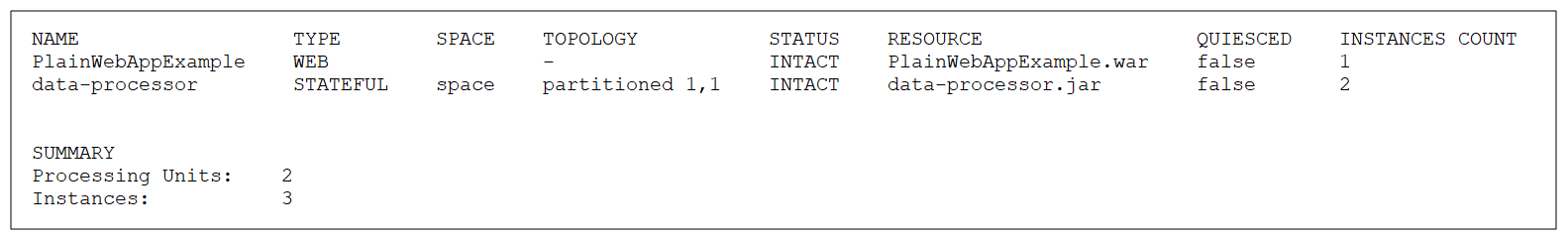
Parameters and Options
None.
Processing Unit instance
Command
gs.{sh/bat} pu list-instances <name>
Description
This command lists all of the instances for a given Processing Unit, along with the Instance ID, Host ID, and Container ID.
Input Example
<GS_HOME>/bin/gs pu list-instances data-processor
<GS_HOME>/bin/gs.sh pu list-instances data-processor
Output Example
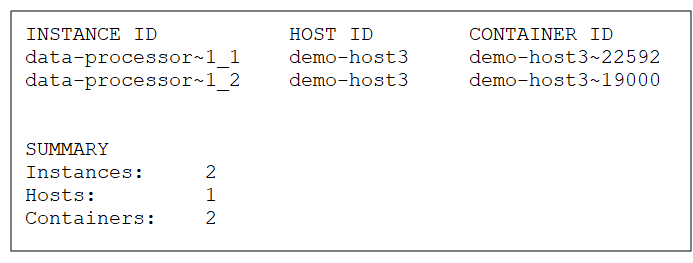
Parameters and Options
| Item | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter | name | Name of Processing Unit to list instances for. |
All Processing Units
Path
GET /pus
Description
The Processing Units are listed with the name, Processing Unit type, file name, topology, number of instances, SLA information, and additional details.
Example Request
curl -X GET --header 'Accept: application/json' 'http://localhost:8090/v2/pus'
Example Response
[
{
"name": "monitorSpace",
"processingUnitType": "stateful",
"resource": "datagrid",
"topology": {
"instances": 1
},
"sla": {
"requiresIsolation": false,
"zones": [],
"maxInstancesPerVM": 0,
"maxInstancesPerMachine": 0
},
"spaces": [
"monitorSpace"
],
"scalable": false,
"status": "intact",
"quiesceDetails": {
"quiesced": false,
"description": "initial"
},
"instances": [
"monitorSpace~1"
]
},
{
"name": "alertSpace",
"processingUnitType": "stateful",
"resource": "datagrid",
"topology": {
"instances": 1
},
"sla": {
"requiresIsolation": false,
"zones": [],
"maxInstancesPerVM": 0,
"maxInstancesPerMachine": 0
},
"spaces": [
"alertSpace"
],
"scalable": false,
"status": "intact",
"quiesceDetails": {
"quiesced": false,
"description": "initial"
},
"instances": [
"alertSpace~1"
]
}
]
Options
None
Specific Processing Unit
Path
GET /pus/{id}
Description
The given Processing Unit is listed with the name, Processing Unit type, file name, topology, number of instances, SLA information, and additional details.
Example Request
curl -X GET --header 'Accept: application/json' 'http://localhost:8090/v2/pus/alertSpace'
Example Response
{
"name": "alertSpace",
"processingUnitType": "stateful",
"resource": "datagrid",
"topology": {
"instances": 1
},
"sla": {
"requiresIsolation": false,
"zones": [],
"maxInstancesPerVM": 0,
"maxInstancesPerMachine": 0
},
"spaces": [
"alertSpace"
],
"scalable": false,
"status": "intact",
"quiesceDetails": {
"quiesced": false,
"description": "initial"
},
"instances": [
"alertSpace~1"
]
}
Options
| Option | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| pu name | Provide the name of the Processing Unit for which you want to see the runtime details. | Yes |
Processing Unit Instance
Path
GET /pus/{id}/instances/{instanceId
Description
The given Processing Unit Instance is listed with the Instance ID, Processing Unit name, Host ID, Container ID, and Partition ID, and Backup ID.
Example Request
curl -X GET --header 'Accept: application/json' 'http://localhost:8090/v2/pus/alertPu/instances/alertPu~1'
Example Response
{
"id": "alertPu~1",
"processingUnitName": "alertPu",
"hostId": "admin",
"containerId": "admin~13972",
"partitionId": 0,
"backupId": 0
}
Options
| Option | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| pu name | Provide the name of the Processing Unit for which you want to see the runtime details. | Yes |
| instanceId | Provide the instanceId of the Processing Unit for which you want to see the runtime details. | Yes |
You can see the following Processing Unit details in the main Processing Units view:
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Name of the Processing Unit. Expand the Processing Unit node to view the name of the Processing Unit instance, and below that the Space name. |
| Status |
Current status of the Processing Unit:
|
| Type | Indicates whether the Processing Unit is stateful or stateless. |
| Host Name | Name of the machine hosting the Processing Unit instance. |
| PID | Process ID of the Processing Unit instance. |
| Application | Client application that is running, if applicable. |
| Zones | If configured, the zone where the Processing Unit is located. |
| CPU | Amount of CPU resources being used by the Processing Unit instance, in percent. |
| Used Heap | Amount of JVM |
If the Space is highlighted, you can click the Actions icon and drill through to the Spaces view to see the Space details.
Refer to the Admin API topics in the Developers Guide.
 In-Memory Data Grid - achieve unparalleled speed, persistence, and accuracy.
In-Memory Data Grid - achieve unparalleled speed, persistence, and accuracy.