Tiered Storage Configuration for Service Grid
For a Tiered Storage![]() Automatically assigns data to different categories of storage types based on considerations of cost, performance, availability, and recovery. overview refer to Intelligent Tiering Overview.
Automatically assigns data to different categories of storage types based on considerations of cost, performance, availability, and recovery. overview refer to Intelligent Tiering Overview.
Initial Load
The initial loading of data into each tier can be a time-consuming process, starting with the System of Record or other external data sources. Additionally, data in both tiers can be updated during the normal course of operations during the day.
During the normal use of Tiered Storage, priority data is stored in the Hot tier, and other data (except transient) is stored in the Warm tier![]() Part of GigaSpaces Tiered Storage Mechanism. Warm tier is SSD (recommended media) storage which is mostly used for data that is read-only and is less frequently used.. If there is data in the Warm tier, it will be faster to recover it rather than recovering it from an external database.
Part of GigaSpaces Tiered Storage Mechanism. Warm tier is SSD (recommended media) storage which is mostly used for data that is read-only and is less frequently used.. If there is data in the Warm tier, it will be faster to recover it rather than recovering it from an external database.
-
Initial load from external data source will be performed as usual if the local Database (DB) is empty (empty = no metadata).
-
If the local DB is not empty, the data of the primary will be loaded from the local disk and backup will perform recovery from primary (delete disk data in init).
-
We use ZooKeeper (ZK) persistent to store the last primary of each partition and where each instance should be located, so election will be performed as before.
-
puto allow auto generation of sla per instance. This is the unit of packaging and deployment in the GigaSpaces Data Grid, and is essentially the main GigaSpaces service. The Processing Unit (PU) itself is typically deployed onto the Service Grid. When a Processing Unit is deployed, a Processing Unit instance is the actual runtime entity..autogenerated-instance-sla="true"
This is the unit of packaging and deployment in the GigaSpaces Data Grid, and is essentially the main GigaSpaces service. The Processing Unit (PU) itself is typically deployed onto the Service Grid. When a Processing Unit is deployed, a Processing Unit instance is the actual runtime entity..autogenerated-instance-sla="true" -
In the case of deploy/undeploy with a different number of partitions, an API needs to be called to clean the internal database and configuration, otherwise the initial load will fail.
Using data persistency, data in both tiers is stored in a system repository. When the data is undeployed, the user has an option to persist the data. Subsequent redeployment of the data is performed at optimum speed.
Log: Source of Data
Recovery from tier layer
Data source recovery
Entries found in warm tier:
Entries inserted to hot tier:
Total Time:
This data can be compared with primary log of the initial run Recovery from external data source:
Entries found in data source
Entries inserted to Space:
Entries ignored:
Total Time:
Transient Objects
-
Transient objects are not kept in SQLite but can still be mirrored to an external source.
-
In this case, after undeploy+deploy, the transient objects will not be in the Space.
-
-
If it is required to load from an external source, delete pu metadata & data.
Tiered Storage Configuration for Space Types
Registering a Space Type with Tiered Storage Configuration
In the Java example below, take note of the highlighted section.
SpaceTypeDescriptor typeDescriptorDoc1 =
new SpaceTypeDescriptorBuilder("SpaceTypeExample")
.addFixedProperty("id", Integer.class)
.addFixedProperty("field1", String.class)
.addFixedProperty("field2", String.class)
.addFixedProperty("field3", String.class)
.addFixedProperty("expireDate", LocalDateTime.class)
.idProperty("id")
.supportsDynamicProperties(false)
.setTieredStorageTableConfig(
new TieredStorageTableConfig()
>.setName("SpaceTypeExample")// set to space type name
>.setCriteria("field1='1'")// see examples below
)
.create()
Tiered Storage Policies in Type Registration
| Example | Hot/Warm Tiers Distribution | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| new TieredStorageTableConfig() .setName("SpaceTypeExample") .setCriteria("field1='1'") Note: Supported operators: = != >= <= and or |
Criteria-Based
|
||||
| new TieredStorageTableConfig() .setName("SpaceTypeExample") .setTimeColumn("expireDate") .setPeriod(Duration.ofMinutes(60)) |
Time-Based
Note: Only the initial value of the expireDate column will define Hot Tier retention of an object. |
||||
| new TieredStorageTableConfig() .setName("SpaceTypeExample") .setTransient(true) |
Memory Only
|
||||
| null (*) or no call to: .setTieredStorageTableConfi |
Warm Tier Only
|
||||
| new TieredStorageTableConfig() .setName("SpaceTypeExample") .setCriteria("all") |
Hot and Warm
|
Underploy-Deploy
In the case of deploying using a different topology:
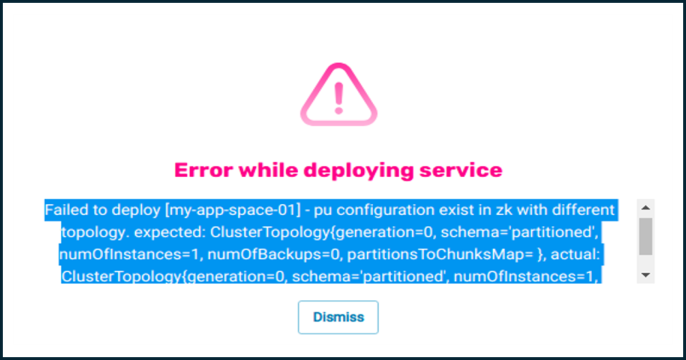
The Undeployed Processing Units (PUs)
The undeployed services can be viewed using the GET /pus/undeployed REST API![]() REpresentational State Transfer. Application Programming Interface
An API, or application programming interface, is a set of rules that define how applications or devices can connect to and communicate with each other. A REST API is an API that conforms to the design principles of the REST, or representational state transfer architectural style..
REpresentational State Transfer. Application Programming Interface
An API, or application programming interface, is a set of rules that define how applications or devices can connect to and communicate with each other. A REST API is an API that conforms to the design principles of the REST, or representational state transfer architectural style..

An example of sample output is shown below.
[
{
"name": "space-10-SNAPSHOT",
"unDeployedAt": "2021-08-03T12:18:25.437",
"isPersistent": true,
"gracefulShutdown": true,
"lastPrimaries": [
{
"partitionId": 1,
"insatnceId": "1_1"
}
],
"spaceInstancesHosts": [
{
"instanceId": "1_0",
"host": "127.0.1.1"
},
{
"instanceId": "1_1",
"host": "127.0.1.1"
}
],
"schema": "partitioned",
"numOfInstances": 1,
"backupsPerPartition": 1
}
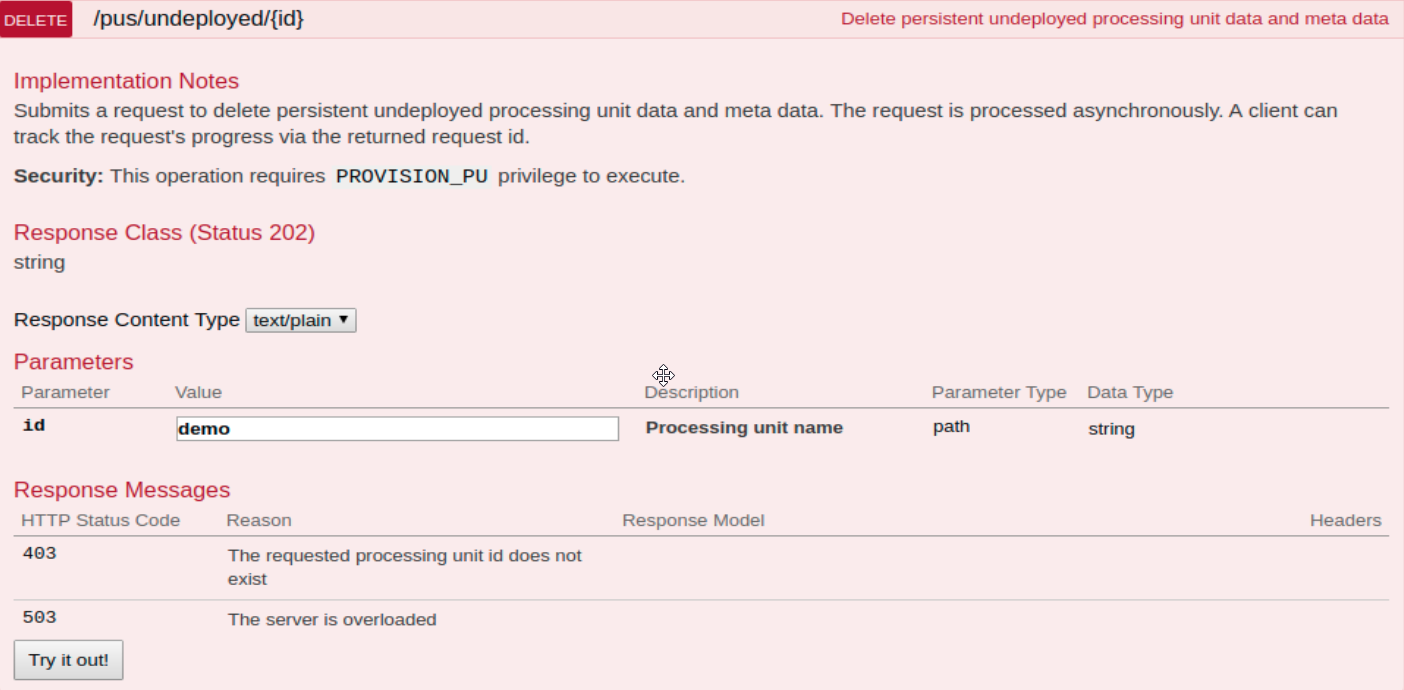
Deleting Previous Data and Metadata
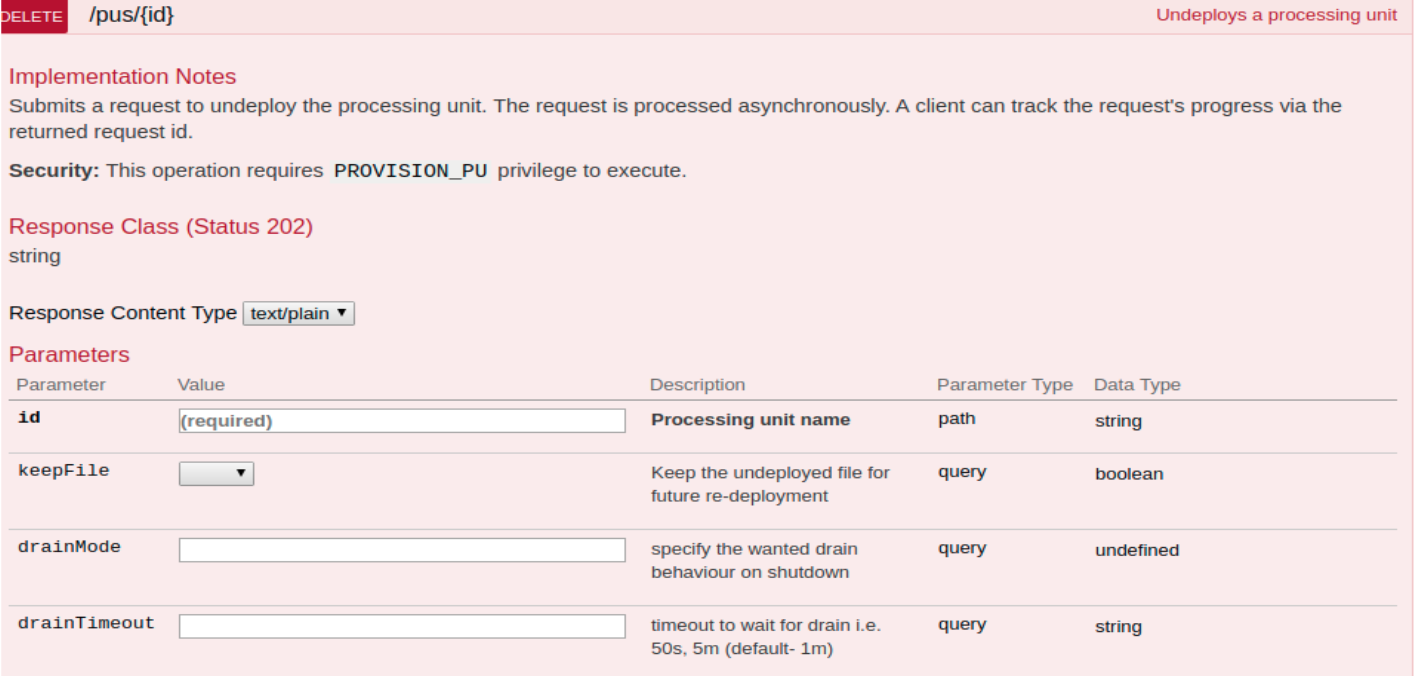
Safe Undeploy: Ensure all Data in Disk is Updated
Added options to undeploy: DrainMode and DrainTimeout
-
NONE - make no attempt to wait for all data to be drained before shutting down
-
REQUIRED - make an attempt to wait for all data to be drained before shutting down,
-
shutdown even if drain wasn't completed before drainTimeout
-
ATTEMPT - make an attempt to wait for all data to be drained before shutting down,
-
shutdown will not occur if drain wasn't completed before drainTimeout
Admin API:
pu.undeployAsync(new UndeployOptions(DrainMode.ATTEMPT,60000L));
CLI:
./gs.sh service undeploy --drain-mode=ATTEMPT --drain-timeout=60000ms test.
If drain was not completed with mode attempt, the PU will be at quiesce status.
Even if undeploy did not drain all, data is considered as consistent and will recover from disk in the case where it is not empty. The same goes for failover with async replication.
Undeploy - REST
The data of undeployed services can be deleted using the DELETE /pus/undeployed/{id} REST![]() REpresentational State Transfer. Application Programming Interface
An API, or application programming interface, is a set of rules that define how applications or devices can connect to and communicate with each other. A REST API is an API that conforms to the design principles of the REST, or representational state transfer architectural style. API.
REpresentational State Transfer. Application Programming Interface
An API, or application programming interface, is a set of rules that define how applications or devices can connect to and communicate with each other. A REST API is an API that conforms to the design principles of the REST, or representational state transfer architectural style. API.
Limitations and Recommendations
| Supported | Not Supported |
|---|---|
|
|
 In-Memory Data Grid - achieve unparalleled speed, persistence, and accuracy.
In-Memory Data Grid - achieve unparalleled speed, persistence, and accuracy.