Logging
This section explains how to configure the logging for GigaSpaces products. You can format the log output, choose file names, and define rollover policies.
Some of the features discussed on this page are not part of the open-source edition, and are only available in the licensed editions (starting with Premium).
GigaSpaces makes logging calls using the Java platform's core logging facilities. For a detailed explanation of the Java logging framework, refer to Java Logging Overview on the Oracle website.
Configuration
The logging configuration is initialized using a configuration file that is read at startup. This configuration file is in the standard java.util.Properties format. It configures custom versions of both java.util.logging.Handler and java.util.logging.Formatter, and default levels for frequently used loggers (categories).
Default Configuration
The default GigaSpaces logger configuration file is located under:
$GS_HOME/config/log/xap_logging.properties
Overriding the Default Configuration
The configuration defined in the xap_logging.properties file may be overridden either by using system properties, or by providing an external configuration file with overrides. This external configuration file should be located in the classpath under:
$GS_HOME/config/log/xap_logging_ext.properties
Any configuration that you want to override in the xap_logging.properties file, should appear in xap_logging_ext.properties with its new value. The same applies for system properties, for example:
-Dcom.gigaspaces.exceptions.level=WARNING
The recommended way to define system properties when starting service grid components is to wrap the original script, e.g. gsc.sh(bat) with a wrapper script which include the setenv.sh(bat) script, which is used by these components, will pick these options automatically and use them as JVM arguments.
Overriding the Configuration File
Your own configuration file may also be used instead of the platform's default. This is done via URL, or by setting the configuration file location using a system property:
-Djava.util.logging.config.file=myfile.properties
GigaSpaces scripts rely on the exported environment variable GS_LOGS_CONFIG_FILE (declared in $GS_HOME/bin/setenv script). The preferred way to apply your override file is to use a wrapper script; export the new setting of this variable and call the original script. This ensures that when setenv.sh(bat) is called from within the platform's scripts, it will pick up the override.
# unix
export GS_LOGS_CONFIG_FILE=myfile.properties
./gsc.sh
If your application initializes the logging facility via the Logging API (e.g. LogManager.readConfiguration(InputStream ins)), you may want to disable the GigaSpaces configuration altogether. When the GigaSpaces logging configuration is disabled, your Java logging settings take their place. This is done using the following system property:
-Dcom.gs.logging.disabled=true
Troubleshooting
To troubleshoot and detect which logging properties file was loaded and from where, set the following system property to true. This property already exists in the scripts (for convenience) and by default is set to false.
-Dcom.gs.logging.debug=true
Verbose System Report
Whenever a service grid component is started, it prints a system report in its log file. Increasing the log level from INFO to CONFIG or beyond will generate a verbose report and include all system properties and environment variables, which can be useful for troubleshooting.
For example, to enable a verbose system report for GSC, change the following log level:
com.gigaspaces.grid.gsc.level = CONFIG
Handlers
Out of the box, GigaSpaces configures its logging with two log Handlers,
-
java.util.logging.ConsoleHandler- A simple handler for writing formatted output to System.err (level is set to ALL). -
com.gigaspaces.logger.RollingFileHandler- A handler that writes formatted output to a file that rolls over if a certain policy is triggered. Refer to Managing Log Files.
Java util logging supports other handlers. MemoryHandler, SocketHandler or any other handler can be used instead of the above. For more information about handlers, refer to this Oracle topic on logging. You can also use one of the open source logging frameworks that supports java.util.logging.
Formatters
Formatters are in charge of formatting the log messages and adding metadata to them (date, time, level, etc).
GigaSpaces configures the logging handler's formatter property with a single Formatter implementation class:
com.gigaspaces.logger.GSSimpleFormatter. This formatter class is based on the java.util.logging.SimpleFormatter class. Refer to Formatting Log Messages for more details.
Exception Visibility
GigaSpaces prints exception stack traces for log messages with level SEVERE or higher.
com.gigaspaces.exceptions.level = SEVERE
Messages with lower levels will only be logged with the exception's toString() value. To force the logger to print the stack trace of exceptions with lower levels, such as Level WARNING, set the com.gigaspaces.exceptions.level property to WARNING.
The stack trace of a java.lang.RuntimeException is always be logged, regardless of the level definition.
Logging Management at Runtime
You can change various logger level settings while the system is up and running, without having to restart. This can be very useful in production environments when you have to troubleshoot the system, but cannot restart it.
Runtime Logging Management via Ops Manager/Command Line/REST-API
The logging options can be changed dynamically via one of the following approaches:
Click the card in the Services area of the Services Overview page. On the top right of the screen, click on the three-dot menu. The following popup will appear:
Click Change Log Level, and the following popup will appear:
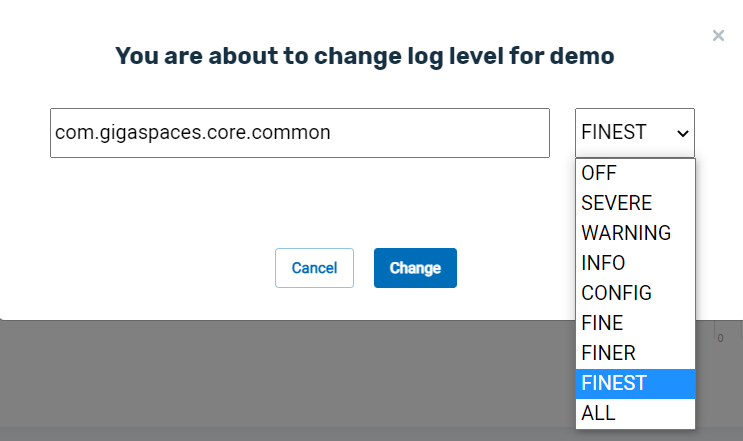
In this example, com.gigaspaces.core.common is the name of the log file that you wish to change. You can see the list of log files in $GS_HOME/config/log/xap_logging.properties
The dropdown list allows you to choose a logging level. In this example, the new logging level is FINEST. Click here for information on logging levels.
Command example:
gs logger set-level --service=demo com.gigaspaces.core.common FINE
Description:
For the log file for service demo com.gigaspaces.core.common, set the log level to FINE..
Path
POST/pus/{id}/log-level
Description
Dynamically change the logging level for a log file used by a service.
Example Request
curl -X POST --header 'Accept: application/json' 'http://localhost:8090/v2/pus?id=demo&log=com.gigaspaces.core.common&level=FINEST'
This example changes the logging level for the log file com.gigaspaces.core.common in service demo to FINEST.
Options:
| Option | Description | Sample Data | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | The name of the service that contains the log you are modifying | demo | Yes |
| log | The name of the log file you wish to change — see the list of log files in $GS_HOME/config/log/xap_logging.properties | com.gigaspaces.core.common | Yes |
| level | The new logging level. Click here for information on logging levels. | FINEST | Yes |
Runtime Logging Management via JMX
To do this, connect to the JMX Bean of the Java logging facility via a monitoring tool such as JConsole. You can start JConsole for a specific running GSC or GSM using the GigaSpaces Management Center (<product>\bin\gs-ui.sh(bat)).
The GigaSpaces Management Center has been deprecated and will be removed in a future release.
To change the logging level in JConsole
-
Traverse to the MBeans tab.
-
Expand the
java.util.loggingtree node and locate the Logging tree node. -
Select the Operations tab.
-
Type the logger's name and level for the arguments of the
setLoggerLevel()method. For example, If you want to changecom.gigaspaces.exceptions.levellevel toWARNING, usesetLoggerLevel(com.gigaspaces.exceptions, WARNING).
You must use the logging level without the .level string, for example com.gigaspaces.core.cluster.replication, and set the value to FINE.
The LoggingMXBean enables you to:
-
Get the name of the log level associated with the specified logger.
-
Get the list of currently registered loggers.
-
Get the name of the parent for the specified logger.
-
Set the specified logger to the specified new level.
Logging Level
The logging level class defines a set of standard logging levels that can be used to control logging output. The logging levels are ordered, and are specified by ordered integers/constants.
Enabling logging at a given level also enables logging at all higher levels.
The supported logging levels (in descending order) are:
-
SEVERE (highest value)
-
WARNING
-
INFO
-
CONFIG
-
FINE
-
FINER
-
FINEST (lowest value)
In addition, there is a level OFF that can be used to turn off logging, and a level ALL that can be used to enable logging of all messages.
Logging Categories
The following logging categories are supported:
-
Client
-
Communication Protocol
-
Class Loader
-
Space (Caching, Query, Replication, etc.)
-
Runtime (GCC, GSM, etc.)
-
Security
-
Web Container
-
Mule Integration
-
Management
For each category, there are specific logger names you should use when configuring the logging level. See the xap_logging.properties file for the exact logger names supported for each category. You can also find all logger names in the com.gigaspaces.logger.Constants class.
The following sections describe the different modules, their logging names, and their default logging levels.
Client General
com.gigaspaces.client.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.client.cluster.liveness.level = INFO
The GigaSpaces Client can be another component or application that connects to a GigaSpaces cluster. Liveness check is functionality that runs inside a GigaSpaces proxy (usually held by a client connecting to a Space) to keep track of the cluster members. Additional information about the GigaSpaces proxy can be found here.
.NET API
The logging configuration file includes declarations of the loggers available at the bridge between .NET and Java.
com.gigaspaces.externaldatasource.dotnet.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.bridge.dispatcher.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.bridge.pbsexecuter.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.dotnet.pu.level = INFO
OpenSpaces
org.openspaces.level = INFO
OpenSpaces wraps the core product with Spring, which enables applying Spring configuration and the Spring life cycle to GigaSpaces applications.
PU
org.openspaces.pu.container.support.level = WARNING
org.openspaces.pu.container.jee.context.ProcessingUnitWebApplicationContext.level = WARNING
Spring
GigaSpaces Spring application logging
com.gigaspaces.spring.level = WARNING
Hibernate
org.hibernate.level = WARNING
JMS API
com.gigaspaces.jms.level = INFO
Comunication Protocol
com.gigaspaces.lrmi.nio.filters.SSLFilterFactory.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.lrmi.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.lrmi.stubcache.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.lrmi.context.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.lrmi.marshal.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.lrmi.watchdog.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.lrmi.classloading.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.lrmi.slow_consumer.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.lrmi.exporter.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.lrmi.communication.transport.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.lrmi.communication.manager.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.lrmi.channel.transport.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.lrmi.channel.manager.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.lrmi.channel.protocol.level = INFO
Class Loader
com.gigaspaces.core.classloadercleaner.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.core.classloadercache.level = INFO
GigaSpaces applications run as part of a GigaSpaces runtime container, and are packaged using the structure described here. Application JARs/classes are packaged in different folders, and some of the classes may be loaded as part of GigaSpaces containers (GSCs). There are multiple class loaders involved when an application is running. More information about the class loaders and their hierarchy can be found here.
Space
Core and Kernel
com.gigaspaces.core.engine.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.core.lease.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.core.types.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.memory-manager.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.kernel.level = CONFIG
com.gigaspaces.core.common.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.core.config.level = CONFIG
com.gigaspaces.container.level = INFO
Core runtime for the GigaSpaces Space component. The above loggers relate to this component and some aspects of this engine, including lease, object types, and Memory Manager.
Filters
com.gigaspaces.filters.level = INFO
The Space filters are described here Java version | .NET version.
Persistency
com.gigaspaces.persistent.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.persistent.shared_iterator.level = INFO
org.hibernate.level = WARNING
The GigaSpaces persistence options are explained here Java version | .NET version. One of the packaged External Data Source implementations uses Hibernate. It is called Hibernate External Data Source, which is described here.
Query
com.gigaspaces.query.level = INFO
GigaSpaces supports SQL queries on data in the Space, and the logger corresponds to this functionality Java version | .NET version.
LRU and Eviction
com.gigaspaces.cache.level = INFO
More information about the LRU policy and eviction behavior is available here.
Notifications
com.gigaspaces.core.notify.level = INFO
The Notification mechanism can be used to identify events related to Space data (write, update, take, etc). Notifications are typically used with a Notify Container. Notifications can also be used via Session-based messaging, which is discussed in detail here.
FIFO
com.gigaspaces.core.fifo.level = INFO
FIFO functionality is applicable for write, read and event (notifications), and is discussed in detail here Java version | .NET version.
Replication
com.gigaspaces.core.cluster.replication.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.core.cluster.replication.redolog.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.core.cluster.sync_replication.level = INFO
When a cluster topology is replicated, the replication functionality is enabled.
Replication between Spaces is one of the core features of GigaSpaces, and is explained in detail here.
Partitioning
com.gigaspaces.core.cluster.partition.level = INFO
When a cluster uses partitioned topology, the data is partitioned across multiple Space instances.
Active-Election
com.gigaspaces.cluster.active_election.level = INFO
When there are multiple instances (primary/backup(s)), an Active-Election process is used by the cluster members to determine which member acts as the primary instance.
POJO
com.gigaspaces.pojo.level = INFO
This logger corresponds to GigaSpaces POJO support. More information is available here.
XA Manager
com.gigaspaces.core.xa.level = INFO
This logger corresponda to the XA Transaction manager running in the Space. More information is available here Java version | .NET version.
Jini Dist. TX Manager
com.sun.jini.mahalo.startup.level = INFO
com.sun.jini.mahalo.destroy.level = INFO
This logger is for the Jini Distributed Transaction manager. More information is available here Java version | .NET version.
SpaceURL, SpaceValidator, SpaceURLParser
com.gigaspaces.common.spaceurl.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.common.spacefinder.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.common.lookupfinder.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.common.resourceloader.level = INFO
The SpaceURL and its constraints are explained here Java version | .NET version. Other loggers are related to this one, and are applicable when a client is trying to create a Space proxy using a URL.
Multicast Notifications
com.gigaspaces.worker.multicast.level = INFO
Space notifications support multicast mode, and this logger corresponds to multicast functionality.
Runtime
Service Container - General
com.gigaspaces.grid.space.SpaceHandler.level = FINE
org.jini.rio.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.start.level = CONFIG
com.gigaspaces.grid.space.GigaSpacesFaultDetectionHandler.level=INFO
com.gigaspaces.grid.lookup.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.management.level = INFO
Lookup Service
com.gigaspaces.core.lookupmanager.level = INFO
com.sun.jini.reggie.level = INFO
net.jini.discovery.LookupLocatorDiscovery.level = INFO
net.jini.lookup.ServiceDiscoveryManager.level = INFO
net.jini.discovery.LookupDiscovery.level = INFO
net.jini.lookup.JoinManager.level = INFO
net.jini.config.level = WARNING
com.sun.jini.start.service.starter.level = INFO
com.sun.jini.thread.TaskManager.level = INFO
The Lookup Service (LUS) is a runtime registry of GigaSpaces components. Each component registers itself to a LUS, which provides visibility to other components. For example, a GSM discovers a GSC by looking at an entry in the LUS, and a GSC discovers a GSM in a similar way. More information about the LUS is available here.
GSM
com.gigaspaces.grid.gsm.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.grid.gsm.peer.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.grid.gsm.feedback.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.grid.gsm.provision.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.grid.gsm.services.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.grid.gsm.service-instances.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.grid.gsm.selector.level = INFO
org.jini.rio.tools.webster.level = INFO
The Grid Service Manager (GSM) manages the applications and maintains the SLAs for deployments. More information about the GSM is available here.
GSC
com.gigaspaces.grid.gsc.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.grid.gsc.GSCFaultDetectionHandler.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.grid.gsm.GSMFaultDetectionHandler.level = INFO
org.openspaces.pu.container.servicegrid.PUFaultDetectionHandler.level = INFO
The Grid Service Container (GSC) is the runtime environment for GigaSpaces applications. More information about GSCs is available here.
GSA
com.gigaspaces.grid.gsa.level = INFO
The Grid Service Agent (GSA) acts as a process manager that can spawn and manage Service Grid processes (operating-system-level processes), such as the Grid Service Manager (GSM), Grid Service Container (GSC), and Lookup Service (LUS). More information about the GSA is available here.
Replication
com.gigaspaces.replication.channel.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.replication.channel.verbose.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.replication.replica.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.replication.node.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.replication.router.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.replication.group.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.replication.backlog.level = INFO
Metrics
com.gigaspaces.metrics.manager.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.metrics.registry.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.metrics.sampler.level = INFO
Security
com.gigaspaces.security.level = INFO
This logger corresponds to the security of GigaSpaces components. This includes configuration and runtime execution of security functionality. More information regarding GigaSpaces security is available here.
Web Container
Any web application default logging level (the logger name for web applications is web.[processing unit name].[instance id]).
web.level = INFO
org.mortbay.level = WARNING
GigaSpaces uses a Jetty container to provide support for Web applications. These loggers correspond to the Web Container. More information about GigaSpaces Web Application support is available here.
Mule Integration
org.mule.level = WARNING
org.mule.MuleServer.level = INFO
org.mule.RegistryContext.level = INFO
org.openspaces.esb.mule.level = WARNING
These loggers correspond to the Mule integration. More information about Mule integration is available in the Mule ESB and Mule Processing Unit topics.
Management
For GUI, browser, cluster view, and JMX logging:
com.gigaspaces.admin.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.admin.ui.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.admin.ui.cluster.view.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.admin.ui.spacebrowser.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.admin.cli.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.jmx.level = INFO
These loggers correspond to the GigaSpaces Management Center. Additional information regarding the user interface is available here.
The GigaSpaces Management Center has been deprecated and will be removed in a future release.
Persistence
For persistence logging:
com.gigaspaces.persistent.level = INFO
com.gigaspaces.persistent.shared_iterator.level = INFO

