General Terms and Concepts
Basic Components
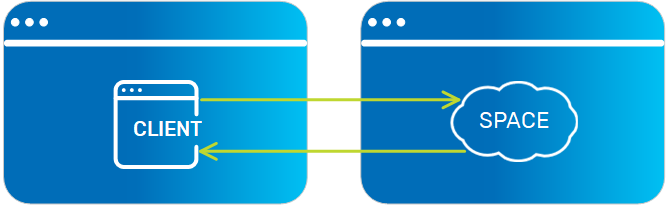
Space
|
|
The cache instance that holds data objects in memory. |
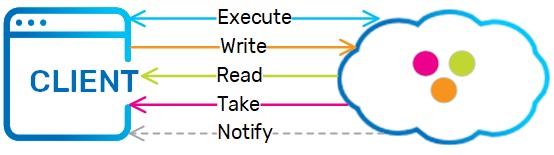
Execute, Read, Write, Take and Notify
|
|
A set of methods used to read, write, take, and register for notification on objects that are stored in the Space. Execute allows sending Tasks to be executed within the Space. Read and Take criteria can be specified via a query or a template (an example object). |
Processing Unit
|
|
A combination of clients and/or an embedded Space instance. This is the fundamental unit of deployment in GigaSpaces. The Processing Unit itself is typically deployed onto the Service Grid. When a Processing Unit is deployed, a Processing Unit instance is the actual runtime entity. |
Processing Unit Configured with an Embedded Space
|
|
A deployable package that instantiates an embedded Space instance, also called a data grid instance. A set of embedded Space instances that run within the Processing Units typically form a data grid. |
Processing Unit Configured with One or More Services
|
|
A deployable package containing one or more services. In the GigaSpaces context, it usually acts as a client that interacts with other Processing Units by utilizing the messaging capabilities of the Space. |
Processing Unit Configured with an Embedded Space and Embedded Services
|
|
A deployable, independent, scalable unit that is the building block of Space-Based Architecture. A client application (which can also be other Processing Units) write objects to the Space, and the Processing Unit that contains this Space consumes these objects or is notified about them and triggers related services. |
Data Grid
In-Memory Data Grid (IMDG)
A set of Space instances, typically running within their respective processing unit instances. The space instances are connected to each other to form a space cluster. The relations between the spaces define the data grid topology.
Data Grid Topologies
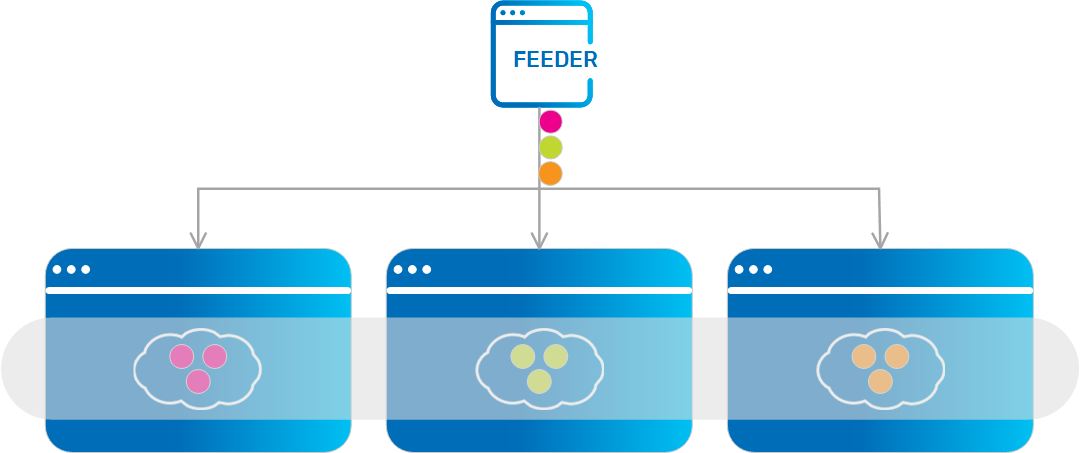
Partitioned Data Grid
|
|
Each Data Grid instance (partition) holds a different subset of the objects in the data grid. When the objects are written to this data grid, they are routed to the proper partition according to a predefined attribute in the object that acts as the routing index. |
Routing
|
|
The mechanism that is in charge of routing the objects into and out of the corresponding partitions. The routing is based on a designated attribute inside the objects that are written to the Space, called the Routing Index. |
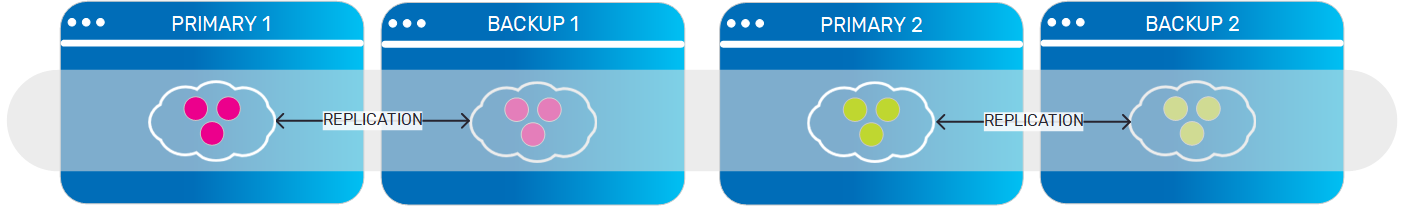
Partitioned Data Grid with High Availability
|
|
A partitioned data grid, with one or more backup instances for each partition. Each data grid instance (partition) holds a different subset of the objects in the data grid, and replicates this subset to its backup instance/s. |