Custom Matching
Overview
Queries are usually indexed and executed using primitive fields (long, float, string, etc.). These fields can be at the root level of the Space object, or embedded within nested objects in the Space object. You can construct a query using a template object or SQL, to specify the criteria you want to use when the matching phase is performed within the Space when looking for the relevant objects.
However, in some cases you may need a custom data type with custom business logic to find matching objects within the Space, instead of the primitive data type comparison. To allow the Space to invoke your business logic when the matching process is conducted, the Comparable interface should be implemented for a class that stores the data you want to use with your custom business logic.
The Comparable implementation should not be done for the Space class itself, but for one of its fields.
You can index the data to speed up the custom matching process; index the field so that its class implements the Comparable interface using the EXTENDED index type as part of the Space class. Indexing the custom type field should be used with caution, because it doesn't support a Comparable.compareTo implementation that performs relative-based matching, which is demonstrated in the example on this page.
In your Comparable class, make sure that the compareTo() and equals() methods always yield the same result, because the GigaSpaces query optimization depends on that equivalence. This is not the case, for example, where the BigDecimal.equals() method takes into account the number of trailing zeros, whereas the BigDecimal.compareTo() method ignores the trailing zeros.
See the Indexing section for additional information about how to enable the EXTENDED index.
Vector Compare Example
The following example is a business logic implementation used to query for vector data (an array of Integer values), using the Euclidean distance formula:
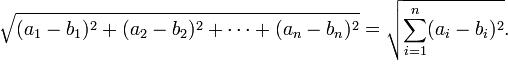
The object that holds the array implements the Comparable interface. The Space class has a getter method for this field indexing, using the EXTENDED index. The actual query involves indexed fields for several sample data points within the vector, together with the custom field:
SQLQuery<Vector> query= new SQLQuery<Vector>(Vector.class ,
"(x0 > ? AND x0 < ? ) " +
"AND (x1 > ? AND x1 < ? ) " +
"AND (x2 > ? AND x2 < ? ) " +
"AND (x3 > ? AND x3 < ? ) " +
"AND (x4 > ? AND x4 < ? ) " +
"AND (x5 > ? AND x5 < ? ) " +
"AND (x6 > ? AND x6 < ? ) " +
"AND (x7 > ? AND x7 < ? ) " +
"AND (x8 > ? AND x8 < ? ) " +
"AND (x9 > ? AND x9 < ? ) " +
"AND (x10 > ? AND x10 < ? ) " +
"AND vectordata <= ?");
The following is an example of a target vector, and a matching vector found using the custom matching implementation:
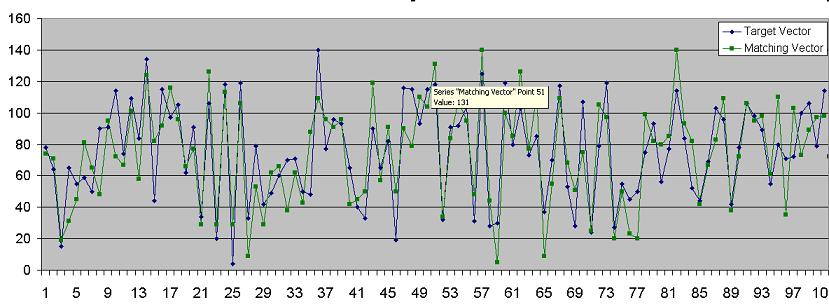
To scale the system, deploy the Space in a partitioned cluster schema. This allows queries such as matching to be executed across all the partitions in parallel, speeding up the query execution time.
The Application tab shows the full query usage. This allows the Comparable.compareTo implementation to be performed on a smaller candidate subset of objects.
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class VectorData implements Serializable, Comparable <VectorData>{
VectorData (int[] data)
{
this.data = data;
}
private static final double THRESHOLD = 200;
private static final int LARGERTHAN = 1;
private static final int EQUALS = 0;
private static final int LESSTHAN = -1;
int data[];
public int[] getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(int[] data) {
this.data = data;
}
public int compareTo(VectorData candidate) throws ClassCastException {
int result = LARGERTHAN;
double sum = 0;
double dist = 0;
int[] candidateData = candidate.getData();
for (int j = 0; j < Vector.VECTOR_SIZE; j++) {
sum += Math.pow(candidateData[j] - this.data[j], 2);
}
dist = Math.pow(sum, 0.5);
if (dist <= THRESHOLD){
result = EQUALS;
}
return result ;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + Arrays.hashCode(data);
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
VectorData other = (VectorData) obj;
if (!Arrays.equals(data, other.data))
return false;
return true;
}
}
import com.gigaspaces.annotation.pojo.SpaceClass;
import com.gigaspaces.annotation.pojo.SpaceId;
import com.gigaspaces.annotation.pojo.SpaceProperty;
import com.gigaspaces.annotation.pojo.SpaceRouting;
import com.gigaspaces.annotation.pojo.SpaceProperty.IndexType;
@SpaceClass
public class Vector {
public Vector (){}
static public int VECTOR_SIZE = 101;
String name;
VectorData vectordata;
@SpaceRouting
@SpaceId
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public VectorData getVectordata() {
return vectordata;
}
public void setVectordata(VectorData vectordata) {
this.vectordata = vectordata;
}
@SpaceProperty ( index = IndexType.EXTENDED)
Integer getX0()
{
if (vectordata !=null)
return vectordata.data[0] ;
else
return null;
}
....
@SpaceProperty ( index = IndexType.EXTENDED)
Integer getX10()
{
if (vectordata !=null)
return vectordata.data[100] ;
else
return null;
}
void setX0(Integer x){};
....
void setX10(Integer x){};
}
static Random rand = new Random();
static int[] baseVector =null;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
GigaSpace gigaspace = new GigaSpaceConfigurer(new UrlSpaceConfigurer("/./space")).gigaSpace();
System.out.println("Writing Vector objects into the space");
int max = 1000;
Vector[] vs = new Vector[max];
for (int i=0;i<max;i++)
{
Vector v = new Vector();
v.setName(i+"");
v.setVectordata(new VectorData(getRandomVector()));
vs[i] = v;
}
gigaspace.writeMultiple(vs);
double MIN_THRESHOLD = 0.85;
double MAX_THRESHOLD = 1.15;
SQLQuery<Vector> query= new SQLQuery<Vector>(Vector.class ,
"(x0 > ? AND x0 < ? ) " +
"AND (x1 > ? AND x1 < ? ) " +
"AND (x2 > ? AND x2 < ? ) " +
"AND (x3 > ? AND x3 < ? ) " +
"AND (x4 > ? AND x4 < ? ) " +
"AND (x5 > ? AND x5 < ? ) " +
"AND (x6 > ? AND x6 < ? ) " +
"AND (x7 > ? AND x7 < ? ) " +
"AND (x8 > ? AND x8 < ? ) " +
"AND (x9 > ? AND x9 < ? ) " +
"AND (x10 > ? AND x10 < ? ) " +
"AND vectordata <= ?");
VectorData vec = new VectorData(getRandomVector());
query.setParameter(1,(int)(MIN_THRESHOLD * vec.getData()[0]));
query.setParameter(2,(int)(MAX_THRESHOLD * vec.getData()[0]));
...
query.setParameter(21,(int)(MIN_THRESHOLD * vec.getData()[100]));
query.setParameter(22,(int)(MAX_THRESHOLD * vec.getData()[100]));
query.setParameter(23,vec);
Vector matchingVectors[] = gigaspace.readMultiple(query ,Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
static int[] getRandomVector()
{
int data[] = new int[Vector.VECTOR_SIZE];
for (int j=0;j<Vector.VECTOR_SIZE;j++)
{
if (baseVector != null)
data[j] = baseVector [j] + rand.nextInt(50);
else
data[j] = rand.nextInt(100);
}
return data;
}

