GigaSpaces Integration with Kafka
| Author | Product Version | Last Updated | Reference | Download |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oleksiy Dyagilev | 14.2 | March 2019 | Apache Kafka | Github link |
Introduction
Apache Kafka is a distributed publish-subscribe messaging system. It is designed to support persistent messaging with a O(1) disk structures that provides constant time performance even with many TB of stored messages. Apache Kafka provides High-throughput even with very modest hardware, Kafka can support hundreds of thousands of messages per second. Apache Kafka supports partitioning the messages over Kafka servers and distributing consumption over a cluster of consumer machines while maintaining per-partition ordering semantics. Many times Apache Kafka is used to perform parallel data load into Hadoop.
This pattern integrates GigaSpaces products with Apache Kafka. GigaSpaces’ write-behind data grid operations to Kafka making it available for the subscribers. Such could be Hadoop or other data warehousing systems using the data for reporting and processing.
GigaSpaces-Kafka Integration Architecture
The GigaSpaces-Kafka integration is done via the SpaceSynchronizationEndpoint interface deployed as a Mirror service. It consumes a batch of data grid operations, converts them to custom Kafka messages and sends these to the Kafka server using the Kafka Producer API.
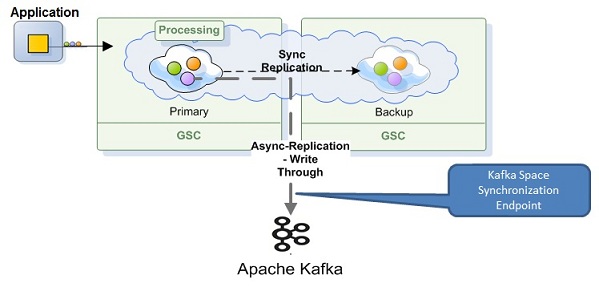
The GigaSpace-Kafka protocol is simple and represents the data and its Space operation. The message consists of the Space operation type (Write, Update , rRemove, etc.) and the actual data object. The data object itself could be represented either as a single object or as a Space Document with key/values pairs (SpaceDocument).
Since a Kafka message is sent over the wire, it should be serialized to bytes in some way. The default encoder utilizes Java serialization mechanism which implies Space classes (domain model) to be Serializable.
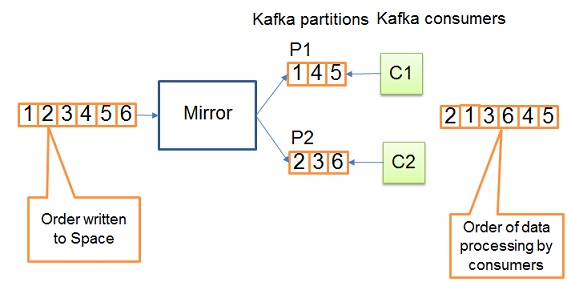
By default, Kafka messages are uniformly distributed across Kafka partitions. Please note, even though Space operations appear ordered in SpaceSynchronizationEndpoint, it doesn’t imply the correct ordering of data processing in Kafka consumers. See the following diagram:
Getting Started
Download the Kafka Example
You can download the example code from here. Unzip into an empty folder.
The example is located under <project_root>/example. It demonstrates how to configure Kafka persistence and implements a simple Kafka consumer that pulls data from Kafka and stores in HsqlDB.
Running the Example
In order to run an example, please follow the instruction below:
Step 1: Install Kafka.
Step 2: Start Zookeeper and Kafka server.
bin/zookeeper-server-start.sh config/zookeeper.properties
bin/kafka-server-start.sh config/server.properties
Step 3: Build the project.
cd <project_root>
mvn clean install
Step 4: Deploy the example to the data grid.
cd example
mvn os:deploy
Step 5: Check the GigaSpaces log files, there should be messages from the Feeder and Consumer.
Configuration
Library Dependency
The following Maven dependency needs to be included in your project in order to use Kafka persistence. This artifact is built from the <project_rood>/kafka-persistence source directory.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.epam</groupId>
<artifactId>kafka-persistence</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
Processing Unit
Here is an example of the Kafka Processing Unit configuration:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:os-core="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.1.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core http://www.openspaces.org/schema/9.1/core/openspaces-core.xsd">
<!--
Spring property configurer which allows us to use system properties (such as user.name).
-->
<bean id="propertiesConfigurer" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"/>
<!--
Enables the usage of @GigaSpaceContext annotation based injection.
-->
<os-core:giga-space-context/>
<!--
A bean representing a space (an IJSpace implementation).
-->
<os-core:space id="space" url="/./space" schema="default" mirror="true">
<os-core:space-type type-name="Product">
<os-core:id property="CatalogNumber"/>
<os-core:basic-index path="Name"/>
<os-core:extended-index path="Price"/>
</os-core:space-type>
</os-core:space>
<!--
OpenSpaces simplified space API built on top of IJSpace/JavaSpace.
-->
<os-core:giga-space id="gigaSpace" space="space" />
</beans>
Mirror service
Here is an example of the Kafka Space Synchronization Endpoint configuration:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:os-core="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core"
xmlns:os-events="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events"
xmlns:os-remoting="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting"
xmlns:os-sla="http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.1.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/core http://www.openspaces.org/schema/9.1/core/openspaces-core.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/events http://www.openspaces.org/schema/9.1/events/openspaces-events.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/remoting http://www.openspaces.org/schema/9.1/remoting/openspaces-remoting.xsd
http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla http://www.openspaces.org/schema/sla/9.1/openspaces-sla.xsd">
<bean id="propertiesConfigurer" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<list>
<value>classpath:kafka.properties</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="kafkaSpaceSynchronizationEndpoint" class="com.epam.openspaces.persistency.kafka.KafkaSpaceSynchronizationEndpointFactoryBean">
<property name="producerProperties">
<props>
<!-- Kafka producer properties. Consult Kafka documentation for a list of available properties -->
<prop key="metadata.broker.list">${metadata.broker.list}</prop>
<prop key="request.required.acks">${request.required.acks}</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
<!--
The mirror space. Uses the Kafka external data source. Persists changes done on the Space that
connects to this mirror space into the Kafka.
-->
<os-core:mirror id="mirror" url="/./mirror-service" space-sync-endpoint="kafkaSpaceSynchronizationEndpoint" operation-grouping="group-by-replication-bulk">
<os-core:source-space name="space" partitions="2" backups="1"/>
</os-core:mirror>
</beans>
For more information on the Mirror service see asynchronous persistence
Producer Properties
Please consult the Kafka documentation for the full list of available producer properties. The default properties applied to Kafka producer are the following:
| Property | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| key.serializer.class | com.epam.openspaces.persistency.kafka. protocol.impl.serializer.KafkaMessageKeyEncoder |
Message key serializer of default Gigaspace-Kafka protocol |
| serializer.class | com.epam.openspaces.persistency.kafka. protocol.impl.serializer.KafkaMessageEncoder |
Message serializer of default Gigaspace-Kafka protocol |
You can override the default properties if there is a need to customize GigaSpace-Kafka protocol. See Customization section below for details.
Space class
In order to associate a Kafka topic with the domain model class, the class needs to be annotated with the @KafkaTopic annotation and declared as Serializable. Here is an example.
@KafkaTopic("user_activity")
@SpaceClass
public class UserActivity implements Serializable {
...
}
Space Documents
To configure a Kafka topic for a SpaceDocuments or Extended SpaceDocument, the property KafkaPersistenceConstants.SPACE_DOCUMENT_KAFKA_TOPIC_PROPERTY_NAME should be added to the SpaceDocument. Here is an example.
public class Product extends SpaceDocument {
public Product() {
super("Product");
super.setProperty(SPACE_DOCUMENT_KAFKA_TOPIC_PROPERTY_NAME, "product");
}
You can also configure the name of the property that defines the Kafka topic for SpaceDocuments. Set spaceDocumentKafkaTopicName to the required value as shown below.
<bean id="kafkaSpaceSynchronizationEndpoint" class="com.epam.openspaces.persistency.kafka.KafkaSpaceSynchrspaceDocumentKafkaTopicNameonizationEndpointFactoryBean">
...
<property name="spaceDocumentKafkaTopicName" value="topic_name" />
</bean>
Kafka Consumers
The Kafka persistence library provides a wrapper around the native Kafka Consumer API for the GigaSpace-Kafka protocol serialization. Please see com.epam.openspaces.persistency.kafka.consumer.KafkaConsumer, for example of how to use it under <project_root>/example module.
Customization
- Kafka persistence was designed to be extensible and customizable.
- If you need to create a custom protocol between a GigaSpaces product and Kafka, provide an implementation of
AbstractKafkaMessage,AbstractKafkaMessageKey, andAbstractKafkaMessageFactory. - If you would like to customize how Space operations are sent to Kafka or how the Kafka topic is chosen for a given entity, provide an implementation of
AbstractKafkaSpaceSynchronizationEndpoint'. - If you want to create a custom serializer, look at
KafkaMessageDecoderandKafkaMessageKeyDecoder. - The Kafka Producer client (which is used under the hood) can be configured with a number of settings; see the Kafka documentation.
