Data Grid with Large Backend Database Support
| Author | XAP Version | Last Updated | Reference | Download |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shay Hassidim | 8.0 | Jan 2011 |
Overview
When having an application using a very large backend database leveraging the IMDG, caching a subset of the application data, while running on-going data eviction policy with read-through policy (i.e. LRU cache policy mode with an External-Data-Source used), the main requirement is to access the database in the most optimal manner when performing queries against the IMDG.
When using readById or readByIds operations looking for a single specific object(s), that cannot be found within the IMDG (a cache miss), the database access is very minimal. Only one raw is retrieved from the database per object lookup activity via the space External Data Source (EDS) implementation.
But when performing queries, using readMultiple with a template or SQLQuery filter, that return a result set that may involve relatively large amount of objects, with an IMDG running in LRU cache policy mode, the probability accessing the database retrieving large amount of data is very high:
- When using
readMultiplehavingInteger.MAX_VALUEas themax_objectsparameter, every partition will access the database (parallel database access). This may overload the database. - When using
readMultiplehavingmax_objects<Integer.MAX_VALUEthe database might be accessed even if there are enough objects matching the query criteria across all the space partitions. - When loading data from database data eviction process may be triggered. This may impact the performance.
- Database access involves reading objects that will not be loaded into the space (non-matching routing value).
Solution
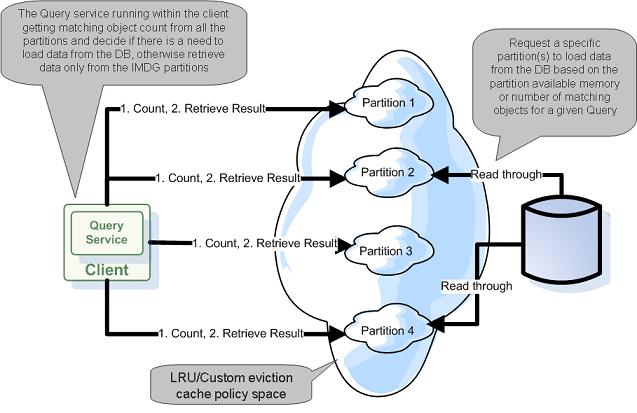
The main motivation with the solution proposed below, is to have better control when a space partition is accessing the database. The space is inspected prior retrieving the data leveraging the ability to count matching objects to a given query very fast (via the in-memory indexes the space maintains). If there is an adequate amount of matching objects, the client will access the relevant space partition(s) and retrieve the data from the space without accessing the database.
Here is the full query execution strategy:
- Check matching object count per partition for a given query.
If there are enough objects within the clustered space:
- If one partition has sufficient amount of objects use it and retrieve objects only from this partition
- If there are multiple partitions with sufficient amount of objects:
- Retrieve in parallel data from the partitions which have enough objects (from the ones with the highest amount of matching objects first).
- Max objects parameter used to query the partition will match the object count to avoid database access.
If there are no enough objects within the clustered space:
- Load data in order - first into the partition with the highest amount of free memory.
- Optional - check with other partitions if they access the database to avoid concurrent database access.
Data Eviction Options
Evicting data from the space can be done using the following options:
- LRU Cache policy - The simplest way to evict data based on available memory. Built-in option.
- Lease - Space objects expire based on TTL specified once the object is written into the space.
- Custom eviction implementation: – Using a Polling Container query the data frequently. – Using the JVM Memory Notification API.
See the Custom Eviction section for details.
Example
With the attached example the clustered space has 600 objects in memory:
- 100 object loaded into partition 1.
- 200 object loaded into partition 2.
- 300 object loaded into partition 3.
The clustered space is using a dummy External Data Source. It does not leverage any database. It prints a message when the space needs to access the database to retrieve data.
The client performs 3 types of queries:
- Query for 50 matching objects - This will return objects from a single partition only without accessing the database.
- Query for 500 matching objects - This will return objects from multiple partitions without accessing the database.
- Query for 700 matching objects - Load data from the database and return objects from all partitions.
Running the Example
To run the example you should first run the IMDG and later run the client. The example below explains how to run these within the IDE, but you can also modify these to run as a PU and deploy these into the GigaSpaces runtime environment.
Running the IMDG
The MyEDS class main method will start IMDG with 3 nodes. Once the IMDG will be started, each partition will load the dummy data.
Running the Client
The Client class main method will start a client that will perform the above queries.
