The Service Grid
The basic unit of deployment in the GigaSpaces XAP platform is the Processing Unit.
Once packaged, a processing unit is deployed onto the GigaSpaces runtime environment, which is called the Service Grid. It is responsible for materializing the processing unit’s configuration, provisioning its instances to the runtime infrastructure and making sure they continue to run properly over time.
When developing your processing unit, you can run and debug the processing unit within your IDE. You will typically deploy it to the GigaSpaces runtime environment when it’s ready for production or when you want to run it in the real-life runtime environment
Architecture
The service grid is composed of a number of components:
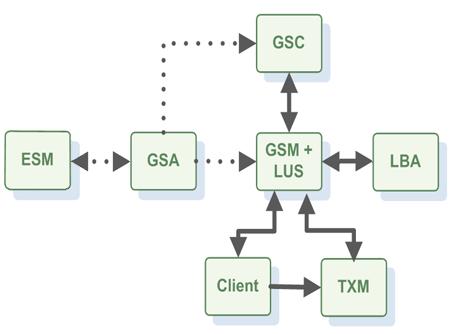
Core Components
A processing unit can be deployed to the Service Grid using one of GigaSpaces deployment tools (UI, CLI, API), which uploads it to the GSM Grid Service Manager, the component which manages the deployment and life cycle of the processing unit). The GSM analyzes the deployment descriptor and determines how many instances of the processing unit should be created, and which containers should run them. It then ships the processing unit code to the running GSC’s Grid Service Container and instructs them to instantiate the processing unit instances. The GSC provides an isolated runtime for the processing unit instance, and exposes its state to the GSM for monitoring. This phase in the deployment process is called provisioning.
Once provisioned, the GSM continuously monitors the processing unit instances to determine if they’re functioning properly or not. When a certain instance fails, the GSM identifies that and re-provisions the failed instance on to another GSC, thus enforcing the processing unit’s SLA.
In order to discover one another in the network, the GSCs and GSMs use a Lookup Service, also called LUS. Each GSM and GSC registers itself in the LUS, and monitors the LUS to discover other GSM and GSC instances.
Finally, the GSA Grid Service Agent component is used to start and manage the other components of the Service Grid (i.e. GSC, GSM, LUS). Typically, the GSA is started with the hosting machine’s startup. Using the agent, you can bootstrap the entire cluster very easily, and start and stop additional GSCs, GSMs and lookup services at will.
All of the above components are fully manageable from the GigaSpaces management interfaces such as the UI, CLI and Admin API.
Optional Components
The Elastic Service Manager (ESM) manages the Elastic Processing Unit together with the GSM.
The Apache Load Balancer Agent is used when deploying web applications.
The Transaction Manager (TXM) is an optional component. When executing transactions that spans multiple space partitions you should use the Jini Transaction Manager or the Distributed Transaction Manager. See the Transaction Management section for details.
