Security
This section provides an understanding of GigaSpaces Security features, where they fit in the GigaSpaces architecture, which components can be secured, and how to configure and customize the security depending on your application security requirements. GigaSpaces Security provides comprehensive support for securing your data, services, or both. GigaSpaces provides a set of authorities granting privileged access to data, and for performing operations on services.
Security Implementations
GigaSpaces comes with an Admin API that can be used for administration and monitoring. Additionally, the following interfaces can also be used:
-
GigaSpaces Management Center
-
Command Line Interface
-
Web Management Console
The administration and monitoring tools interact with the application layers as follows.
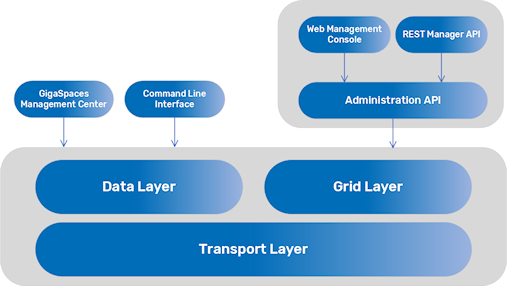
Refer to Administration Tools for details about the configuration options.
Securable Layers
GigaSpaces security can be applied in three separate layers. You can enable security for any of the layers individually, or you can enable all of them for maximum security.
-
The data layer - You can declare a secured Space
 Where GigaSpaces data is stored. It is the logical cache that holds data objects in memory and might also hold them in layered in tiering. Data is hosted from multiple SoRs, consolidated as a unified data model. or Processing Unit
Where GigaSpaces data is stored. It is the logical cache that holds data objects in memory and might also hold them in layered in tiering. Data is hosted from multiple SoRs, consolidated as a unified data model. or Processing Unit This is the unit of packaging and deployment in the GigaSpaces Data Grid, and is essentially the main GigaSpaces service. The Processing Unit (PU) itself is typically deployed onto the Service Grid. When a Processing Unit is deployed, a Processing Unit instance is the actual runtime entity..
This is the unit of packaging and deployment in the GigaSpaces Data Grid, and is essentially the main GigaSpaces service. The Processing Unit (PU) itself is typically deployed onto the Service Grid. When a Processing Unit is deployed, a Processing Unit instance is the actual runtime entity.. -
The grid layer - You can declare the data grid as secured. Includes the grid components (GSA
 Grid Service Agent.
This is a process manager that can spawn and manage Service Grid processes (Operating System level processes) such as The Grid Service Manager, The Grid Service Container, and The Lookup Service. Typically, the GSA is started with the hosting machine's startup. Using the agent, you can bootstrap the entire cluster very easily, and start and stop additional GSCs, GSMs and lookup services at will., GSM
Grid Service Agent.
This is a process manager that can spawn and manage Service Grid processes (Operating System level processes) such as The Grid Service Manager, The Grid Service Container, and The Lookup Service. Typically, the GSA is started with the hosting machine's startup. Using the agent, you can bootstrap the entire cluster very easily, and start and stop additional GSCs, GSMs and lookup services at will., GSM Grid Service Manager.
This is is a service grid component that manages a set of Grid Service Containers (GSCs). A GSM has an API for deploying/undeploying Processing Units. When a GSM is instructed to deploy a Processing Unit, it finds an appropriate, available GSC and tells that GSC to run an instance of that Processing Unit. It then continuously monitors that Processing Unit instance to verify that it is alive, and that the SLA is not breached., GSC
Grid Service Manager.
This is is a service grid component that manages a set of Grid Service Containers (GSCs). A GSM has an API for deploying/undeploying Processing Units. When a GSM is instructed to deploy a Processing Unit, it finds an appropriate, available GSC and tells that GSC to run an instance of that Processing Unit. It then continuously monitors that Processing Unit instance to verify that it is alive, and that the SLA is not breached., GSC Grid Service Container.
This provides an isolated runtime for one (or more) processing unit (PU) instance and exposes its state to the GSM., GigaSpaces Manager).
Grid Service Container.
This provides an isolated runtime for one (or more) processing unit (PU) instance and exposes its state to the GSM., GigaSpaces Manager). -
The transport layer - Provides a generic network filter with SSL support.
Configuring Security
Security is configured via a property file that includes required and custom properties. For more information, refer to the following parts of the Security section in this Administration guide:
-
Space and Processing Unit - Includes configuration options for the properties file.
-
Grid components - Includes configuration options for the grid components.
-
Web Management Console - Includes configurations for authenticating with secure data grid components.
-
REST Manager API - Includes security and SSL configurations for secured RESTful API
 REpresentational State Transfer. Application Programming Interface
An API, or application programming interface, is a set of rules that define how applications or devices can connect to and communicate with each other. A REST API is an API that conforms to the design principles of the REST, or representational state transfer architectural style. support.
REpresentational State Transfer. Application Programming Interface
An API, or application programming interface, is a set of rules that define how applications or devices can connect to and communicate with each other. A REST API is an API that conforms to the design principles of the REST, or representational state transfer architectural style. support.
When no property file is configured, there is a fallback implementation mainly used for testing or to get you started. This implementation stores the user credentials in a local file and can be used to demonstrate that security has been applied.
Refer to the following sections for more information about the GigaSpaces security implementations:
-
To read more about the GigaSpaces file-based configuration options, refer to Default File-Based Security.
-
To write your own implementation, refer to Reference Implementation, which uses MongoDB.
-
For other custom security implementations, refer to Custom Security. One such custom security implementation is the Spring Security Bridge.
-
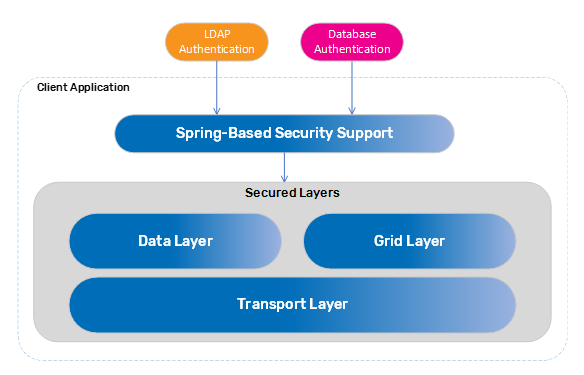
For LDAP
 Lightweight Directory Access Protocol.
An open, vendor-neutral, industry standard application protocol for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services over an Internet Protocol (IP) network. implementation, refer to LDAP Authentication.
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol.
An open, vendor-neutral, industry standard application protocol for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services over an Internet Protocol (IP) network. implementation, refer to LDAP Authentication. -
For SSO
 Single sign-on (SSO) is an authentication scheme that allows a user to log in with a single ID to any of several related, yet independent, software systems. openID implementation, refer to Single Sign-On for Service Grid.
Single sign-on (SSO) is an authentication scheme that allows a user to log in with a single ID to any of several related, yet independent, software systems. openID implementation, refer to Single Sign-On for Service Grid. -
File Based security implementation, refer to File-Based Security.
Dependencies
In order to use the security implementation, include the $GS_HOME/lib/optional/security/xap-security.jar file on your classpath or use Maven dependencies:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.gigaspaces</groupId>
<artifactId>xap-security</artifactId>
<version>17.0-m1</version>
</dependency>
For more information on dependencies, refer to Maven Artifacts.
Hello World Example
The Hello World example provides a step-by-step guide to deploying a Processing Unit with a secured Space, accessing it from a remote proxy, and declaring principals using the administration tools.
Spring Security
Spring Security is one of the most mature and widely used Spring projects. GigaSpaces provides a Spring-based security bridge to enable an extensible implementation to LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) or database authentication.
For more information, refer to Spring Security Bridge.
 In-Memory Data Grid - achieve unparalleled speed, persistence, and accuracy.
In-Memory Data Grid - achieve unparalleled speed, persistence, and accuracy.