Smart DIH - Application Life Cycle & Performance
Application Life Cycle
The following diagram represents the Smart DIH![]() Smart DIH allows enterprises to develop and deploy digital services in an agile manner, without disturbing core business applications. This is achieved by creating an event-driven, highly performing, efficient and available replica of the data from multiple systems and applications, platform life Cycle:
Smart DIH allows enterprises to develop and deploy digital services in an agile manner, without disturbing core business applications. This is achieved by creating an event-driven, highly performing, efficient and available replica of the data from multiple systems and applications, platform life Cycle:
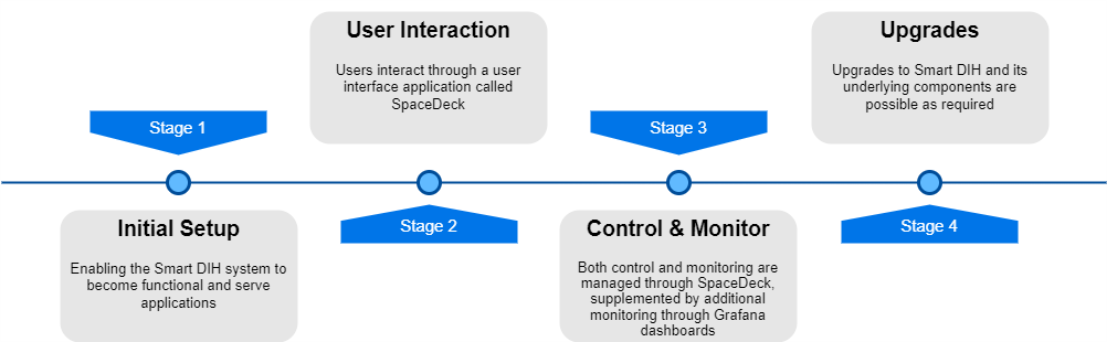
Initial Setup
The following steps are required in order to install the Smart DIH![]() Digital Integration Hub.
An application architecture that decouples digital applications from the systems of record, and aggregates operational data into a low-latency data fabric. system
Digital Integration Hub.
An application architecture that decouples digital applications from the systems of record, and aggregates operational data into a low-latency data fabric. system
-
Hardware and Network Setup - Either on-premise or cloud
-
Network Configuration - Virtual Network, Routers, VPN
-
Compute Resources - including cpu/memory, Disk
-
Security Setup - Firewalls, Gateways, access rights
-
-
SOR
 System of Record. This is an information storage and retrieval system that stores valuable data on an organizational system or process. This record can contain multiple data sources and exist at a single location or multiple locations with remote access. Agent Installation - File and database configuration
System of Record. This is an information storage and retrieval system that stores valuable data on an organizational system or process. This record can contain multiple data sources and exist at a single location or multiple locations with remote access. Agent Installation - File and database configuration -
Kubernetes
 An open-source container orchestration system for automating software deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. and Application Installation - This is where the controller, data-grid and streaming (Kafka
An open-source container orchestration system for automating software deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. and Application Installation - This is where the controller, data-grid and streaming (Kafka Apache Kafka is a distributed event store and stream-processing platform. Apache Kafka is a distributed publish-subscribe messaging system.
A message is any kind of information that is sent from a producer (application that sends the messages) to a consumer (application that receives the messages).
Producers write their messages or data to Kafka topics. These topics are divided into partitions that function like logs.
Each message is written to a partition and has a unique offset, or identifier. Consumers can specify a particular offset point where they can begin to read messages.) are provisioned
Apache Kafka is a distributed event store and stream-processing platform. Apache Kafka is a distributed publish-subscribe messaging system.
A message is any kind of information that is sent from a producer (application that sends the messages) to a consumer (application that receives the messages).
Producers write their messages or data to Kafka topics. These topics are divided into partitions that function like logs.
Each message is written to a partition and has a unique offset, or identifier. Consumers can specify a particular offset point where they can begin to read messages.) are provisionedFor installation instructions refer to our Smart DIH Kubernetes Installation Guide
-
-
Configure the IDP
 An identity provider, or IDP, stores and manages users' digital identities. IDP and SSO can work together to authenticate users., Roles and Service Accounts (performed by the Admin)
An identity provider, or IDP, stores and manages users' digital identities. IDP and SSO can work together to authenticate users., Roles and Service Accounts (performed by the Admin) -
Setup Data Sources - point to the SOR agent and setup connection configuration
-
Set up Spaces - define the data-grid spaces for holding the data
-
Set up Pipelines - define the data that goes into the data-grid
-
Set up Services - define the micro-service/s that consume the data from the data-grid (either by SQL or Code) and the APIs
Refer to our SpaceDeck User Guide for comprehensive information.
-
Control, Logging & Monitoring
Control of Smart DIH is managed through SpaceDeck. Platform logs can also be accessed via SpaceDeck. For more advanced logging queries and ELK stack can be attached to the pods (components) logs. And example of such a service is Amazon OpenSearch.
Monitoring can be performed by both utilizing the tools that integrated within SpaceDeck and using dashboards in Grafana![]() Grafana is a multi-platform open source analytics and interactive visualization web application. It provides charts, graphs, and alerts for the web when connected to supported data sources.. Upon startup a few dashboards are uploaded to Grafana including data-grid metrics.
Grafana is a multi-platform open source analytics and interactive visualization web application. It provides charts, graphs, and alerts for the web when connected to supported data sources.. Upon startup a few dashboards are uploaded to Grafana including data-grid metrics.
Refer to our SpaceDeck User Guide for comprehensive information.
Updates & Upgrades
The user can update the Smart DIH platform in the following ways:
-
Add Spaces
-
Update/Add pipelines
-
Update/Add services
-
Upgrade Kubernetes
-
Upgrade the platform
Refer to our SpaceDeck User Guide and Smart DIH Kubernetes Installation Guide for additional information.
Reliability
Many of the Smart DIH components contain the appropriate redundancy and are spread across multiple availability zones. The following components maintain this ability:
-
Data-Grid - Special primary/backup technology maintains high availability of the cached data. The Kubernetes nodes are setup with anti-affinity
 This describes the relationship between VMs and hosts or when related to Kubernetes between pods. Anti-Affinity will keep VM and hosts separated and using Kubernetes an anti-affinity rule tells the scheduler not to place the new pod on the same node if the label on the new pod matches the label on another pod. In this case, anti-affinity allows you to keep pods away from each other. It also allows you to prevent pods of a particular service from scheduling on the same nodes as pods of another service that are known to interfere with the performance of the pods of the first service. mode for the primary and backup copies.
This describes the relationship between VMs and hosts or when related to Kubernetes between pods. Anti-Affinity will keep VM and hosts separated and using Kubernetes an anti-affinity rule tells the scheduler not to place the new pod on the same node if the label on the new pod matches the label on another pod. In this case, anti-affinity allows you to keep pods away from each other. It also allows you to prevent pods of a particular service from scheduling on the same nodes as pods of another service that are known to interfere with the performance of the pods of the first service. mode for the primary and backup copies. -
Zookeeper
 Apache Zookeeper. An open-source server for highly reliable distributed coordination of cloud applications. It provides a centralized service for providing configuration information, naming, synchronization and group services over large clusters in distributed systems. The goal is to make these systems easier to manage with improved, more reliable propagation of changes. - Zookeeper that holds some configurations needs a quorum of instances that span over multiple zones.
Apache Zookeeper. An open-source server for highly reliable distributed coordination of cloud applications. It provides a centralized service for providing configuration information, naming, synchronization and group services over large clusters in distributed systems. The goal is to make these systems easier to manage with improved, more reliable propagation of changes. - Zookeeper that holds some configurations needs a quorum of instances that span over multiple zones. -
Kafka - Kafka is configured by default with a replication factor higher than one. So there are always additional copies of the data in multiple zones.
-
Flink
 Apache Flink is an open-source, unified stream-processing and batch-processing framework developed by the Apache Software Foundation. The core of Apache Flink is a distributed streaming data-flow engine written in Java and Scala. Flink executes arbitrary dataflow programs in a data-parallel and pipelined manner. (in the transformation layer)- Launching a few instances of the task manager ensures that tasks can be run continuously.
Apache Flink is an open-source, unified stream-processing and batch-processing framework developed by the Apache Software Foundation. The core of Apache Flink is a distributed streaming data-flow engine written in Java and Scala. Flink executes arbitrary dataflow programs in a data-parallel and pipelined manner. (in the transformation layer)- Launching a few instances of the task manager ensures that tasks can be run continuously.
Performance
GigaSpaces IMDG![]() In-Memory Data Grid.
A simple to deploy, highly distributed, and cost-effective solution for accelerating and scaling services and applications. It is a high throughput and low latency data fabric that minimizes access to high-latency, hard-disk-drive-based or solid-state-drive-based data storage. The application and the data co-locate in the same memory space, reducing data movement over the network and providing both data and application scalability. (in-memory data grid) is a technology that manages data queries from the data-grid. Read and writes queries are executed in a few milliseconds (depending on the complexity). Due to this, the services accessing the data-grid can benefit from its high performance.
In-Memory Data Grid.
A simple to deploy, highly distributed, and cost-effective solution for accelerating and scaling services and applications. It is a high throughput and low latency data fabric that minimizes access to high-latency, hard-disk-drive-based or solid-state-drive-based data storage. The application and the data co-locate in the same memory space, reducing data movement over the network and providing both data and application scalability. (in-memory data grid) is a technology that manages data queries from the data-grid. Read and writes queries are executed in a few milliseconds (depending on the complexity). Due to this, the services accessing the data-grid can benefit from its high performance.
For information about Smart DIH refer back to the Smart DIH contents page and choose another topic.
 In-Memory Data Grid - achieve unparalleled speed, persistence, and accuracy.
In-Memory Data Grid - achieve unparalleled speed, persistence, and accuracy.