Unicast Discovery
There are many cases when you need to use a unicast-based services discovery. For example if you want to use unicast with multicast (using Jini Groups), which is the default, or when you do not have multicast enabled, or you prefer not to use multicast.
In such cases, the Jini lookup discovery enables the user to discover services (spaces, GSC![]() Grid Service Container.
This provides an isolated runtime for one (or more) processing unit (PU) instance and exposes its state to the GSM., GSM
Grid Service Container.
This provides an isolated runtime for one (or more) processing unit (PU) instance and exposes its state to the GSM., GSM![]() Grid Service Manager.
This is is a service grid component that manages a set of Grid Service Containers (GSCs). A GSM has an API for deploying/undeploying Processing Units. When a GSM is instructed to deploy a Processing Unit, it finds an appropriate, available GSC and tells that GSC to run an instance of that Processing Unit. It then continuously monitors that Processing Unit instance to verify that it is alive, and that the SLA is not breached., processing units
Grid Service Manager.
This is is a service grid component that manages a set of Grid Service Containers (GSCs). A GSM has an API for deploying/undeploying Processing Units. When a GSM is instructed to deploy a Processing Unit, it finds an appropriate, available GSC and tells that GSC to run an instance of that Processing Unit. It then continuously monitors that Processing Unit instance to verify that it is alive, and that the SLA is not breached., processing units![]() This is the unit of packaging and deployment in the GigaSpaces Data Grid, and is essentially the main GigaSpaces service. The Processing Unit (PU) itself is typically deployed onto the Service Grid. When a Processing Unit is deployed, a Processing Unit instance is the actual runtime entity. etc.) using unicast protocol.
This is the unit of packaging and deployment in the GigaSpaces Data Grid, and is essentially the main GigaSpaces service. The Processing Unit (PU) itself is typically deployed onto the Service Grid. When a Processing Unit is deployed, a Processing Unit instance is the actual runtime entity. etc.) using unicast protocol.
Please refer to the Lookup Service Configuration or the Networking How Tos section for more details.
Discovery Order
When using the unicast lookup service discovery option, you may specify multiple locators. This means, a client that is looking to bootstrap its space proxy, may search for the proxy location within one or more lookup services that may be running on specific hosts.
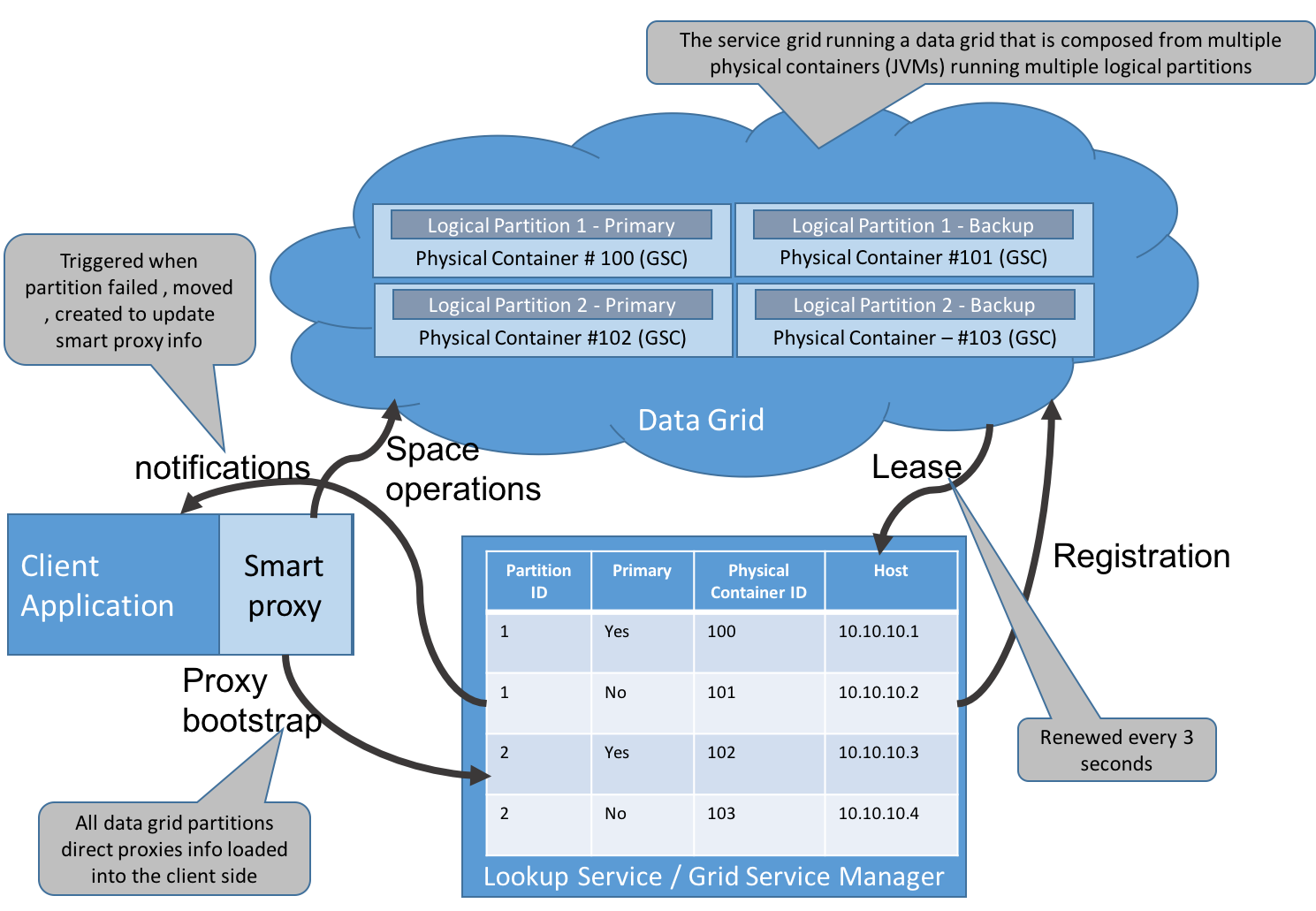
When multiple locators are specified, a parallel search will be conducted across all the given host names (or IPs) for a matching space name. Once found, the proxy and its cluster information (primaries , backups) will be populated. This means, the search may not have a pre-defined deterministic order, as a different lookup service may be used every time. When having a large number of clients using multiple locators (large compute grid environment with many workers, a large web application with many instances), the space proxy bootstrap will be distributed across all discovered lookup services. This allows the system to load-balance the overall lookup activity across all running lookup services.
You will have to make sure the GigaSpaces agent (GSA![]() Grid Service Agent.
This is a process manager that can spawn and manage Service Grid processes (Operating System level processes) such as The Grid Service Manager, The Grid Service Container, and The Lookup Service. Typically, the GSA is started with the hosting machine's startup. Using the agent, you can bootstrap the entire cluster very easily, and start and stop additional GSCs, GSMs and lookup services at will.) and its managed processes, specifically the GCSs , have the same locators configuration (GS_LOOKUP_LOCATORS environment variable) as the client, to allow these to register themselves within all running lookup services.
Grid Service Agent.
This is a process manager that can spawn and manage Service Grid processes (Operating System level processes) such as The Grid Service Manager, The Grid Service Container, and The Lookup Service. Typically, the GSA is started with the hosting machine's startup. Using the agent, you can bootstrap the entire cluster very easily, and start and stop additional GSCs, GSMs and lookup services at will.) and its managed processes, specifically the GCSs , have the same locators configuration (GS_LOOKUP_LOCATORS environment variable) as the client, to allow these to register themselves within all running lookup services.
If the first lookup service discovered dose not have a matching lookup entry that matches the desired space name, the next discovered lookup is used.
For example – with the following code examples the GigaSpaces proxy or the Admin that may hold many GigaSpaces proxies , a parallel lookup discovery will be conducted across Host1 and Host2 specified as the locators settings. The mySpace space will be bootstrapped using one of the lookup services running on Host1 and Host2:
GigaSpace gigaSpace = new GigaSpaceConfigurer(new SpaceProxyConfigurer("mySpace").lookupLocators("Host1, Host2")).gigaSpace();
GigaSpace gigaSpace = new GigaSpaceConfigurer(new UrlSpaceConfigurer("jini://*/*/mySpace?locators=Host1,Host2")).gigaSpace();
Admin admin = new AdminFactory().addLocators(“Host1”, “Host2”).createAdmin();
Configuring the lookup locators property
Services will use the locators property to locate the Jini Lookup Service to lookup other services registered on it. The locators property is configured using the GSLOOKUP_LOCATORS environment variable or the -Dcom.gs.jini_lus.locators system property.
By default it is left blank. It accepts a comma separated list of host:port. This list should include the hosts (and ports) where the Jini Lookup Service (or GSM) is running. The default port is 4174.
For example, considering the GSM(+LUS![]() Lookup Service.
This service provides a mechanism for services to discover each other. Each service can query the lookup service for other services, and register itself in the lookup service so other services may find it.) is running on linux-lab1:4174 and linux-lab2:4174 machines:
Lookup Service.
This service provides a mechanism for services to discover each other. Each service can query the lookup service for other services, and register itself in the lookup service so other services may find it.) is running on linux-lab1:4174 and linux-lab2:4174 machines:
-Dcom.gs.jini_lus.locators=linux-lab1:4174,linux-lab2:4174
This will influence the GS_LOOKUP_LOCATORS environment variable in setenv script, which you may also modify directly.
Locating services using locators
Once the services are started with the locators settings, then any client should be able to find a service, using unicast discovery.
To lookup a Space![]() Where GigaSpaces data is stored. It is the logical cache that holds data objects in memory and might also hold them in layered in tiering. Data is hosted from multiple SoRs, consolidated as a unified data model. service using the unicast protocol, add the locators SpaceURL attribute to the space URL string.
Where GigaSpaces data is stored. It is the logical cache that holds data objects in memory and might also hold them in layered in tiering. Data is hosted from multiple SoRs, consolidated as a unified data model. service using the unicast protocol, add the locators SpaceURL attribute to the space URL string.
For both unicast AND multicast discovery, use:
jini://*/./mySpace?locators=linux-lab1:4174,linux-lab2:4174&groups=gigaspaces-16.4-XAPPremium-ga
When the locators attribute is used in conjunction with the jini://* prefix and groups attribute, the discovery will be unicast AND multicast.
Unicast discovery only
If you want unicast only, you should disable multicast altogether. For unicast discovery only, you should disable multicast using -Dcom.gs.multicast.enabled=false system property, and use:
jini://linux-lab1:4174,linux-lab2:4174/./mySpace?locators=linux-lab1:4174,linux-lab2:4174
For troubleshooting purposes you should verify that the services (spaces, GSC, GSM, processing units etc.) print correct settings for the locators while they initialize. You can turn on the relevant logging if required.
Unicast Port
To change the lookup service listening port use the com.sun.jini.reggie.initialUnicastDiscoveryPort system property. The default value is the one assigned to the com.gs.multicast.discoveryPort.
Set the GS_LOOKUP_LOCATORS system property in $GS_HOME\bin\setenv.bat/sh to match the port number you defined (in this case, host:1234). That is required if you specify an explicit unicast/locators port, otherwise the service will use the default port if not set explicitly.
For more information, see the description of the com.gs.multicast.discoveryPort system property.
Discovery Intervals
When a lookup service fails and is brought back online, a client (such as a GSC, space or a client with a space proxy) needs to re-discover and federate again. In order to make that happen, Jini unicast discovery must retry connections to the remote lookup service. The default unicast retry protocol provides a graduating approach, increasing the amount of time to wait before the next discovery attempts are made - upon each invocation, eventually reaching a maximum time interval over which discovery is re-tried. In this way, the network is not flooded with unicast discovery requests referencing a lookup service that may not be available for quite some time (if ever). The default time to wait between unicast retry attempts (in milliseconds) are:
long[] sleepTime = {1000, 5000, 10000, 15000, 20000, 30000, 60000};
The retry logic only begins once the discovered lookup service is discarded. In the above configuration, the minimum retry interval is 1 second and the maximum is 1 minute. These settings are recommended for both short disconnections and recurring retry attempts when a lookup service is unreachable for a longer period.
To tune the unicast retry intervals, the com.gigaspaces.unicast.interval system property is used to control the behavior of this LookupLocatorDiscovery utility. A comma separated list of values defining the intervals to wait between subsequent retries. Values are declared in milliseconds.
Example:
-Dcom.gigaspaces.unicast.interval=5000
Will cause the LookupLocatorDiscovery utility to wait 5 seconds between retries
-Dcom.gigaspaces.unicast.interval=5000,10000
Will cause the LookupLocatorDiscovery utility to first wait 5 seconds, then 10 seconds between retries. This declaration provides a graduating approach (similar in approach to the default settings).
You will need to set this property to take affect for GSM and GSC startup. You should see a similar log message to "Set unicast interval to 5000".
 In-Memory Data Grid - achieve unparalleled speed, persistence, and accuracy.
In-Memory Data Grid - achieve unparalleled speed, persistence, and accuracy.