SpaceDeck – Administration
Access the Administration Screen
If a user role is defined as an Admin, the Administration screens can be accessed via the cog at the bottom left hand corner.
In order to create, delete or update Connection (Identify Provider) or Roles Management settings, the user should be assigned the appropriate role. These are specified below.
An explanation of all the available permissions can be found in the Security Overview page.
General Setup
Populate the Connection fields in order to configure SSO![]() Single sign-on (SSO) is an authentication scheme that allows a user to log in with a single ID to any of several related, yet independent, software systems. login using a predefined IDP
Single sign-on (SSO) is an authentication scheme that allows a user to log in with a single ID to any of several related, yet independent, software systems. login using a predefined IDP![]() An identity provider, or IDP, stores and manages users' digital identities. IDP and SSO can work together to authenticate users..
An identity provider, or IDP, stores and manages users' digital identities. IDP and SSO can work together to authenticate users..
For user management through the IDP, roles and groups are created and then certain roles can be assigned to the user, for example admin. Via SpaceDeck![]() GigaSpaces intuitive, streamlined user interface to set up, manage and control their environment. Using SpaceDeck, users can define the tools to bring legacy System of Record (SoR) databases into the in-memory data grid that is the core of the GigaSpaces system. roles are then created with the same name which was created in the IDP and permissions are then assigned accordingly for each role.
GigaSpaces intuitive, streamlined user interface to set up, manage and control their environment. Using SpaceDeck, users can define the tools to bring legacy System of Record (SoR) databases into the in-memory data grid that is the core of the GigaSpaces system. roles are then created with the same name which was created in the IDP and permissions are then assigned accordingly for each role.
In order to be able to configure the Connection (Identify Provider) fields the user has to be assigned the specific permission of Manager Identify Providers, otherwise an error 403 (Forbidden) response will be displayed.
An explanation of all the available roles and permissions can be found on the Security Overview page.
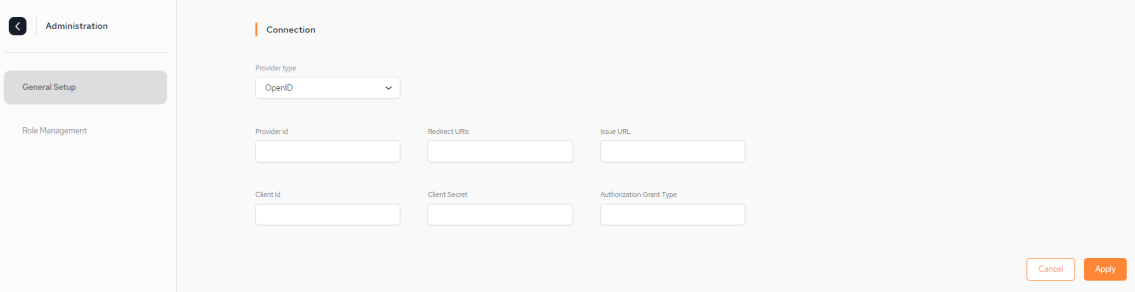
Connection Fields
-
Provider type – The protocol the IDP supports. Currently GigaSpaces supports using any IDP that supports OpenID Connect (OIDC
 OpenID Connect (OIDC) is an open authentication protocol that works on top of the OAuth 2.0 framework. Targeted toward consumers, OIDC allows individuals to use single sign-on (SSO) to access relying party sites using OpenID Providers (OPs), such as an email provider to authenticate their identities.).
OpenID Connect (OIDC) is an open authentication protocol that works on top of the OAuth 2.0 framework. Targeted toward consumers, OIDC allows individuals to use single sign-on (SSO) to access relying party sites using OpenID Providers (OPs), such as an email provider to authenticate their identities.). -
Provider id – This is a generic ID that will be used as a name for the auth-config creator.
-
Redirect URIs – Upon successful sign-in, this endpoint in our server will receive the data from the IDP.
-
Issue URL – URL of the IDP issuer. For example, Okta, JumpCloud, Azure Active Directory.
-
Client Id – Unlike the Provider ID, this ID serves as a unique identifier which the IDP generates to the user so they can identify with it,
-
Client Secret – This is a secret key that is used with the Client ID in order to improve security.
-
Authorization Grant Type – Each IDP has rules regarding how roles are grouped. These rules have an arbitrary name provided by the IDP. The roles user must use this name to create the roles.
Once the connection details are entered, click Apply.
Role Management
Each role that is configured will have certain privileges (permissions) assigned to it.
The roles should be configured by the company IT manager in the config map of the Kubernetes![]() An open-source container orchestration system for automating software deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. environment or through IDP setup.
An open-source container orchestration system for automating software deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. environment or through IDP setup.
Default Roles
If there is no configuration in the config map (this is not recommended), there is one default roles that is included with the installation which cannot be edited via SpaceDeck and this is ROLE_ADMIN.
To see which privileges (permissions) are applied to a role (in this case ROLE_ADMIN), click the role name:

From the IDP side the default role of ROLE_ADMIN will not be created automatically during launch. Therefore, the admin should manually create a group (role) in the IDP with the same name as the default role name in the config map.
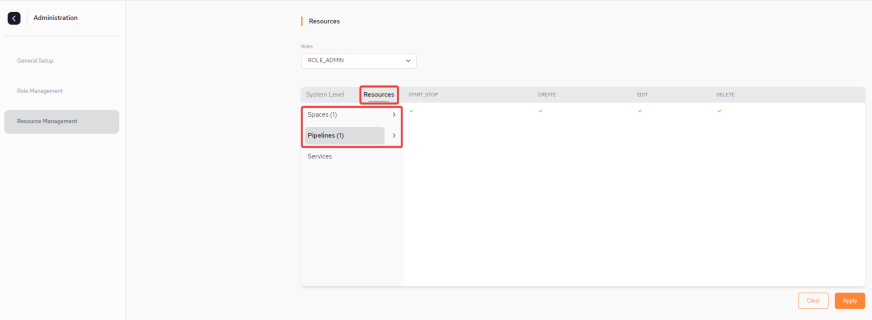
Below are two screen-shots showing the Resource Management menu which displays all the permissions applied for the default ROLE_ADMIN at Monitor System Level and at Resources Level. Note that at Resources level, permissions can be applied per Space![]() Where GigaSpaces data is stored. It is the logical cache that holds data objects in memory and might also hold them in layered in tiering. Data is hosted from multiple SoRs, consolidated as a unified data model. and Pipeline.
Where GigaSpaces data is stored. It is the logical cache that holds data objects in memory and might also hold them in layered in tiering. Data is hosted from multiple SoRs, consolidated as a unified data model. and Pipeline.
An explanation of all the available permissions for each level can be found n the Security Overview page.
System Level - Monitor with permissions for MONITOR_PU![]() This is the unit of packaging and deployment in the GigaSpaces Data Grid, and is essentially the main GigaSpaces service. The Processing Unit (PU) itself is typically deployed onto the Service Grid. When a Processing Unit is deployed, a Processing Unit instance is the actual runtime entity. and MONITOR_JVM
This is the unit of packaging and deployment in the GigaSpaces Data Grid, and is essentially the main GigaSpaces service. The Processing Unit (PU) itself is typically deployed onto the Service Grid. When a Processing Unit is deployed, a Processing Unit instance is the actual runtime entity. and MONITOR_JVM![]() Java Virtual Machine. A virtual machine that enables a computer to run Java programs as well as programs written in other languages that are also compiled to Java bytecode.:
Java Virtual Machine. A virtual machine that enables a computer to run Java programs as well as programs written in other languages that are also compiled to Java bytecode.:
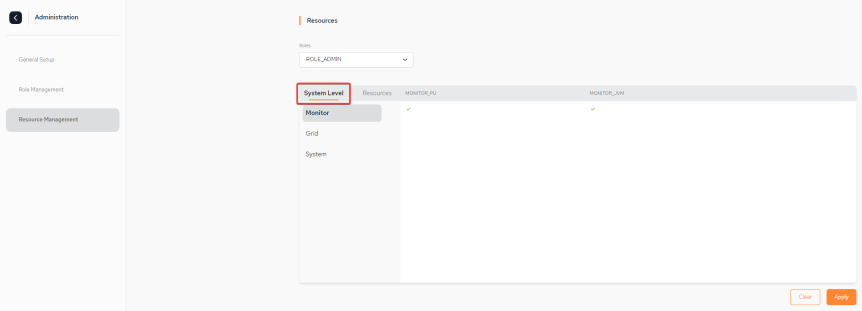
Resources Level - Pipeline with permissions for START_STOP, CREATE, EDIT and DELETE:
Creating a new Role
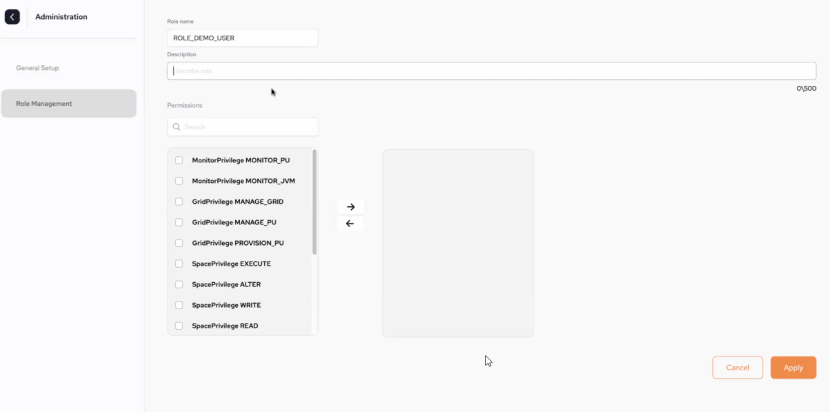
Create a new role by clicking New + to access the role setup page.
On the setup page:
-
Provide a name for the new role. In our example it is ROLE_DEMO_USER.
-
Provide a description of the role.
-
Select which permissions the role should have by selecting from the list and using the right-arrow to move the role into the list on the right.
-
An explanation of all the available permissions can be found on the Security Overview page.
-
Click Apply
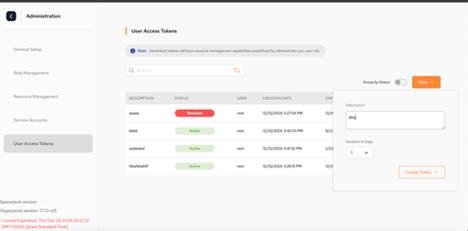
Access Tokens
The Access Tokens view allows you to manage user access tokens.
You can create new tokens, revoke active tokens, and delete expired tokens.
To create a new access token:
-
Click New. A dialog box appears.
-
Fill in a Description for the access token, and the Duration in Days for which the token should remain active.
-
Click Create Token.
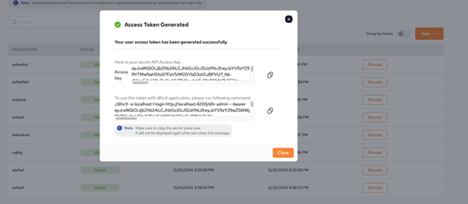
After the new token is created, a dialog box appears showing the secret API access key.
Additionally, the user is provided with a command to log in to the DIHCTL application using the new token.
The access key must be saved securely, as it will not be available again after the dialog box is closed.
 In-Memory Data Grid - achieve unparalleled speed, persistence, and accuracy.
In-Memory Data Grid - achieve unparalleled speed, persistence, and accuracy.