General Terms and Concepts
Basic Components
Space
|
|
The cache instance that holds data objects in memory and might also hold them in layered in tiering. |
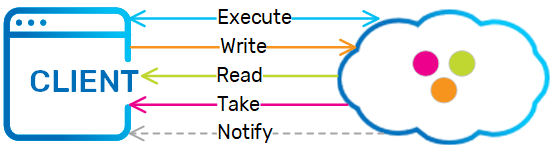
Execute, Read, Write, Take and Notify
|
|
A set of methods used to read, write, take, and register for notification on objects that are stored in the Space |
Service
Processing Unit (PU)
|
|
A combination of clients and/or an embedded Space instance. This is the fundamental unit of deployment in the data grid. The Processing Unit |
Processing Unit Configured with One or More Services
|
|
A deployable package containing one or more services. In the GigaSpaces context, it usually acts as a client that interacts with other Processing Units by utilizing the messaging capabilities of the Space. |
Processing Unit Configured with an Embedded Space and Embedded Services
|
|
A deployable, independent, scalable unit that is the building block of Space-Based Architecture. A client application (which can also be other Processing Units) write objects to the Space, and the Processing Unit that contains this Space consumes these objects or is notified about them and triggers related services. |
Data Grid
In-Memory Data Grid (IMDG)
A set of Space instances, typically running within their respective processing unit instances. The space instances are connected to each other to form a space cluster. The relations between the spaces define the data grid topology.
Data Grid Topologies
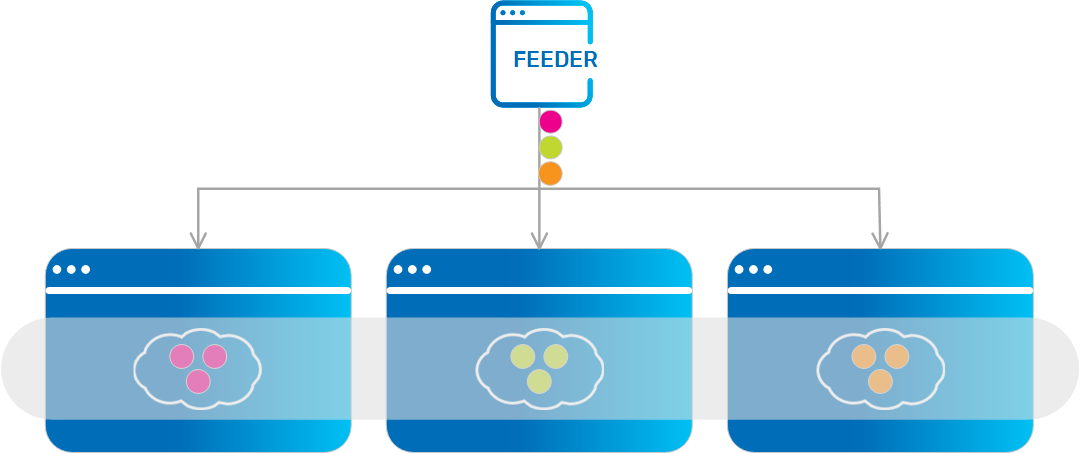
Partitioned Data Grid
|
|
Each partition holds a different subset of the objects. When the objects are written to this data grid, they are routed to the proper partition according to a predefined attribute in the object that acts as the routing |
Routing (refer to the data partitioning page)
|
|
The mechanism that is in charge of routing the objects into and out of the corresponding partitions. The routing is based on a designated attribute inside the objects that are written to the Space, called the Routing Index. |
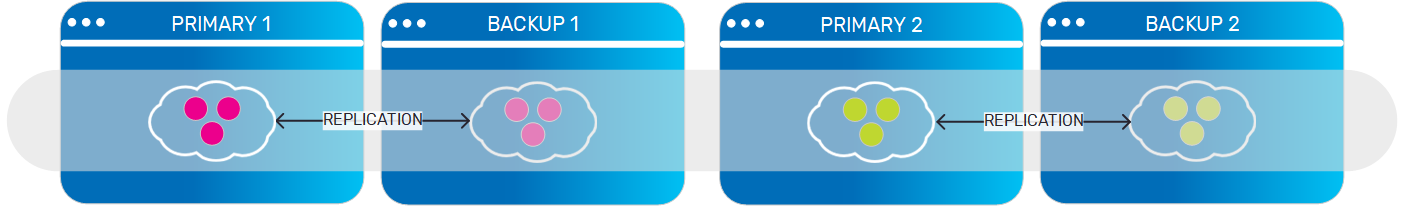
Partitioned Data Grid with High Availability
|
|
A partitioned data grid, with backup for each partition. Each data grid instance (partition) holds a different subset of the objects in the data grid, and replicates this subset to its backup instance. |
Runtime Components
Processing Unit Container
A container that hosts a Processing Unit. The Processing Unit can run only inside a hosting Processing Unit Container. In Service Grid this is referred to as the GSC![]() Grid Service Container.
This provides an isolated runtime for one (or more) processing unit (PU) instance and exposes its state to the GSM. (Grid Service Container) and in Kubernetes this is referred to as the Pod.
Grid Service Container.
This provides an isolated runtime for one (or more) processing unit (PU) instance and exposes its state to the GSM. (Grid Service Container) and in Kubernetes this is referred to as the Pod.
Types of Processing Unit Containers
Integrated Processing Unit Container
A container that runs the Processing Unit inside a development environment (e.g. IntelliJ IDEA, Eclipse).
Processing Unit Container (SLA-Driven Container)
When working with Service Grid orchestration![]() This is the automated configuration, management, and coordination of computer systems, applications, and services. Orchestration strings together multiple tasks in order to execute and easily manage a larger workflow or process. These processes can consist of multiple complex tasks that are automated and can involve multiple systems. Kubernetes, used by GigaSpaces, is a popular open source platform for container orchestration., the PU SLA is managed by the Service Grid. For more information: the-sla-overview.
This is the automated configuration, management, and coordination of computer systems, applications, and services. Orchestration strings together multiple tasks in order to execute and easily manage a larger workflow or process. These processes can consist of multiple complex tasks that are automated and can involve multiple systems. Kubernetes, used by GigaSpaces, is a popular open source platform for container orchestration., the PU SLA is managed by the Service Grid. For more information: the-sla-overview.
In the Kubernetes environment, client services SLA will be managed by Kubernetes. The PU SLA will be managed by the XAP![]() GigaSpaces eXtreme Application Platform.
Provides a powerful solution for data processing, launching, and running digital services manager.
GigaSpaces eXtreme Application Platform.
Provides a powerful solution for data processing, launching, and running digital services manager.
Service Grid
A built-in orchestration tool which contains a set of Grid Service Containers (GSCs) managed by a Grid Service Manager. The containers host various deployments of Processing Units and data grids.
Each container can be run on a separate physical machine. This orchestration is available for Smart Cache only. For Smart DIH![]() Digital Integration Hub.
An application architecture that decouples digital applications from the systems of record, and aggregates operational data into a low-latency data fabric., we recommend using our Kubernetes orchestration.
Digital Integration Hub.
An application architecture that decouples digital applications from the systems of record, and aggregates operational data into a low-latency data fabric., we recommend using our Kubernetes orchestration.
Grid Service Container (GSC)
A component that hosts Processing Unit instances. A machine can run one or more GSC processes. Each GSC communicates with a manager component (GSM![]() Grid Service Manager.
This is is a service grid component that manages a set of Grid Service Containers (GSCs). A GSM has an API for deploying/undeploying Processing Units. When a GSM is instructed to deploy a Processing Unit, it finds an appropriate, available GSC and tells that GSC to run an instance of that Processing Unit. It then continuously monitors that Processing Unit instance to verify that it is alive, and that the SLA is not breached. which is part of the GigaSpaces Manager). The GSC receives requests to start/stop a Processing Unit (PU) instance, and sends information about the machine that runs it (operating system, processor architecture, current memory and CPU stats), the software installed on it, and the status of Processing Unit instances currently running on it.
Grid Service Manager.
This is is a service grid component that manages a set of Grid Service Containers (GSCs). A GSM has an API for deploying/undeploying Processing Units. When a GSM is instructed to deploy a Processing Unit, it finds an appropriate, available GSC and tells that GSC to run an instance of that Processing Unit. It then continuously monitors that Processing Unit instance to verify that it is alive, and that the SLA is not breached. which is part of the GigaSpaces Manager). The GSC receives requests to start/stop a Processing Unit (PU) instance, and sends information about the machine that runs it (operating system, processor architecture, current memory and CPU stats), the software installed on it, and the status of Processing Unit instances currently running on it.
Grid Service Manager (GSM) - XAP Only
The GSM is a part of the GigaSpaces Manager that manages and monitors deployments of Processing Units (PUs).
 In-Memory Data Grid - achieve unparalleled speed, persistence, and accuracy.
In-Memory Data Grid - achieve unparalleled speed, persistence, and accuracy.