Filters
A Space Filter is a special hook point inside the engine that enables integration with external systems, or implementation of user defined logic. There are two ways to implement such a filter and integrate it with the space, both of which are covered in this page.
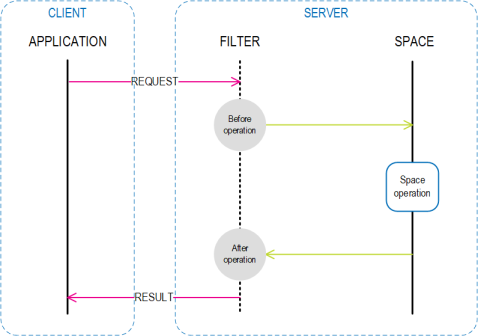
Integrating the Space Filter with a Space
A space filter is integrated into a space upon creation of that space.
Each space filter that integrates with a space, needs a SpaceFilterConfig instance that defines it.
A SpaceFilterConfig can be created in two ways, depending on the implementation of the filter itself.
Implementing the ISpaceFilter Interface
If the filter implements the ISpaceFilter Interface, then a SpaceFilterConfig needs to be created for it, and each operation that needs to be filtered should be added to the FilterOperations list, as in the following code:
SpaceFilterConfig mySpaceFilterConfig = new SpaceFilterConfig();
mySpaceFilterConfig.FilterOperations = new List<FilterOperation>(new FilterOperation[]{ FilterOperation.BeforeWrite });
mySpaceFilterConfig.Filter = new MySpaceFilter();
Implementing a Space Filter using SpaceFilterOperationDelegate
If the filter is based on the SpaceFilterOperationDelegate, then a SpaceFilterConfig needs to be created. This is done with the appropriate SpaceFilterConfigFactory, either AttributeSpaceFilterConfigFactory, or MethodNameSpaceFilterConfigFactory, using the CreateSpaceFilterConfig() method.
Once a SpaceFilterConfig is created, it needs to be used when starting the space.
spaceConfig.SpaceFiltersConfig = new List<SpaceFilterConfig>();
spaceConfig.Add(mySpaceFilterConfig);
ISpaceProxy embeddedSpace = GigaSpacesFactory.FindSpace("/./mySpace", spaceConfig);
A space can have multiple space filters integrated in it. Simply create a SpaceFilterConfig instance per filter, and add it to the SpaceFiltersConfig list.
ISpaceFilterEntry interface
An ISpaceFilterEntry represents an object in the context of a filter operation, and allows you to interact with it.
This interface consists of 2 methods and 2 properties.
public interface ISpaceFilterEntry
{
// Gets the object type
Type ObjectType { get; }
// Gets the object itself
object GetObject();
// Update the object contained within this entry state
void UpdateObject(object obj);
// Gets the notify type (relevant for Notification filter operations)
DataEventType NotifyType { get; }
}
When using the ISpaceFilterEntry, performance issues should be taken into consideration. This interface is designed to be used in a lazy evaluation fashion. GetObject and UpdateObject are evaluated only when called, and they reduce performance. Therefore they should only be used when necessary.
ISpaceFilter Interface
The ISpaceFilter interface implements IDisposable and consists of 3 additional methods.
public interface ISpaceFilter : IDisposable
{
void Init(ISpaceProxy proxy, string filterId, IDictionary<string, string> customProperties, FilterPriority priority)
{
// performs operation on initialization
}
void Process(SecurityContext securityContext, ISpaceFilterEntry entry, FilterOperation operation)
{
// performs single entry filter operations
}
void Process(SecurityContext securityContext, ISpaceFilterEntry firstEntry, ISpaceFilterEntry secondEntry, FilterOperation operation)
{
// performs two entries filter operations, such as update
}
//IDisposable implementation
void Dispose()
{
// performs operation when the filter is being disposed
}
}
The FilterOperation enum specifies which space operation is being executed and at which stage. For example, a write operation will result in two filter Process method calls, one before the write is executed (BeforeWrite) and one after the write is executed (AfterWrite). These give the filter two hook points to intervene in the process.
Both Process methods receive either one or two ISpaceFilterEntry entries. These entries represent the objects in the context of the filtered operation. For example, in the case of a BeforeWrite filter operation, the space filter entry will contain the object that is being written to the space.
If the filter uses the proxy received by the Init method, one should be careful not to cause recursive calls. For example, if your filter is filtering Before Write operations, and inside one of the Process methods there's a call to write, an infinite loop might occur.
SpaceFilterConfig
The SpaceFilterConfig is used to start a space integrated with a space filter.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the space filter. |
| IsActiveWhenBackup | States if this filter is active when the space is in backup mode. |
| IsSecurityFilter | States if this filter is a security filter. |
| ShutdownSpaceOnInitFailure | States if the space should shutdown on filter init failure. |
| Priority | The filter's priority. |
| FilterOperations | The list of operations to be filtered. |
| CustomProperties | List of properties to be passed to the filter on initialization. |
| Enabled | Is this filter enabled. |
| Filter | The filter itself (an instance implementing ISpaceFilter). |
A filter is integrated into a space upon creation of that space, and each space filter that integrates with a space needs a SpaceFilterConfig instance that defines it.
The following code starts an embedded space, with a space filter that implements ISpaceFilter:
SpaceFilterConfig mySpaceFilterConfig = new SpaceFilterConfig();
mySpaceFilterConfig.FilterOperations = new List<FilterOperations>(new FilterOperation[]{ FilterOperation.BeforeWrite });
mySpaceFilterConfig.Filter = new MySpaceFilter();
SpaceConfig spaceConfig = new SpaceConfig();
spaceConfig.SpaceFiltersConfig = new List<SpaceFilterConfig>();
spaceConfig.SpaceFiltersConfig.Add(mySpaceFilterConfig);
ISpaceProxy embeddedSpace = GigaSpacesFactory.FindSpace("/./mySpace", spaceConfig);
FilterOperation and its Relevance to Priority
Filters are grouped by priorities, and activated by a specific operation.
Filters with higher priorities are activated closer to the hook point. This means that:
- Before filters (filters with lower priorities), will be activated first.
- After filters (filters with higher priorities), will be activated first.
For example, if two filters are activated at BeforeWrite and AfterWrite operation, the filter with the higher priority is activated last at the BeforeWrite operation, and first at the AfterWrite operation. Doing that keeps this filter activation closer to the actual space operation, hence, closer to the hook point.
Space Filter Operation Delegate
An ISpaceFilter implementation that acts as an adapter, delegating the execution of the filter life-cycle methods and specific operation, to pluggable reflection-based methods.
Using it, dismisses the need to implement the ISpaceFilter interface, and gives a more declarative filtering method.
There are two ways to use the SpaceFilterOperationDelegate:
- Attribute-based implementation.
- Method name-based implementation.
Attribute-Based Implementation
The filter itself is a class that doesn't need to implement any interface. Instead, the filter methods are marked with specific attributes.
public class SimpleAttributeFilter
{
[OnFilterInit]
public void Initialize()
{
// performs operation on initialization
}
[BeforeWrite]
public void ReportBeforeWrite()
{
Console.WriteLine(DateTime.Now + ": Before Write");
}
}
To use this class as the filter, simply use the AttributeSpaceFilterConfigFactory to create a SpaceFilterConfig instance, and use when starting a space integrated with the space filter.
AttributeSpaceFilterConfigFactory filterConfigFactory = new AttributeSpaceFilterConfigFactory();
filterConfigFactory.Filter = new SimpleAttributeFilter();
// use this filter config when starting a space
SpaceFilterConfig filterConfig = filterConfigFactory.CreateSpaceFilterConfig();
The AttributeSpaceFilterConfigFactory creates a SpaceFilterConfig instance, using a fully constructed SpaceFilterOperationDelegate as its Filter instance. The SpaceFilterOperationDelegate acts as the ISpaceFilter implementation, and delegates the filter operation to the SpaceAttributeFilter instance.
Method Name-Based Implementation
A method name-based filter has the same basic principle as the one above. However, instead of using attributes to mark the method, the method names are specified by properties.
public class SimpleMethodNameFilter
{
public void Initialize()
{
// performs operation on initialization
}
public void ReportBeforeWrite()
{
Console.WriteLine(DateTime.Now + ": Before Write");
}
}
...
MethodNameSpaceFilterConfigFactory filterConfigFactory = new MethodNameFilterConfigFactory();
filterConfigFactory.Filter = new SimpleAttributeFilter();
filterConfigFactory.OnFilterInit = "Initialize";
filterConfigFactory.BeforeWrite = "ReportBeforeWrite";
// use this filter config when starting a space
SpaceFilterConfig filterConfig = filterConfigFactory.CreateSpaceFilterConfig();
How the SpaceFilterOperationDelegate Works
The SpaceFilterOperationDelegate holds a map of FilterOperationDelegateInvoker for each filtered operation, which contains the logic that is used to delegate the filter operation to the supplied method.
The supplied method parameters (e.g. in the code example above, the ReportBeforeWrite method) must maintain a certain structure:
-
A no parameter method callback - e.g.
ReportBeforeWrite(). -
A single parameter: the parameter can either be an
ISpaceFilterEntry, or the actual template object wrapped by the entry.If using actual types, this delegate filters out all the types that are not assignable to it - e.g.
ReportBeforeWrite(ISpaceFilterEntry entry), orReportBeforeWrite(SimpleMessage message). - Two parameters: the first one maps to the previous option, the second one is the
FilterOperation- e.g.ReportBeforeWrite(SimpleMessage message, FilterOperation operation). - Three parameters: the first two map to the previous option, the third one is a
SecurityContext- e.g.ReportBeforeWrite(SimpleMessage message, FilterOperation operation, SecurityContext securityContext).
Some filter operations have two entries, and therefore have a similar, but different structure:
-
A no parameter method callback - e.g.
ReportAfterUpdate() -
A single parameter: the parameter can either be an
ISpaceFilterEntryor the actual template object wrapped by the entry.If using actual types, this delegate filters out all the types that are not assignable to it - e.g.
ReportAfterUpdate(ISpaceFilterEntry entry), orReportAfterUpdate(SimpleMessage message). - Two parameters: the first one maps to the previous option, the second is the same as the first one, since multiple entries always have two entries (mainly for update operations).
- Three parameters: the first two map to the previous option, the third one is the
FilterOperation. - Four parameters: the first three map to the previous option, the fourth one is a
SecurityContext.
The filter initialization method parameter structure is different. It can receive no parameters, or one parameter which is an ISpaceProxy.
If your filter needs to do things upon termination, implement the IDisposable interface, and the Dispose() method will be invoked when the space is shutting down.
When your filter method needs to update the entry itself, ISpaceFilterEntry should be used, and a call to UpdateObject needs to be made.
Example
The Space Filter Demo demonstrates the different ways to implement a space filter and how to integrate it in a space.
The example can be found at <GigaSpaces root>\Examples\SpaceFilter
This demo shows three equivalent space filter implementations, and a console application that runs the same demo sequence three times, once per filter implementation:
Censorship Filters
This demo data object is the Message class. This class contains one string property Content that holds the content of the message. The purpose of each filter, is to log certain Message related operations (Take, Write), and to censor messages that contain illegal words, before entering the space. All filters extend the MessageCensorship class, which implements the CensorMessage method that contains the censorship logic. The MessageCensorship receives an array of illegal words, and uses that to censor a message when CensorMessage is called.
Demo Sequence
The demo sequence consists of: creating the relevant Space Filter, creating a SpaceFilterConfig to configure the filter, starting a space with the filter integrated in it, and executing a short sequence of writing and taking Message objects into and from the space.
// Write a simple hello message to the space - the filter will log this message to the console.
space.Write(new Message("Hello"));
// Take and print the hello message from the space - the filter will log this operation to the console.
Console.WriteLine("Took message from space: " + space.Take(new Message()).Content);
// Write a message that contains an illegal word to the space - the filter will censor this message before it reaches the space, and log this to the console.
space.Write(new Message("Hello badword"));
// Take and print the censored message from the space - the filter will log this operation to the console.
Console.WriteLine("Took message from space: " + space.Take(new Message()).Content);
Console.WriteLine("Writing an object instance (Not Message), no monitor message should appear after this line");
// This object can not be assigned into Message - the filter will not operate on this object.
space.Write(new object());
Message Censorship Attribute Filter
This filter is implemented, using an attribute to mark the filter operation methods. This filter is based on the Attribute-based SpaceFilterOperationDelegate]
public class MessageCensorshipAttributeFilter : MessageCensorship, IDisposable
{
[...]
[OnFilterInit]
public void Initialize()
{
Reporter.Log("--------------------------------------------");
Reporter.Log("MessageCensorshipAttributeFilter initialized.");
Reporter.Log("--------------------------------------------");
}
public void Dispose()
{
//If implementing IDisposable, the Dispose method will be called when the space shuts down
Reporter.Log("--------------------------------------------");
Reporter.Log("MessageCensorshipAttributeFilter closed.");
Reporter.Log("--------------------------------------------");
}
[BeforeTake]
//Only filter objects that can be assigned to Message
public void LogTake(Message message)
{
Reporter.Log("Taking message from space.");
}
[BeforeWrite]
public void LogAndCensorizeWrite(ISpaceFilterEntry entry)
{
//Only operate if the filter entry type is Message, use ObjectType to filter the relevant object types for better performance.
if (typeof(Message).IsAssignableFrom(entry.ObjectType))
{
//Gets the actual message inside the entry, when calling this method only then the object is actually being evaluated.
Message message = (Message)entry.GetObject();
if (CensorMessage(message))
{
//Updates the actual message inside the filter entry, this method must be used if the value needs
//to be updated inside the filter entry, this is done in a lazy manner.
//
//When it is needed to update the entry value the paramter that should be used is ISpaceFilterEntry, otherwise the value
//will only be updated locally.
entry.UpdateObject(message);
Reporter.Log("Message being written to space contains bad words.");
}
else
Reporter.Log("Writing message to space: " + message.Content);
}
}
}
The different attributes are used to mark which method needs to be invoked, according to the different filter operations. The parameters that the method signature contains, must be of a specific structure(SpaceFilterOperationDelegate.
Each space filter needs a SpaceFilterConfig that defines it in order to integrate in a space. The attribute-based filter uses the AttributeSpaceFilterConfigFactory.
//Create an attribute based space filter delegate configurer
AttributeSpaceFilterConfigFactory attributeSpaceFilterConfigFactory = new AttributeSpaceFilterConfigFactory();
attributeSpaceFilterConfigFactory.Filter = new MessageCensorshipAttributeFilter(IllegalWords);
spaceConfig.SpaceFiltersConfig = new SpaceFilterConfig[]{attributeSpaceFilterConfigFactory.CreateSpaceFilterConfig()};
//Start a space with the configured filter
space = GigaSpacesFactory.FindSpace("/./spaceAttributeFilterDemo", spaceConfig);
In this example, we can see that the LogAndCensorizeWrite method receives an ISpaceFilterEntry as its single parameter, and not the Message object like the LogTake method. That's because this method might need to update the value of the message when it needs to be censored. This can only be done using the entry.UpdateObject method.
Another important thing to notice is that the LogAndCensorizeWrite method first checks if the Message type from the entry.ObjectType, can be assigned into Message, and only then gets the actual Message object. This is done to decrease the performance impact of the filter, because the evaluation of GetObject and UpdateObject is done in a lazy fashion.
This filter class implements IDisposable, to demonstrate that when a filter class implements the IDisposable interface, it is disposed of when the space shuts down.
Message Censorship Method Names Filter
This filter is implemented using method names to mark the filter operation methods. This filter is based on the Method name-based SpaceFilterOperationDelegate.
public class MessageCensorshipMethodNamesFilter : MessageCensorship, IDisposable
{
[...]
public void Initialize()
{
Reporter.Log("--------------------------------------------");
Reporter.Log("MessageCensorshipAttributeFilter initialized.");
Reporter.Log("--------------------------------------------");
}
public void Dispose()
{
//If implementing IDisposable, the Dispose method will be called when the space shutdown
Reporter.Log("--------------------------------------------");
Reporter.Log("MessageCensorshipAttributeFilter closed.");
Reporter.Log("--------------------------------------------");
}
//Only filter objects that can be assigned to Message
public void LogTake(Message message)
{
Reporter.Log("Taking message from space.");
}
public void LogAndCensorizeWrite(ISpaceFilterEntry entry)
{
//Only operate if the filter entry type is Message, use ObjectType to filter the relevant object types for better performance.
if (typeof(Message).IsAssignableFrom(entry.ObjectType))
{
//Gets the actual message inside the entry, when calling this method only then the object is actually being evaluated.
Message message = (Message)entry.GetObject();
if (CensorMessage(message))
{
//Updates the actual message inside the filter entry, this method must be used if the value needs
//to be updated inside the filter entry, this is done in a lazy manner.
//
//When it is needed to update the entry value the paramter that should be used is ISpaceFilterEntry, otherwise the value
//will only be updated locally.
entry.UpdateObject(message);
Reporter.Log("Message being written to space contains bad words.");
}
else
Reporter.Log("Writing message to space: " + message.Content);
}
}
}
This filter implementation is very similar to the attribute-based one, except that there are no marker attributes. The method that needs to be invoked according to the filter operation, is specified by name when creating theMethodNameSpaceFilterConfigFactorythat creates theSpaceFilterConfig` for this filter.
//Create a method based space filter delegate configurer
MethodNameSpaceFilterConfigFactory methodNameSpaceFilterConfigFactory = new MethodNameSpaceFilterConfigFactory();
methodNameSpaceFilterConfigFactory.Filter = new MessageCensorshipMethodNamesFilter(IllegalWords);
methodNameSpaceFilterConfigFactory.BeforeWrite = "LogAndCensorizeWrite";
methodNameSpaceFilterConfigFactory.BeforeTake = "LogTake";
methodNameSpaceFilterConfigFactory.OnFilterInit = "Initialize";
spaceConfig.SpaceFiltersConfig = new SpaceFilterConfig[] { methodNameSpaceFilterConfigFactory.CreateSpaceFilterConfig() };
//Start a space with the configured filter
space = GigaSpacesFactory.FindSpace("/./spaceMethodFilterDemo", spaceConfig);
The same structure for the filter operation method applies here as well.
Message Censorship Space Filter
This filter implements the ISpaceFilter interface directly.
public class MessageCensorshipSpaceFilter : MessageCensorship, ISpaceFilter
{
[..]
public void Dispose()
{
Reporter.Log("--------------------------------------------");
Reporter.Log("MessageCensorshipSpaceFilter closed.");
Reporter.Log("--------------------------------------------");
}
public void Init(ISpaceProxy proxy, string filterId, IDictionary<string, string> customProperties, FilterPriority priority)
{
Reporter.Log("--------------------------------------------");
Reporter.Log("MessageCensorshipSpaceFilter initialized.");
Reporter.Log("--------------------------------------------");
}
public void Process(SecurityContext securityContext, ISpaceFilterEntry entry, FilterOperation operation)
{
//Only operate if the filter entry type is Message, use ObjectType to filter the relevant object types for better performance.
if (typeof(Message).IsAssignableFrom(entry.ObjectType))
{
switch (operation)
{
case FilterOperation.BeforeTake:
Reporter.Log("Taking message from space.");
break;
case FilterOperation.BeforeWrite:
//Gets the actual message inside the entry, when calling this method only then the object is actually being evaluated.
Message message = (Message) entry.GetObject();
if (CensorMessage(message))
{
//Updates the actual message inside the filter entry, this method must be used if the value needs
//to be updated inside the filter entry, this is done in a lazy manner.
entry.UpdateObject(message);
Reporter.Log("Message being written to space contains bad words.");
}
else
Reporter.Log("Writing message to space: " + message.Content);
break;
}
}
}
public void Process(SecurityContext securityContext, ISpaceFilterEntry firstEntry, ISpaceFilterEntry secondEntry, FilterOperation operation)
{
}
}
All the filter operations are represented by the operation parameter in the Process method. A switch on the operation, delegates the operation to the corresponding filtering action.
When implementing ISpaceFilter, a SpaceFilterConfig needs to be created, and each filter operation that should be filtered, needs to be specified in it.
//Create configuration for space filter
SpaceFilterConfig spaceFilterConfig = new SpaceFilterConfig();
spaceFilterConfig.Filter = new MessageCensorshipSpaceFilter(IllegalWords);
spaceFilterConfig.FilterOperations = new FilterOperation[]{FilterOperation.BeforeWrite, FilterOperation.BeforeTake};
SpaceConfig spaceConfig = new SpaceConfig();
spaceConfig.SpaceFiltersConfig = new SpaceFilterConfig[]{spaceFilterConfig};
//Start a space with the configured filter
ISpaceProxy space = GigaSpacesFactory.FindSpace("/./spaceFilterDemo", spaceConfig);

