Security for Smart Cache Service Grid
This is an introduction to data grid security, where it fits in the data grid architecture, which components can be secured, and how to configure and customize the security depending on your application security requirements. Data grid Security provides comprehensive support for securing your data and services.
Some security features are part of the open source edition, while others are only available with the commercial (licensed) editions.
Securing Data Grid Components
This security feature is only available with the commercial (licensed) editions.
Data grid has security built over the major component, GSA, GSM, GSC and Processing Unit with Space data. Each one of these components can be configured according to your application security requirements.
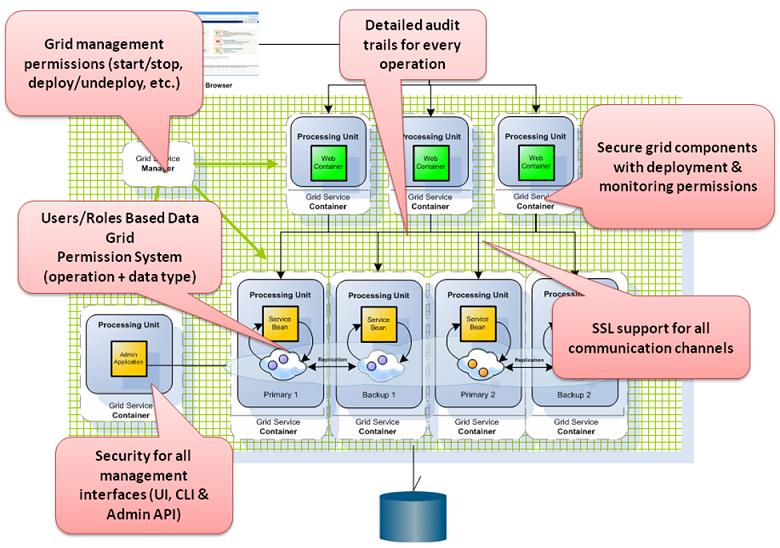
For information about Authentication, Authorization and Security Roles (Privileges) refer to the Security Overview page.
Managing Roles - FSM Based Security (GS-UI)
This security feature is only available with the commercial (licensed) editions.
FSM based security, is NOT the default security in Service Grid orchestration. The default is spring based security.
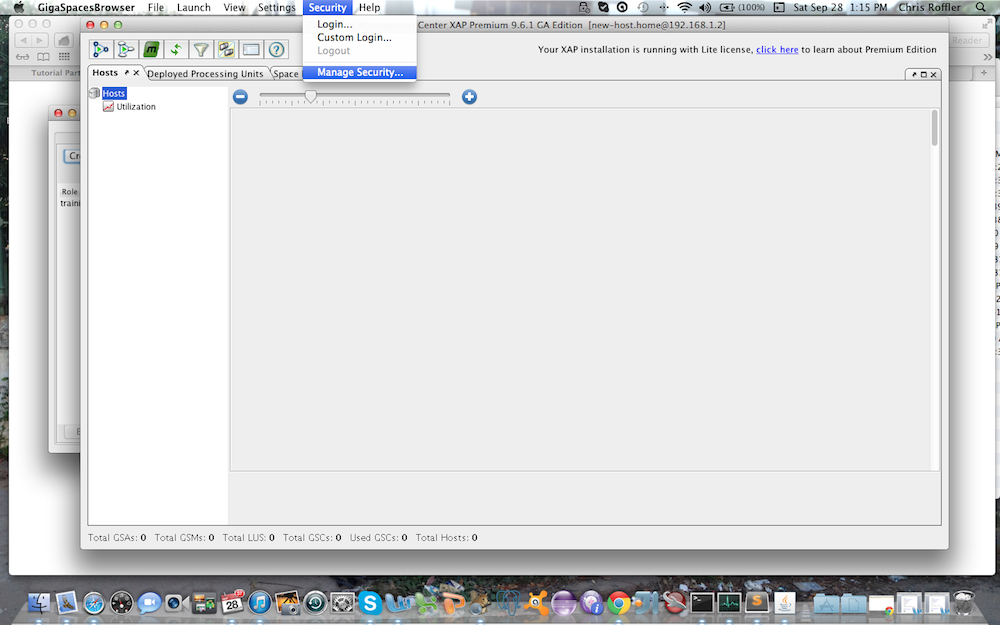
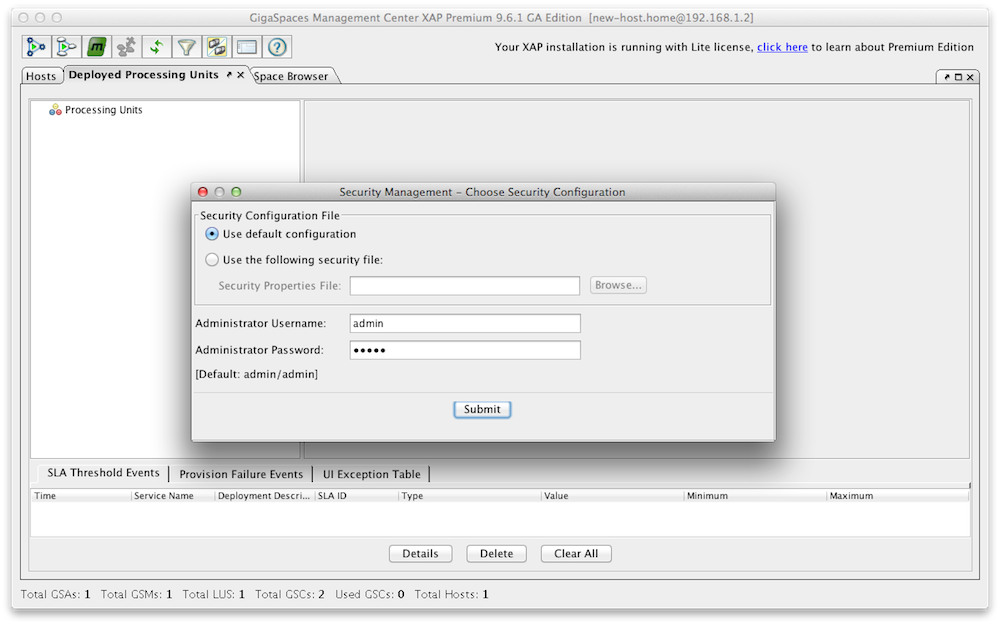
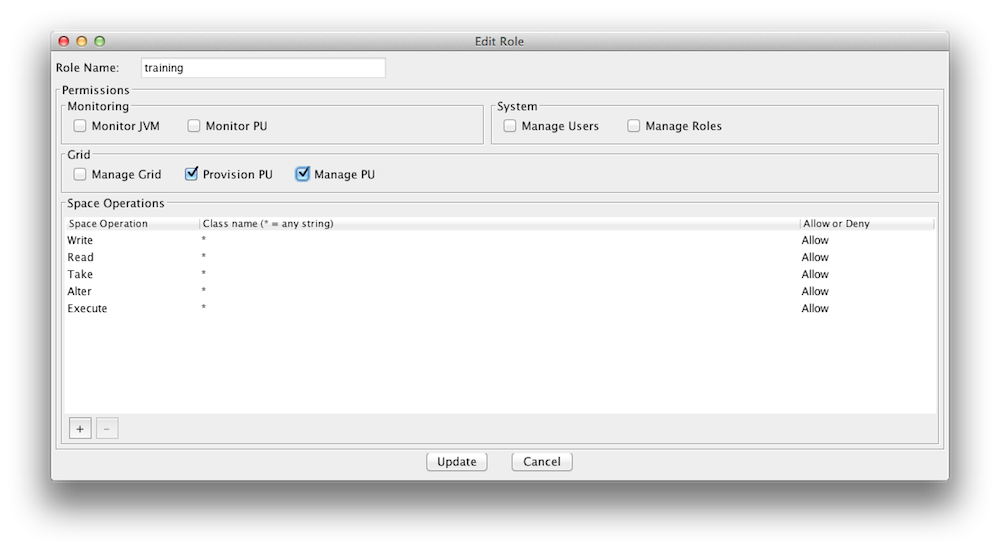
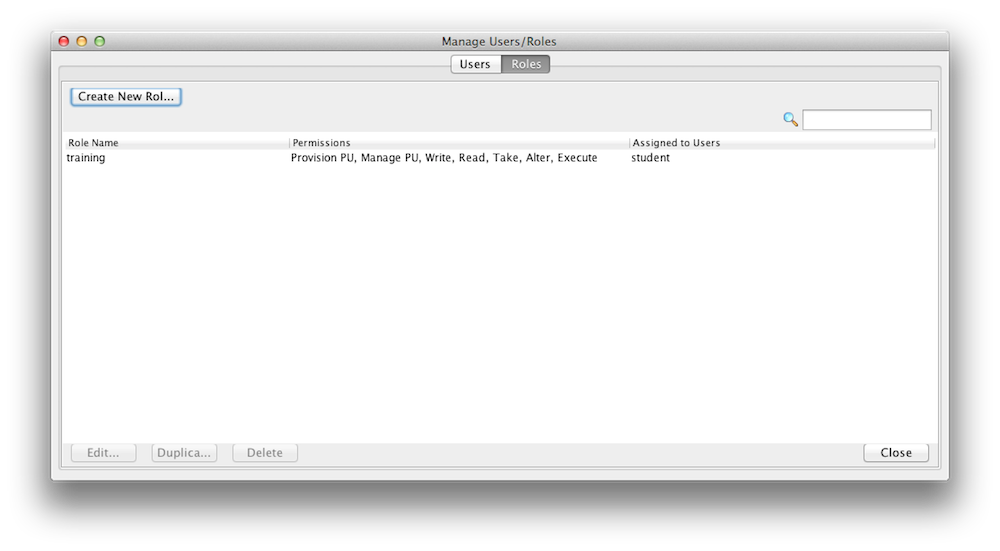
You can create new roles and users with a configuration file or with the Admin UI. Here is an example how you use the Admin UI to create/update roles. Lets create a role called "training" that can access and interact with our xapTutorialSpace, but does not have monitoring authority. Start the Admin UI:
GS_HOME\bin\gs-ui.sh
The default username and password for the security are admin/admin.
|
Start GigaSpaces Management Center |
Select Security options |
Log in |
Create a Role |
Display Roles |
You may have noticed that you can assign fine grained access control for space operations (read/write/etc) per space class(slide 4).
For more information, see the GigaSpaces Management Center page in the Administration guide.
Managing Users and Roles - File Based Security (GS-UI)
This security feature is only available with the commercial (licensed) editions.
File based security, is NOT the default security in Service Grid orchestration. The default is spring based security.
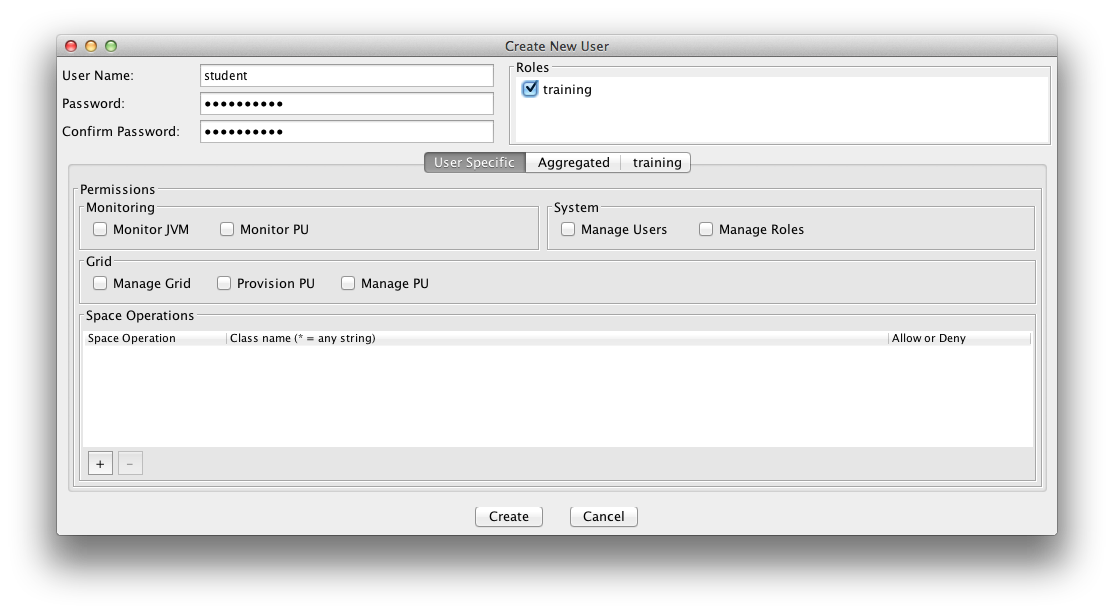
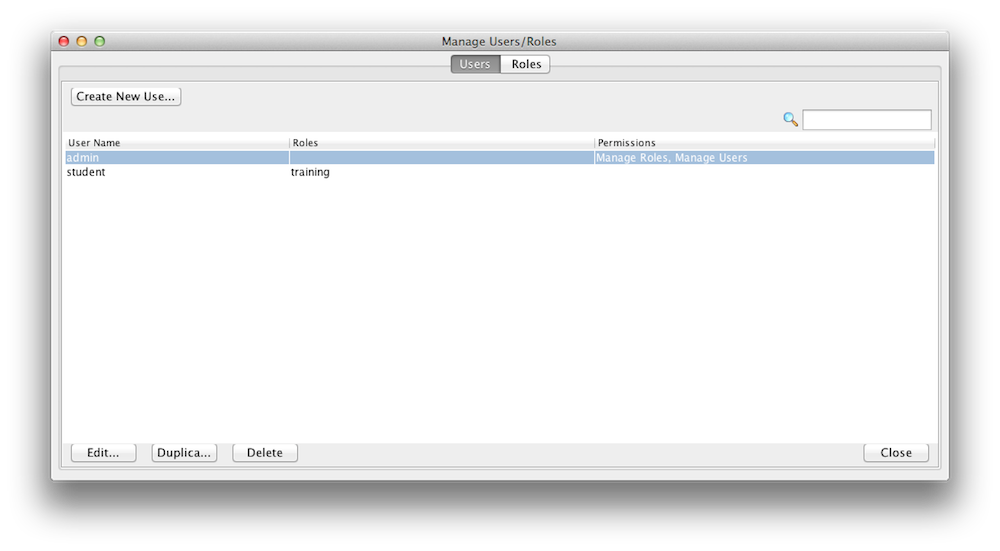
A user is assigned roles. You can create new roles and users with a configuration file or with the Admin UI. Here is an example how you use the Admin UI to create/update users. Lets create a user called student and assign the role training we have just created in the step above. A user can have multiple roles.
|
Log in |
Create User |
Display Users |
You can create Users and Roles via the API. Here is an example:
public void createUser() {
Properties securityProperties = new Properties();
SecurityManager securityManager = SecurityFactory
.createSecurityManager(securityProperties);
directoryManager = securityManager.createDirectoryManager(new User(
"admin", "admin"));
// Create a new Role
this.createRole();
// Create the User
User user = new User("student", "student123", new RoleAuthority("training"));
// Register the new User
UserManager userManager = directoryManager.getUserManager();
userManager.createUser(user);
}
private Role createRole() {
RoleManager roleManager = directoryManager.getRoleManager();
Role role = new Role("training",
new SpaceAuthority(SpacePrivilege.READ),
new SpaceAuthority(SpacePrivilege.WRITE),
new SpaceAuthority(SpacePrivilege.TAKE));
roleManager.createRole(role);
return role;
}
For more information, see the GigaSpaces Management Center page in the Administration guide.
How to Access a Secured Space
A secured embedded Space protects access (to data) which is granted only to users with sufficient privileges. Here is an example how to create a secure space with no internal services:.
EmbeddedSpaceConfigurer configurer = new EmbeddedSpaceConfigurer("xapTutorialSpace").secured(true);
GigaSpace gigaSpace = new GigaSpaceConfigurer(configurer).gigaSpace();
<os-core:embedded-space id="space" space-name="xapTutorialSpace">
<os-core:security secured="true" />
</os-core:space>
When a remote Space proxy connects to a secured Space, it must provide security credentials (username and password).
public void setupSpace()
{
SpaceProxyConfigurer configurer = new SpaceProxyConfigurer("xapTutorialSpace").credentials("student", "password");
GigaSpace gigaSpace = new GigaSpaceConfigurer(configurer).gigaSpace();
}
<os-core:space-proxy id="space" space-name="xapTutorialSpace">
<os-core:security username="student" password="student123" />
</os-core:space-proxy>
For more information, see the Securing the Data Layer page in the Security section of the Administration guide.
Grid Security
Grid Security is enabled in data grid by setting a global system property. This system property can be set when using the deployment scripts, or it can be appended in the setenv.sh/bat script in the GS_HOME/bin directory. Once the Grid Security is enabled, you can use the predefined roles and user names to protect and control the grid access.
-Dcom.gs.security.enabled=true
This property affects the GSA, GSM, GSC and standalone PU instances with a space.
For more information, see the Securing the Grid Services page in the Security section of the Administration guide.
Transport Security
The transport layer can be secured using an SSL communication filter.
For more information, see the Securing the Transport Layer page in the Security section of the Administration guide.